* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
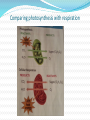
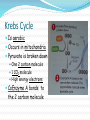
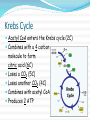
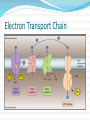
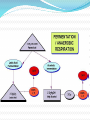
Overview of Cellular Respiration Section 4.4 Cellular respiration makes ATP by breaking down sugars. If a step requires oxygen, it is called aerobic. If a step occurs in the absence of oxygen, it is called anaerobic. It takes place in three steps: Glycolysis Krebs cycle Electron transport chain Cellular respiration The equation for cellular respiration is: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 H2O + 6 CO2 + energy The equation for photosynthesis is: 6 H2O + 6 CO2 + light energyC6H12O6 + 6 O2 Comparing photosynthesis with respiration Glycolysis Is anaerobic Occurs in the cytoplasm One 6 carbon glucose molecule is broken down into two three carbon pyruvate molecules. Produces 2 ATP molecules Krebs Cycle Is aerobic Occurs in mitochondria Pyruvate is broken down One 2 carbon molecule 1 CO2 molecule High energy electrons CoEnzyme A bonds to the 2 carbon molecule Krebs Cycle Acetyl CoA enters the Krebs cycle (2C) Combines with a 4 carbon molecule to form citric acid (6C) Loses a CO2 (5C) Loses another CO2 (4C) Combines with acetyl CoA. Produces 2 ATP Electron Transport Chain Is aerobic Occurs in mitochondria NADH and FADH2 donate electrons and transport hydrogen ions. Produces 34 ATP molecules Hydrogen ions and electrons combine with oxygen to produce water. Electron Transport Chain Aerobic respiration Aerobic respiration can produce up to 38 ATP molecules from 1 molecule of glucose. Most ATP is produced in the electron transport chain. Anaerobic Respiration Also called fermentation In the absence of oxygen If there is no oxygen to accept electrons or hydrogen ions NADH and FADH2 cannot be converted to NAD+ and FAD2+ Citric acid is not broken down in the Krebs cycle Acetyl CoA cannot enter the Krebs cycle Anaerobic respiration Pyruvate has to be broken down another way. In yeasts: Pyruvate ethanol and CO2 Produces 2 ATP molecules In animals: Pyruvate lactic acid Produces 2 ATP molecules Uses of fermentation Cheese Alcohol Breads