* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA Replication
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
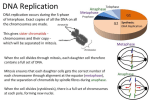
DNA Replication C483 Spring 2013 1. Double stranded DNA that has been labeled with radioactive 14C is used as the template for replication. Replication is carried out in a medium containing only unlabeled nucleotides. After two rounds of replication, what percent of double stranded DNA molecules are radioactive? A) 25% B) 50% C) 75% D) 100% 2. Which of these statements is false? A) The primosome is part of the replisome B) DNA polymerase I is part of the replisome C) DNA polymerase III is part of the primosome D) The Klenow Fragment is part of DNA Polymerase I 3. Which of these statements is false? DNA Polymerase III contains A) 5’3’ exonuclease activity for proofreading B) 5’3’ polymerase activity of elongation of the DNA strand. C) Subunits to aid in processivity. D) Subunits that act as “sliding clamps.” 4. Because the replisome synthesizes both strands of DNA simultaneously A) Okazaki fragments are formed in the leading strand. B) The leading strand is synthesized 5’3’, but the lagging strand is synthesized 3’5’ C) The replisome needs to have primase activity to make RNA primers for the lagging strand D) Proofreading activity is required for the leading strand, but not the lagging strand. 5. Which of these activit(ies) is the last one in the process of lagging strand synthesis? A) Ligase B) Polymerase C) 5’3’ exonuclease D) primase History of Nucleic Acid Biochemistry Miescher (1869) Discovers nucleic acid He called “nuclein” Avery, MacLeod, McCarty (1944) Kossel (1901) Discovers five nucleobases A, G, C, T, U Franklin and Wilkins Watson and Crick (1953) Semiconservative Replication • Template • Protein machinery – DNA polymerase • Three stages – Initiation – Elongation – Termination E. Coli chromosome • • • • • Circular, double stranded Origin Replication forks Bidirectional Replisome – DNA polymerase is essential part of the replisome Bacterial DNA Polymerase II • DNA Polymerase I and II involved in repair and polymerization of part of one strand • DNA Polymerase III is major component of replisome • Multi-subunit, asymmetric dimer • Many activities Polymerase Activity • dNTP is substrate • Added to 3’ end of growing chain – PRIMER is required • 5’ 3’ growth • Selectivity based on Hbonding – TEMPLATE is required • Pyrophosphate generated Processivity • Replisome stays attached to replication fork • Beta subunit is a sliding clamp • Higher efficiency • Few replisomes needed Polymerase III Proofreads • Incorrect base pair every 105 bp • Epsilon subunit is proofreader • Unmatched base pairs have different conformation • 3’5’ exonuclease activity • 99% of errors corrected here • 99% of remaining errors are repaired Polymerase Synthesizes Both Strands Simultaneouly! • Synthesis is 5’ 3’ • Leading Strand built on the 3’5’ template • Lagging Strand built on the 5’3’ template – Discontinuous – Okazaki fragments Primase • RNA primer is needed for each polymerization • RNA primer is made by primase enzyme – Part of the primosome complex • Primosome, along with DNA Polymerase III, is part of replisome Closing the Nick • Three actions needed • Removal of RNA primer – DNA polymerase I • Filling in the nick with DNA – DNA polymerase I • Forming bond between adjacent fragments – DNA ligase DNA Polymerase I • Two activities similar to DNA polymerase III – 5’3’ polymerase • Extend chain – 3’5’ exonuclease • Proofreading • Unique activity – 5’3’ exonuclease • Removes RNA primer Klenow Fragment • DNA polymerase I was first discovered – Kornberg Nobel prize • Can be cut into two pieces that retain activity • Klenow fragment – Bigger piece with 5’3’ exonuclease removed – “Usable” form of DNA polymerase III Three Step Process Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Mechanism of Ligase Answers 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. B C A C A