* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protein Synthesis (Translation)
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
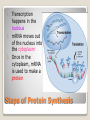
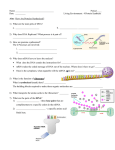
12.3 Protein Synthesis (Translation) Watch these animations and try to explain what is going on. ◦ Animation 1 ◦ Animation 2 1. 2. 3. Transcription happens in the nucleus mRNA moves out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm Once in the cytoplasm, mRNA is used to make a protein Steps of Protein Synthesis How does m-RNA tell the cell what to do? mRNA is a message that codes for a protein Proteins are made in the cytoplasm which work to keep the cell alive Translation or protein synthesis is the process of making a protein Proteins are made up of amino acids (small building blocks) There are 20 different types of amino acids 1. mRNA moves out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm NUCLEUS mRNA Process of Translation 2. mRNA attaches to a ribosome (rRNA) 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) decodes the mRNA and brings amino acids to build up the protein Anticodon (3 bases on tRNA): Matches up to codons on mRNA 4. Protein (chain of amino acids) detaches from ribosome and goes off to work in the cell -Each mRNA codon (3 bases) = 1 Amino Acid -Amino Acids link together= 1 Protein Reading the Genetic Code Start Codon= AUG (Methionine) Stop Codon= UAA, UAG, UGA (codes for NOTHING!) WHY? mRNA: AUG CCC GUA UGA Amino Acid Chain: Met-Pro-Val-Stop mRNA: AUG UCG GCA UAA Amino Acid Chain: Met-Ser-Ala-Stop Practice Using Your Codon Chart Practicing the process Transcription Translation