* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
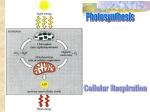
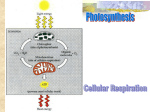
Light + 6 CO2 + 2H20 → C6H12O6 + 602 Step 1: Trap energy from Sunlight Chlorophyll a Chlorophyll b Accessory pigments Absorb certain wavelengths of light while reflecting others. Light-dependent reactions Light-independent reactions Plants use electron carriers to transport high-energy electrons from chlorophyll to other molecules. NADP+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) is a carrier molecule. NADP+ picks up two high-energy electrons, along with a hydrogen ion (H+). It is then converted into NADPH. The NADPH can then carry the high-energy electrons to be used in chemical reactions elsewhere in the cell. Light dependent reactions: Light dependent water is split NADPH and ATP are produced (Step 2) Chemiosmosis mechanism by which ATP is produced by the flow of H ions against a concentration gradient Light Independent Reactions – Calvin Cycle Calvin Cycle (light-indep rxns) Carbon fixation Step 3: With CO2, convert temporary chemical energy into organic compounds (glucose). http://faculty.nl.edu/jste/calvin_cycle.htm Factors that Affect the Rate Photosynthesis Using glucose and oxygen to make ATP for the cell’s metabolism. Overview of Cell Respiration •Anaerobic •Occurs in the cytoplasm •Glucose is converted to two pyruvic molecules with the help of 2 ATP •Net yield of 2 ATP are made •2NADH are also produced Products: 2 Pyruvic Acid 2 NADH 2 ATP Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport Chain Occurs in the mitochondria NAD NADH Oxygen is required for reaction to occur Pyruvic acid is needed from glycolysis Enzyme-directed reactions which produce CO2, ATP, FADH2 and NADH How many times does the Kreb cycle go around for one glucose molecule? How much ATP is produced in this cycle? How much ATP has been produced so far with Krebs and Glycolysis? •Electron Transport Chain •Aerobic •All NADH and FADH2 produced gives up their electrons to a series of electron accepting proteins. •Main production of ATP occurs here. Synthesis of ATP in ETC Example of Anaerobic Respiration