* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hallucinogens - People Server at UNCW
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
Non-specific effect of vaccines wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
5-HT3 antagonist wikipedia , lookup
5-HT2C receptor agonist wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Lysergic acid diethylamide wikipedia , lookup
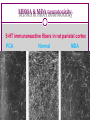
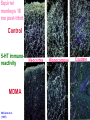
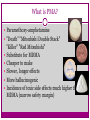
Psychedelics CHAPTER 12 Psychedelic/Hallucinogens Called by many different names Psychotogens Psychotomimetics Psychedelics Primary effect is to produce perceptual changes & hallucinations Can influence several sensory systems, perception of time, space & events Different Types of Psychedelics Serotonergic LSD Psilocybin/Psilocin DMT - Ayahuaca Bufotenine Ololiuqui Catecholamine-like Mescaline MDMA (ecstasy) MDA MDE DOM Myristin and Elemicin Cholinergic Muscarine Scopolamine Glutamatergic PCP Ketamine Dextromethorphan Opioid Salvinorin A Serotonergic Psychdelics LYSERGIC ACID DIETHYLAMIDE (LSD) Lysergic acid – Derived from ergot alkaloids Ergot is a poisonous fungus that infects rye & other grains & grasses Albert Hoffman: 1938 - synthesized #25 in series of new molecules doing ergot alkaloid chemistry 1943 - returned to #25 making new batch & absorbed some through skin LSD in the USA Came to U.S. in 1950s in two ways: • Clinical usage: Supplied to psychologists and psychiatrists • • encouraged their taking drug Military Usage: U.S. military and CIA as incapacitating agent and truth drug U.S. government gave LSD to unsuspecting individuals to study effects LSD in the USA 1960s - popular use advocates East Coast: Timothy Leary (clinical psychologist at Harvard) West Coast: Ken Kesey (noted author) graduate student in California got dose in psychology study shortly after this goes to work in psychiatry year later, writes One Flew Over The Cuckoo's Nest LSD in the USA Spread through country with huge publicity until peak 1968 to 1972 Schedule I in 1968 Stuffy politicians didn’t know what to do because LSD was used by white, middle to upper class, college students Early 1990s - LSD came back LSD & Neurotransmission Binds to 5-HT2A receptors agonist effect Increases amount of sensory information getting to cortex through overriding filter mechanisms This is how the drug influences perception, especially for vision Pharmacology of LSD Pharmacological Effects Effects heavily dependent on dose taken not just intensity of effects, but type of effects Low doses = mild perceptual alterations comparable to effects of marijuana use, but greater clarity Effects of LSD High Doses progression through mental and emotional experiences 6-12 hrs duration Each trip unique, highly dependent upon setting and personal expectations Can alter subjects’ emotional feelings during trip by experimenter’s previous behavior warm and supportive or suspicious and nonsupportive Effects of LSD Effects of drug come on in about 30 min first signs are autonomic activation followed by overt behavioral signs - loosening of emotional inhibitions giddiness, laughter for no reason mood euphoric and expansive, but labile mood swings notable abnormal color sensations, luminescence colors reported as more brilliant Effects of LSD space and time disorders added depth with loss of perspective - up/down altered close in space influenced more than distant general slowing of time reported LSD Hallucinations gratings, latticework, honeycomb, chessboard, tunnels, funnels, alleys, cones, vessels, and spirals can be present with eyes open or closed involve bright light in center with figures moving in from periphery forms appear to move in depth and take on color shades, red common Sounds can take on visual forms music may take on enhanced meaning or intensity LSD & Bad Trips Psychological impact - traumatizing, imagery dark, insights appalling Usually occur in novice users, feel out of control Generally negative set and setting are key contributing factors Can lead to suicide or prolonged psychotic