* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GLYCOLYSIS UP - Hudson City Schools / Homepage
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
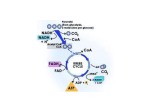
SUGAR UP QUESTIONS Or Review to Chapter 6 Honors BiologyTest Respiratory System • 1. nostril • 2. nasal cavity 3. Pharynx 4. Epiglottis (flap) 5. Larynx (voice box) 1. 2. 4. 3. 5. Respiratory System (cont) 6. Esophagus (to stomach) 7. Trachea 6. 7. 8. R. lung 9. Pleura (lining) 8. 9. Respiratory System (cont) • 10. bronchi • 11. bronchioles 10. • 12. diaphragm 11. 12. Respiratory System (cont) • • • • • To the heart: pulmonary vein 13. alveoli 14. pulmonary artery 14. 15. capillary bed 16. alveolar duct 16. 17. alveolus From the heart 13. 15. Respiratory System • What is another name for the trachea? Where is it? • Windpipe and located below epiglottis Where is the L. pulmonary artery? R. Pulmonary vein • L. pulmonary artery is 3 • R. pulmonary vein is 4 Label and describe what is going on here: • Answer next slide What electron carriers are at “D” and at “E”? “D” = NADH “E” = FADH2 + NADH What waste gas leaves at “H”? H = Carbon Dioxide What processes are at A, B, C? A (glycolysis) B (Krebs cycle) C (ETC and chemiosmosis) What is at “I” “F” “G”? __I “I” = 2 ATP, “F”= 2 ATP, “G” = 34 ATP? 18. Which process is the anaerobic one in yeast? • • • • • • A. glycolysis B. Krebs Cycle C. Chemiosmosis D. ETC E. alcoholic fermentation F. lactic acid fermentation • ANSWER: alcoholic fermentation 19.Which is the movement of H+ ions across ATP synthase? • • • • • • A. glycolysis B. Krebs Cycle C. Chemiosmosis D. ETC E. alcoholic fermentation F. lactic acid fermentation • ANSWER: chemiosmosis 20. Which is the splitting of glucose into two 3-carbon compounds? • • • • • • A. glycolysis B. Krebs Cycle C. Chemiosmosis D. ETC E. alcoholic fermentation F. lactic acid fermentation • ANSWER: glycolysis 21. Which is also called the citric acid cycle? • • • • • • • A. glycolysis B. Krebs Cycle C. Chemiosmosis D. ETC E. alcoholic fermentation F. lactic acid fermentation G. TCA cycle • ANSWER: Krebs cycle and TCA 22. Which is the movement of electrons from high energy to low? • • • • • • A. glycolysis B. Krebs Cycle C. Chemiosmosis D. ETC E. alcoholic fermentation F. lactic acid fermentation • ANSWER: ETC 23. Which is the anaerobic process in animals’ muscles? • • • • • • A. glycolysis B. Krebs Cycle C. Chemiosmosis D. ETC E. alcoholic fermentation F. lactic acid fermentation • ANSWER: lactic acid fermentation 24. How many carbons are in each pyruvic acid molecule? • 2 3 • ANSWER: 3 6 34 38 40 25. How many ATP’s are formed when one molecule of glucose break down (net) in glycolysis only? • 2 3 6 • ANSWER: 2 (net) 34 38 40 26. What is the number of FADH2 formed per pyruvate molecule in glycolysis? • • • • • • • 0 1 2 3 4 6 ANSWER 0 27. How many ATP’s are formed during the ETC and chemiosmosis? • 2 3 • ANSWER: 34 6 34 38 40 28. How many net ATP’s are formed from the breakdown of one glucose molecule TOTAL from cellular respiration (Krebs + ETC/chemiosmosis) and glycolysis? • 2 3 • ANSWER: 38 6 34 38 40 29. How many ATP’s are needed to get the glucose in glycolysis to start breaking down? • 2 3 • ANSWER: 2 6 34 38 40 30. How many ATP are made in the Energy Payoff Phase of Glycolysis? • • • • 1 2 3 4 • ANSWER: 4 HEY!!!!! • 1 NADH = __________ ATP • 1 FADH2 = _________ ATP • 3 • 2 31. Where does FERMENTATION occur? • • • • A. Cytoplasm B. Matrix C. Inner membrane of mitochondrion D. Intermembrane space of mitochondrion • ANSWER: cytoplasm (fermentation and glycolysis) 32. Where does Krebs CYCLE occur? • • • • A. Cytoplasm B. Matrix C. Inner membrane of mitochondrion D. Intermembrane space of mitochondrion • ANSWER: matrix 33. Where does ETC occur? • • • • A. Cytoplasm B. Matrix C. Inner membrane of mitochondrion D. Intermembrane space of mitochondrion • ANSWER: inner membrane • • • • 34. Where do H+ ions collect before they pass through the ATP synthase? A. Cytoplasm B. Matrix C. Inner membrane of mitochondrion D. Intermembrane