* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Macromolecules: Fundamental Components of Life
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
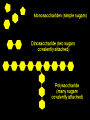
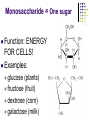
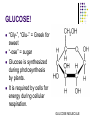
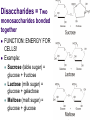
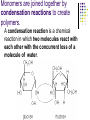
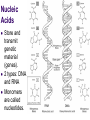
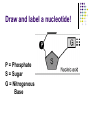
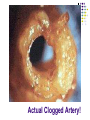
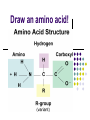
Macromolecules: What cells are made of CA BIOLOGY STANDARD: Students know most macromolecules (polysaccharides, nucleic acids, proteins, lipids) in cells and organisms are synthesized from a small collection of simple precursors. A Macromolecule is… An extremely large molecule, called a polymer, made up of many smaller molecules called monomers. They are found in your cells, tissues and the food you eat. They are composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorous. 4 types of Macromolecules: Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic acids Polymers and Monomers Poly=many (polymer = many molecules strung together) Mono=one (monomer = one molecule) Carbohydrates •Composed of C, H and O atoms in a C1H2O1 ratio. •3 types- monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides FUNCTIONS: •Used for Energy (50%-60% of your calories should come from carbs!) •Used for Cell Structure •In plant cell walls •In insect exoskeletons 3 Types of Carbohydrates Simple Carbohydrates Monosaccharides (Mono = “one” saccharide = sugar) Disaccharides (Di = “two”) Complex Carbohydrates Polysaccharides (Poly = “many”) Monosaccharide = One sugar Function: ENERGY FOR CELLS! Examples: glucose (plants) fructose (fruit) dextrose (corn) galactose (milk) GLUCOSE! “Gly-”, “Glu-” = Greek for sweet “-ose” = sugar Glucose is synthesized during photosynthesis by plants. It is required by cells for energy during cellular respiration. GLUCOSE MOLECULE Disaccharides = Two monosaccharides bonded together FUNCTION: ENERGY FOR CELLS! Example: Sucrose (table sugar) = glucose + fructose Lactose (milk sugar) = glucose + galactose Maltose (malt sugar) = glucose + glucose Polysaccharides are long strings of monosaccharides bonded together. Three types: Starch- Energy Can be digested; Plants store extra glucose as starch EX: potato, rice, grains, pasta, vegetables Fiber- Can’t be digested by humans prevents constipation and colon cancer and clogged arteries Found in structure of plants = cellulose EX: oat bran, skin of fruits, whole grains, vegetables Glycogen- used to store extra glucose in the liver for times when you haven’t eaten! Monomers are joined together by condensation reactions to create polymers. A condensation reaction is a chemical reaction in which two molecules react with each other with the concurrent loss of a molecule of water. Polymers are broken apart by hydrolysis reactions. Hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule is cleaved into two parts by the addition of a molecule of water. Nucleic Acids Store and transmit genetic material (genes). 2 types: DNA and RNA Monomers are called nucleotides. How do you build a Nucleic Acid? The building blocks of nucleic acids are nucleotides containing a nitrogenous base, sugar and a phosphate. Draw and label a nucleotide! P = Phosphate S = Sugar G = Nitrogenous Base Lipids are fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins Lipids are hydrophobic (scared of water) and non-polar Functions: Energy storage Cell membranes Hormone formation Healthy skin and hair Insulation and protection of body organs What does a lipid look like? Lipids are made up of 3 fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule Saturated fats are… Fats that have no double bonds between the carbon atoms of the fatty acid chain and are thus fully saturated with hydrogen atoms. Atherosclerosis The process of the arteries becoming progressively narrower. Caused by eating too many saturated fats Actual Clogged Artery! Unsaturated Fats are… Fats in which there is at least one double bond within the fatty acid chain. A fat molecule is monounsaturated if it contains one double bond, and polyunsaturated if it contains more than one double bond. Where double bonds are formed, hydrogen atoms are eliminated. Proteins (polypeptides) are made of amino acids joined by peptide bonds in a linear chain and folded into a globular form. FUNCTIONS: Enzymes that speed up biochemical reactions Provide structure and support: Actin and myosin in muscle Cytoskeleton- maintains cell shape. Components of skin, hair and nails (keratin), ligaments, tendons How do we build proteins? Made up of many amino acids There are 20 different amino acids! Different order of amino acids produces a different structure and function. Draw an amino acid! The Bottom Line All of these Macromolecules are synthesized (made) from simple precursors (building blocks): Monosaccharides make up Polysacharides Amino acids make up Proteins Fatty acids and Glycerol make up Lipids Nucleotides make up Nucleic Acids Exit Slip What are the four macromolecules that are necessary for life? Polysaccharides are made up of ______? Proteins are made up of ________? Lipids are made up of _________? Nucleic acids are made up of _________? HW: Read Ch. 2.3 and do the section review. YOUR ASSIGNMENT: MACROMOLECULE MODEL AND VIDEO Choose one of the macromolecules. Use a visual- drawing or something else. Create a short educational video (30 seconds) explaining the important aspects of your macromolecule. (see your worksheet) HOMEWORK: Read 2-4 on Enzymes and answer the section review.