* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Antibody Production and Use in Immunodetection
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Major histocompatibility complex wikipedia , lookup
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Immunoprecipitation wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
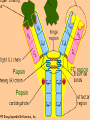
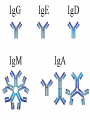
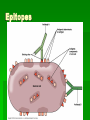
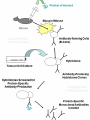
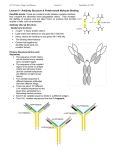
Antibody Production and Use in Immunodetection Introduction for ELISA and Western Blotting Techniques Papsin Pepsin FC region Antibody(Immunoglobin-Ig molecules Glycoproteins(MW-150kd)composed of two identical heavy polypeptide chains (MW- 50 kd) and two light chains (MW25kd each) The amino terminal of the chains show variable amino-acid composition(V) and the C-terminal regions are constant (C) - Antigen binds to the V region of the heavy and light chains -Each Ig is bivalent and can bind two identical antigens - Heavy and light chains are held together by non-covalent bonds and covalent disulfide interactions -The two heavy chains are held together by disulfide bonds at the hinge region -Treatment with proteolytic enzyme, pepsin generates a F(ab)2 fragment -The enzyme, papsin, cleaves the Ig molecule at the hinge region to generate two identical Fab fragments and a FC region. IgG Classes The different Ig classes differ in their aminoacid sequences at the FC region 1) IgG Has gamma heavy chains 75% of the total Ig in human serum Secondary immune response in most antigens Can cross the placenta Most commonly used in biotech 2) – IgM -Has Mu heavy chains -Forms pentamers -B-cell antigen receptor. Primary immune response to most antigens 3) IgA Has alpha heavy chains Found in both monomeric and dimeric forms Primary defense mechanism in membrane secretions (eg. Tears and saliva) Present in breast milk Ig Classes Ig molecules also can be catagorized into two subclasses depending on their type of light chains: 1) Kappa (k) light chain. 2) Lambda heavy chain Epitopes Immunogen An antigen (non-self) that initiates an immune response High MW > 6000d (6kd) Chemical complexity Proteins are strong immunogens Carbohydrates with complex structure are immunogenic Lipids are immunogenic Nucleic acids are poor immunogens Poor or non-imunogens can become immunogenic by conjugation to a carrier protein (eg. BSA) Inject antigen multiple times in the presence of an immune boosting compound called adjuvant Test for the presence of antibodies and titer: The Collect blood samples Centrifuge and collect the serum Recombinant Antibody An engineered recombinant DNAcoding for an antibody molecule or the binding portion of an antibody molecule is inserted in bacteria,yeast or human cells The expressed antibody is pulled from the cells No animal is used Recombinant Antibody The technique can be used to make libraries of antibody molecules with slightly different amino acid sequences that can further tested to find the one with the most affinity for an antigen The recombinant DNA can be engineered to encode a human antibody molecule with the binding portion of a mouse. This type of antibody is called “humanized” or Chimeric antibody. It eliminates the problem of using animal antibodies on humans and triggering an immune response. Applications ELISA Western Blotting Immunochemistry Immunoflouresence Theraputic (Herceptin)