space of mitochondrion • ANSWER: intermembrane space 35. Where is the ATP synthase located?? • • • • A. Cytoplasm B. Matrix C. Inner membrane of mitochondrion D. Intermembrane space of mitochondrion • ANSWER: inner membrane 36. How is the ETC different than burning glucose with a flame? • ETC breaks down glucose gradually • • A flame burns glucose all at once 34% of energy captured (ETC), rest is lost as heat 37. Which electron carrier(s) (is) are in glycolysis? • FADH NADH • NADH • Which electron carriers are in Krebs cycle? • BOTH NADH and FADH2 38. What is the final electron acceptor of the ETC? • • • • A. oxygen B. NAD+ C. FAD D. Jimin Leeeeee • ANSWER: oxygen 39. Where do each of these come from to form water in cellular respiration? • • • • • • H+ NADH and FADH2 Oxygen Breathing in Electrons NADH and FADH2 (released to ETC) 41.What is the difference? • Between calorie and Calorie? • calorie = heat it takes to raise 1 gram of water 1 degree Celsius • Calorie = 1000 calories • Calorie = 1 kcal So… • 50 calories • 0.05 Calories • 0.05 kcal 1 Calorie = 1000 calories • 1 Calorie = 1000 calories = 1 kcal • 1 calorie = .001 Calorie = .001 kcal 42. What is another name for… • • • • • • The Krebs Cycle? A. Calvin Cycle B. Lactic Acid Cycle C. Citric Acid Cycle D. Pyruvic Acid Cycle E. TCA cycle • ANSWER: C + E 43. Which enzyme… • Grooms pyruvic acid so it can enter the Krebs cycle? • A. Lactase • B. Coenzyme A • C. Coenzyme K • D. Protease • ANSWER: B 43. What is cut off… • Pyruvic acid so it can enter the Krebs cycle? • A. oxygen • B. nitrogen • C. hydroxide • D. carbon dioxide • ANSWER: D 44. What is formed at the end of glycolysis (3-C molecule)? • • • • Carbon dioxide Pyruvate G3P NADH • ANSWER: pyruvate (pyruvic acid) 45. What is the product at the end of ETC/chemiosmosis with H+ and with oxygen? • • • • Pyruvic acid ATP Water Carbon dioxide • ANSWER: water 46. What product forms with ethanol (ethyl alcohol) in yeast fermentation? • ATP • Water • Carbon dioxide • Ethanol • ANSWER: carbon dioxide 47. What product forms at the end of anaerobic fermentation in muscles of animals? • • • • • Carbon dioxide Water Pyruvic acid Lactic acid Ethanol • ANSWER: lactic acid 48. What is an intermediate formed at the end of the Energy Investment Phase of glycolysis? • • • • Pyruvate G3P OAA Citric acid • ANSWER: G3P 49. What forms as a waste product in yeast + glucose if oxygen is not present ? • ethanol 50. ADP • HOW DIFFERENT IS ATP? • ANSWER: ATP has one more phosphate attached • ATP stores more energy 51.NAD+ • HOW DIFFERENT IS NADH? • Answer: NADH Picked up electrons and hydrogen. 52. FAD • How different is FADH2 ? • ANSWER: FADH2 has picked up electrons and 2 hydrogen. 53. Glucose • How different is pyruvic acid? • ANSWER: Glucose is 6-C and pyruvic acid is 3-C made from glucose splitting. Is it ANAEROBIC OR AEROBIC? • • • • • Glycolysis Krebs cycle Chemiosmosis Fermentation ETC • • • • • Anaerobic Aerobic Aerobic Anaerobic Aerobic 54. What is the difference between anaerobic and aerobic? • A. with oxygen • B. without oxygen • ANSWER: anaerobic is without oxygen • Aerobic is with oxygen 55. What causes the electrons to flow down the ETC? • e- are passed from one protein to another from high energy to lower pulled by the final oxygen acceptor • (the escaped energy is used to move the H+ across the inner membrane of the mitochondrion) 55. What is the final electron acceptor? • OXYGEN 56. What is the respiratory system disorder? • Involuntary muscles of the air tubes constrict making breathing difficult • Asthma • Spasmic contractions of the diaphragm causing the snapping of the glottis • hiccups 56. What is the respiratory system disorder? • Infection of overuse of the vocal cords causing loss of sound. • Laryngitis • Chronic expansion of the alveoli so they cannot spring back. • emphysema 56. What is the respiratory system disorder? • Infection of the lining of the air tubes causing soreness, swelling the irritation for a raspy cough. • bronchitis • A sore throat. Its an inflammation or