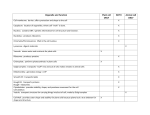
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protein Creation Pathway
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Protein Creation Pathway Place your keyboard aside click on the NUCLEUS to begin the tutorial The Nucleus The nucleus (flashing circle) is nicknamed the “control center” of a cell. But why? The nucleus contains DNA in its active form and this DNA will ultimately be used as a blueprint to create proteins for use throughout the body. The process of creating a protein begins in the nucleus. Click the arrow to zoom inside and view a nucleus. See the dark spot inside the nucleus? This is the nucleolus. Give it a click. Nucleolus The Nucleolus The nucleolus is a dense region within the nucleus. This organelle (tiny cell part) is responsible for creating thousands of ribosomes. Ribosomes play an important role in the creation of proteins as we will see later. Click the Nucleolus to see an artists drawing. Nucleus The Nucleolus The nucleolus is a dense region within the nucleus. This organelle (tiny cell part) is responsible for creating thousands of ribosomes. Ribosomes play an important role in the creation of proteins as we will see later. These organelles are 3-dimensional. But they often look flat when viewed through a microscope. To proceed, answer the question below. What are the monomers of a protein called? monosaccharide Fatty acid Nucleotide Amino acid Doh! Try Again! Monomer Polymer Carbohydrate Monosaccharide Polysaccharide Lipid Fatty acid Lipid Protein Amino acid Protein Nucleic Acid Nucleotide Nucleic acid Review the chart. Click the button to return. Correct! Ribosomes By far, the ribosomes are the most numerous of all organelles. Remember, they are created by the nucleolus. After exiting the nucleus they themselves are responsible for the production of proteins within the cell. Because they are so small, they resemble tiny dots in this picture. After they exit the nucleus, they are often attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Click HERE to see the ER and attached ribosomes. Ribosomes By far, the ribosomes are the most numerous of all organelles. Remember, they are created by the nucleolus. After exiting the nucleus they themselves are responsible for the production of proteins within the cell. Because they are so small, they resembles tiny dots in this picture. After they exit the nucleus, the ribosomes are often attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Let’s review. Which organelle creates the ribosomes? Nucleus Nucleolus Rough ER Doh! Try Again! Click the button to return. Correct! The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosomes are created by the nucleolus and then exit the nucleus. As they exit the nucleus, they begin to create proteins through a process called translation. The rough ER is called “rough” because it is covered with ribosomes. The rough ER is basically a tunnel system to move ribosomes to other parts of the cell. In this sense, you can compare the rough ER to a subway, and the passengers are the ribosomes. Click to see the rough ER. The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosomes are created by the nucleolus and then exit the nucleus. As they exit the nucleus, they begin to create proteins through a process called translation. The rough ER is called “rough” because it is covered with ribosomes. The rough ER is basically a tunnel system to move ribosomes to other parts of the cell. In this sense, you can compare the rough ER to a subway, and the passengers are the ribosomes. Since the ribosomes exit the nucleus and flow into the rough ER, the rough ER is attached to the outside of the nucleus. The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum See the dots? Those are the ribosomes. Ribosomes are created by the nucleolus and then exit the nucleus. As they exit the nucleus, they begin to create proteins through a process called translation. The rough ER is called “rough” because it is covered with ribosomes. The rough ER is basically a tunnel system to move ribosomes to other parts of the cell. In this sense, you can compare the rough ER to a subway, and the passengers are the ribosomes. Since the ribosomes exit the nucleus and flow into the rough ER, the rough ER is attached to the outside of the nucleus. The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum See the dots? Those are the ribosomes. Ribosomes are created by the nucleolus and then exit the nucleus. As they exit the nucleus, they begin to create proteins through a process called translation. The rough ER is called “rough” because it is covered with ribosomes. The rough ER is basically a tunnel system to move ribosomes to other parts of the cell. In this sense, you can compare the rough ER to a subway, and the passengers are the ribosomes. Since the ribosomes exit the nucleus and flow into the rough ER, the rough ER is attached to the outside of the nucleus. The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum We need to review before we go further. Ribosomes are created by the nucleolus and then exit the nucleus. As they exit the nucleus, they begin to create proteins through a process called translation. The rough ER is called “rough” because it is covered with ribosomes. The rough ER is basically a tunnel system to move ribosomes to other parts of the cell. In this sense, you can compare the rough ER to a subway, and the passengers are the ribosomes. Since the ribosomes exit the nucleus and flow into the rough ER, the rough ER is attached to the outside of the nucleus. Let’s Review Which step happens first? Click the correct sentence. The ribosomes exit the nucleus The ribosomes begin to make proteins as they travel along the rough ER. The nucleolus creates ribosomes Correct! Check the animation. Then click which happens next. 1st step: The nucleolus creates ribosomes The ribosomes exit the nucleus The ribosomes begin to make proteins as they travel along the rough ER. Correct! Check the animation. Then click which happens next. 1st step: The nucleolus creates ribosomes 2nd step: The ribosomes exit the nucleus The ribosomes begin to make proteins as they travel along the rough ER. Correct! Remember, we are tracing the path of protein creation. 1st step: The nucleolus creates ribosomes 2nd step: The ribosomes exit the nucleus 3rd step: The ribosomes begin to make proteins as they travel along the rough ER. Protein Functions Remember, the ribosomes were traveling along the rough ER while making proteins. Proteins are used in a wide variety of cell activities, such as growing hair, carrying oxygen, and digesting foods. Many proteins are created by one cell, but needed by another. Therefore many proteins need to be exported. That’s the job of the Golgi Body (named after Camillo Golgi). Click the arrow to see the Golgi Bodies. The Golgi body receives the proteins that were created by the ribosomes. The Golgi body packages the protein inside a protective envelope called a vesicle. Doesn’t the Golgi body resemble a stack of pancakes? Vesicles Vesicles float away from the Golgi body with finished proteins inside. The proteins are released from the cell and are used throughout the body. Let’s do some review. Use your worksheet to help you with the answers. 1) Which organelle creates ribosomes? vesicle Golgi body nucleus rough ER ribosome nucleolus Correct! Review #2 Which organelle transports the ribosomes from the nucleus to the Golgi body? vesicle Golgi body nucleus rough ER ribosome nucleolus Correct! Review #3 Which organelle creates proteins? vesicle Golgi body nucleus rough ER ribosome nucleolus Correct! Review #4 Which organelle packages finalized proteins for shipment? vesicle Golgi body nucleus rough ER ribosome nucleolus Correct! Review #5 Which organelle protects a finished protein as it exits the cell? vesicle Golgi body nucleus rough ER ribosome nucleolus Correct! Review #6 Click on the nucleolus. Correct! Review #7 Click on the Golgi body…remember pancakes. Correct! Review #8 Click on the rough ER. Correct! Review #9 Click on the organelle that packages proteins for shipment outside of the cell. Correct! Golgi Body! Review #10 Click on the organelle that creates ribosomes. Correct! Nucleolus! I hope this tutorial was helpful. This will be posted on my website for you to review at any time. Turn in your handout. Feel free to start over if you would like to do some review.