* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Team Hockey: Glucose and ATP
Survey
Document related concepts
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
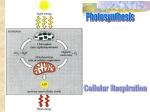
Team Hockey: Glucose and ATP Created By: Nathan Stout & Samir Mohandes Period 1 Key Concepts • What is the maximum amount of ATP that can be yielded from one glucose molecule? • How much of a cell’s energy is obtained from glucose? • Which process produces the majority of a cell’s ATP? Glucose • Monosaccharide, important biological carbohydrate. • Begins Cellular Respiration in cells. • One glucose molecule produces up to 38 ATP. • Cells obtain 40% of their energy from glucose. Glycolysis • Uses glucose to create energy molecules (ATP, NADH) • Makes Pyruvate for Citric Acid Cycle (part of aerobic respiration). • Produces 6-carbon and 3-carbon intermediate compounds (used for many purposes). Citric Acid Cycle • Ideally produces 2 ATP, and about 17 NADH. • Complicated series of chemical reactions that produce many necessary compounds, including amino acids. Oxidative Phosphorylation • Final step in the Cellular Respiration process. • Most of ATP produced in this step (up to 34). • About 17 NADH (from Citric Acid Cycle) made into 2 ATP each, producing around 34 ATP. 1. What is the maximum amount of ATP that can be yielded from one glucose molecule? A. B. C. D. 32 34 36 38 ATP ATP ATP ATP 1. What is the maximum amount of ATP that can be yielded from one glucose molecule? D: 38 ATP 2. How much of a cell’s energy is obtained from glucose? A. B. C. D. 20% 40% 60% 80% 2. How much of a cell’s energy is obtained from glucose? B: 40% 3. Which process produces the majority of a cell’s ATP? A. B. C. D. Citric Acid Cycle Oxidative Phosphorylation Glycolysis Mitosis 3. Which process produces the majority of a cell’s ATP? B: Oxidative Phosphorylation