infection of the lining of the throat. • pharyngitis 56. What is the respiratory system disorder? • An infection of the lung air sacs and alveoli- they fill with fluids and breathing is labored. • pneumonia • An infection of the membranes surrounding the lungs, painful to breathe. • pleurisy 57. What is the formula for cellular respiration? • C6H12O6 • + 6 O2 • 6 CO2 + 6 H2O • + ATP What is the equation for cellular respiration? • C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP 58. What is the difference between substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation? • See the next slide 2 Ways to Make ATP • Substrate-Level • Oxidative Phosphorylation Phosphorylation • (without a • diffusion of membrane; it occurs particles through a in the cytoplasm or membrane matrix of produces ATP mitochondrion with • -loses ehelp of an enzyme) 59. How is pyruvate “cut and groomed” to enter the Krebs cycle? • Cut = remove carbon as carbon dioxide • Groomed is acetyl group is attached to Coenzyme A 60. Fill in the total number formed in the Krebs cycle for 2 pyruvates: • • • • ATP NADH FADH2 CO2 • • • • 2 6 2 4 61. CONTRAST • SLOW TWITCH MUSCLES • Thin fibers • Many mitochondrion • Aerobic • Many myoglobin • Dark Meat • Long Distance runs • FAST TWITCH MUSCLES • Thick fibers • Few Mitochondrion • Anaerobic • Few myoglobin • Light Meat • Sprinters, weight lifting 62. WHAT IS AT EACH AREA? C. D. folds E. A. B. Intermembrane space (Fold) 63. In the following equation, what is oxidized and what is reduced? • 63. In the following equation, what is oxidized and what is reduced? ANSWER Lose e- and lose H Gain e- and gain H LEO goes GER 64. What is OAA? • Oxaloacetate combines with acetyl group to form citric acid OAA 65. What causes ATP synthase to produce ATP? • As the H+ ions that collected in the intermembrane space pass through the ATP synthase, it moves and causes the P to join ADP to form ATP 66.Match the poisons • Cyanide • Oligomycin • DNP • rotenone • Blocks ETC to kill insects and fish in ponds-Blocks first protein in ETC • Blocks fourth protein in ETC; used in Tylenol tampering • Antibiotic blocks H+ passage • Quickens metabolic rateenergy all lost as heat 66.Match the poisons • Cyanide • Oligomycin • DNP • rotenone ANSWERS • Blocks fourth protein in ETC; used in Tylenol tampering • Antibiotic blocks H+ passage • Quickens metabolic rateenergy all lost as heat • Blocks first protein in ETC and Blocks ETC to kill insects and fish in ponds 67. How does pyruvate change in Alcoholic fermentation • Gives off carbon dioxide • Regenerates NADH to NAD+ • Forms alcohol (ethanol) Lactic acid fermentation • Forms lactic acid • DOES NOT FORM carbon dioxide • Does regenerate NADH to NAD+ 68. How are these different? Obligate anaerobes • Organisms that require anaerobic conditions (NO OXYGEN) Facultative anaerobes • Organisms that can live in or not live in aerobic conditions 69. What is the smallest rotary motor known? • ATP synthase What runs it? • Proton concentration (H+) gradient from the intermembrane space • WHAT DOES IT MAKE? • ATP 70. Which process… • Means “sugar breaking?” • A. glycolysis • B. Krebs cycle • C. ETC • D. chemiosmosis • ANSWER: A 71. What process… • Regenerates NAD+ so glycolysis can continue? • A. Krebs cycle • B. fermentation • C. glycolysis • D. chemiosmosis • ANSWER: B 72. See question 64 73. In a redox reaction how do you know if a molecule has been oxidized? Reduced? • Oxidized = loss of electrons = loss of H+ • Reduced = gain of electrons = gain of H+ 74-77 What is at “A” and “C”? “A” = ETC “C” = ATP Synthase Where do the H+ ions collect? H+ ions collect at “B” H+ H+ H+ H+ Where is the Krebs Cycle? H+ H+ H+ H+ “D” has the Krebs Cycle H+ H+ H+ H+ KREBS CYCLE When electrons are passed in the ETC, what direction does the energy flow? • Low to high • High to low • Even throughout • ANSWER: High to low What is phosphorylation? • Addition of a phosphate • Addition of a hydrogen • Addition of an oxygen • ANSWER: Addition of a phosphate • Like ADP + P = ATP • Adding P to