* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neurophysiol
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of antiandrogens wikipedia , lookup
5-HT2C receptor agonist wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
5-HT3 antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
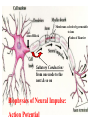
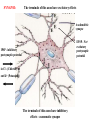
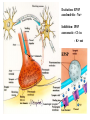
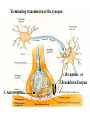
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
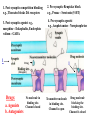
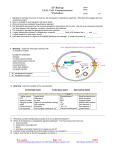
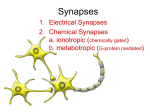
Midterm 1 Need: ID, Pen, Pencil 25 multiple-choice (50%) –Ch 1,3 2/3 essays (50%) – SQ 1-12 Axon Hillock Membrane- selectively permeable to ions Nodes of Ranvier Saltatory Conduction: from one node to the next & so on Biophysics of Neural Impulse: Action Potential Ions: Neuron polarized 1. 2. 3. Electrostatic pressure Diffusion Na – K “Pumps” Proteins-Neuron depolarized Neuron hyperpolarized SYNAPSE: The terminals of this axon have excitatory effects Axodendritic synapse EPSP - Na+ excitatory postsynaptic potential IPSP - inhibitory postsynaptic potential in Cl - (Chloride) or out K+ (Potassium) The terminals of this axon have inhibitory effects - axosomatic synapse Excitation: EPSP axodendritic - Na+ Inhibition: IPSP axosomatic - Cl- in - K+ out P + P IN OUT EPSP Ca++channels open Ionotropic receptor Ion channel Types of Receptors: • 1. Ionotropic receptor— coupled to ion channel and directly opens it (fast acting). • 2. Metabotropic receptor– indirectly opens ion channel (slow acting). It activates G-protein in post-synaptic neuron which (a) opens ion channel, or (b) activates 2nd messenger (e.g., cyclic AMP) which then opens ion channel (b is more common). Terminating transmission at the synapse: 1. Re-uptake or 2.Breakdown Enzyme 3. Autoreceptors 1. Post-synaptic competition blocking e.g., Thorazin blocks DA receptors 3. Post-synaptic agonist e.g., morphine - Enkephalin, Endorphin valium - GABA 1 2. Pre-synaptic Reuptake block e.g., Prozac - Serotonin (5-HT) 4. Pre-synaptic agonist e.g., Amphetamine - Norepinephrine 1 Drug (Receptor) Drugs: a. Agonists b. Antagonists No molecule in binding site. Channel closed Transmitter molecule in binding site. Channel is open Drug molecule blocking the binding site. Channel is closed