* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immunoglobulin
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunoprecipitation wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
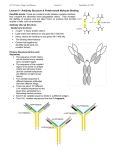
Immunoglobulin Justas Arasimavičius Immunoglobulin Element of adaptive immune mechanism Better known as antibody It recognize the foreign objects How they work (examples) Animation1 Animation2 Structure of immunoglobulin Two identical heavy (H) chains and two identical light (L) chains combine to form this Y-shaped antibody molecule Disulfide bonds Bonds between two amino acids result of the SH (sulfhydral) group of one amino acid covalently bonding to the SH group of another amino acid Stronger than hydrogen bonds Eg. Hair proteins are held together by disulfide bonds Heavy chains The heavy chains each have four domains Variable domains (VH) Constant domains (CH1,2,3) Light chain The light chains are constructed of two domains Variable (VL) Constant (CL) Structure of immunoglobulin The fragment antigen binding (Fab fragment) The fragment crystallizable region (Fc region) Antibodies bind to antigens by reversible, noncovalent interactions, including hydrogen bonds and charge interactions How variety is maintained The variable heavy chain is coded combining 3 genes (VH, DH, JH) The variable light chain is coded combining 2 genes (VL, JL) Most likely humans produce between 107 and 109 different shaped Fabs Antibody Fab region Antibody (Fab) molecular surface, with the PorA antigen superimposed. The dark colored groove on the surface of the antibody matches precisely the shape of the PorA antigen Any changes in the sequence of PorA in this region can disrupt antibody binding http://www.bact.wisc.edu/themicrobialworld/neisseria.html Antigen binding some pictures Antigen binding some pictures Structure of immunoglobulin Functional consequences: (VH) and (VL) are positioned to stereochemically react with antigen The stem is good for mediate effector functions Hinge Two disulfide bonds in the hinge region unite the two heavy chains The hinge allows the two antigen-binding Fab regions of each antibody molecule to move Conclusion Changes in the antigen binding site conformation are vital for antigen recognition Herewith the variety of antibody conformation is vital for our health Reference http://www.callutheran.edu/Academic_Programs/Departments/BioDev/omm/jmol/ig_div/start.html http://en.wikipedia.org/ http://www.path.cam.ac.uk/~mrc7/mikeimages.html http://www.tulane.edu/~biochem/med/igg.htm http://www.biology.arizona.edu/IMMUNOLOGY/tutorials/antibody/structure.html http://student.ccbcmd.edu/courses/bio141/lecguide/unit5/humoral/abystructure/abystructure.html http://www.mun.ca/biochem/courses/3107/Topics/Antibodies.html Abul K. Abbas, Andrew H. Lichtman. Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System. Second Edition 2004