glucose to break into pyruvic acid 78. Which is inhalation? Which is inhalation? Contract Relax Volume decrease Vol. increase Which is the diaphragm relaxing? Which is the diaphragm relaxing? EXTENDED RESPONSE HINTS • 1. NAD+ to NADH and back to NAD+ • Example: glycolysis, Kreb cycle, ETC • Show when it forms NAD+ to NADH and then loses them at the ETC (LEO goes GER) ETC and ATP synthase Team • 2. H+/e- source from NADH and FADH2 EXTENDED RESPONSE HINTS • 3. Pulmonary arteries • Carry deoxygenated LUNGS • Pulmonary veins • Carry oxygenated Normal arteries carry oxygenated Heart to body Normal veins carry deoxygenated • Arteries always away from the heart • Veins always to the heart 3 EXTENDED RESPONSE HINTS #4 • • • • • • • Anaerobic respiration Aerobic resp. Does not requires O2 Requires oxygen Occurs in cytoplasm Occurs in mitoch. Only needs enzymes Needs membranes act as ETC, ATP synthase Only makes 2 ATP makes 34 + 2 ATP Just a bunch more of •Great questions Where does it take place? • 1. cellular respiration • 2. Krebs cycle • 3. lactic acid fermentation • 4. alcoholic fermentation • 5. gives off CO2 as a waste product CHOICES: • C = cytoplasm • M = mitochondrion • IM = inner membrane • IMS = inter membrane space • MX = matrix Where does it take place? • 1. cellular respiration • 2. Krebs cycle • 3. lactic acid fermentation • 4. alcoholic fermentation • 5. gives off CO2 as a waste product • M • MX • C • C • MX Where does it take place? • • • • ETC Glycolysis Citric acid cycle NADH and FADH2 (gives up e-) • H+ ions collect when NADH and FADH2 give up e- CHOICES: • C = cytoplasm • M = mitochondrion • IM = inner membrane • IMS = inter membrane space • MX = matrix Where does it take place? • • • • ETC Glycolysis Citric acid cycle NADH and FADH2 (gives up e-) • H+ ions collect when NADH and FADH2 give up e- • IM • C • MX • MX to IM • IMS What number? 2 3 4 6 34 38 ATP to start glycolysis? ANSWER: 2 Total ATP made from glycolysis to pyruvic acid? ANSWER: 4 What number? 2 3 4 6 34 38 Net ATP made from glucose to pyruvic acid? ANSWER: 2 ATP from Krebs cycle? ANSWER: 2 What number? 2 3 4 6 34 38 ATP from ETC and chemiosmosis? ANSWER: 34 Total ATP from one glucose broken down (glycolysis + Krebs cycle + ETC/chemiosmosis) ? ANSWER:38 What number? 2 3 4 6 34 38 Number of carbons in glucose? ANSWER: 6 Number of carbons in pyruvic acid? ANSWER: 3 What molecule is it? • That grooms pyruvic acid to enter the Krebs cycle? ANSWER: coenzyme A What molecule is it? That is the final (ultimate) electron acceptor? ANSWER: oxygen What molecule is it? That forms when pyruvic acid breaks down in muscles (anaerobically)? ANSWER: lactic acid What 2 molecules… • That form when pyruvic acid breaks down in yeasts (anaerobically)? • ANSWER: carbon dioxide and ethanol (ethyl alcohol) What molecule is it? • An electron carrier formed from glycolysis? • ANSWER:NAD+ to NADH What molecule is it? • 2 electron carriers formed in the Krebs cycle? • ANSWER: NADH and FADH2 What molecule… • Forms after H+ ions go through ATP synthase? • ANSWER: ATP What molecule is it? • That is formed after H+ ions join with oxygen? • ANSWER: H2O What molecule is it? • That forms as a one-carbon waste product in the Krebs cycle? • ANSWER: carbon dioxide What molecule is it? • That is a 6-carbon molecule that forms temporarily in the Krebs cycle (2-C acetyl CoA and a 4-C compound)? • ANSWER: citric acid Which is the form in each that is filled carrying e-? • NAD+ or NADH? • FADH2 or FAD? • ANSWER: NADH and FADH2 As e- go down the ETC, do they do it…? • Gradually (step by step) • OR • Quickly (all at once)? • ANSWER: gradually Pyruvic acid gets “cut and groomed” by what and to go where? • ANSWER: • BY Coenzyme A to go into the Krebs cycle What is chemiosmosis? • The diffusion of _____________ from ______ concentration to ___________ concentration across a ________________. • ANSWER: H+ ions, High to Low, membrane Where do the H+ ions collect after the NADH and FADH2 dropped them off and they got pulled to here? • ANSWER: • Intermembrane Space