reaction Can usually be talked down from a bad trip LSD & Flashbacks Spontaneous recurrence of trip after period of normalcy can occur after long periods of abstinence more common after multiple high dose use prolonged afterimages for days and weeks after tripping mechanism unknown can be brought on by other drugs or setting most commonly reported in low light situations not intrinsically dangerous and usually go away Psilocybin/Psilocin Magic Mushrooms, Liberty Caps Central America and northwestern U.S. Last about 6-10 hours Need a lot to get same effect as LSD 5-HT2A agonist Same basic effects as LSD Mushrooms occasionally toxic DMT Dimethyltriptamine 5-HT2A agonist Alkaloid Often smoked Main ingredient in Ayahuasca Same effects as LSD Bufotenine Dimethyl-serotonin A product of abnormal serotonin breakdown Like LSD and others Can occur in urine of people with psychiatric disorders Psychosis Paranoia Depression Ololiuqui Substance found in morning glory seeds Similar to LSD Significant nausea, vomiting and cramping Tolerance/Dependence Not significant producers of tolerance or dependence No withdrawal either People and animals do not self-administer Problems related to the things people do while under the influence Accidents Suicide Aggression/violence Toxic reactions Catecholamine-like Psychedelics Mescaline Active drug in peyote Structurally similar to NE However, most of the effect is mediated by our friend, the 5-HT2A agonist action Legal for members of the Native American Church Ecstasy MDMA (methylene-dioxy-methamphetamine) Synthesized in 1912 Structurally related to amphetamines Sympathomimetic Weak in altering perceptual functions But strong effects on emotions - empathogen Used in combo with psychotherapy O CH 3 O CH 2 CH MDMA NH CH 3 Pharmacodynamics Monoamine neurotransmission increase synaptic DA and 5-HT blocks 5-HT transporter enters neuron and causes release of 5-HT Ecstasy Effects Stimulant effects typically noted shortly after ingestion increased heart rate increased blood pressure dry mouth decreased appetite increased alertness elevated mood jaw clenching Subjective Effects euphoria increased physical and emotional energy heightened sensual awareness subjective feeling of increased closeness or enhanced communication Cognitive Effects memory loss Ecstasy Effects X Tox Malignant hyperthermia and dehydration Idiopathic toxic response (not common but nasty) Renal failure Rhabdomyolysis – disintegration of muscle tissue Street X is even more of a problem because it’s not always X or may have other drugs X Tox Potent neurotoxin 1-2 times street dose depletes forebrain 5-HT (not DA) Kills the transporter receptor (SSRI) Degeneration of 5-HT terminals Fine axons from dorsal raphe Can get 30% loss with single injection Up to 80% with repeated injections Can induce psychiatric disturbance in vulnerable individuals. Treatment refractory depression MDMA & MDA neurotoxicity 5-HT immunoreactive fibers in rat parietal cortex PCA Normal MDA 9.9 Squirrel monkeys 18 mo post-trtmt Control 5-HT immunoreactivity MDMA McCann et al. (1997) Neocortex Hippocampus Caudate What is PMA? Paramethoxy-amphetamine "Death" "Mitsubishi Double Stack" "Killer" "Red Mitsubishi" Substitute for MDMA Cheaper to make Slower, longer effects More hallucinogenic Incidence of toxic side effects much higher than MDMA (narrow safety margin) Designer Psychedelics DOM, MDA, DMA, MDE, TMA, AMT, 5MeO-DIPT All structurally related to mescaline and methamphetamine; therefore MDMA. MDA is a metabolite of MDMA. May be responsible for much of the MDMA effect. Myristin and Elemicin Found in nutmeg and mace Structurally similar to mescaline Significant nausea and vomiting The sick usually limit use Glutamatergic Psychedelics DISSOCIATIVE ANESTHETICS Phencyclidine PCP NMDA receptor antagonist Blocks the function of glutamate Used as an analgesic and anesthetic Can be administered by any route Oddly enough, animals self-administer (euphoria) Induces amnesia and true psychosis Hallucinations, paranoia, agitation, dissociation Higher doses lead to stupor, coma seizures, death A perfect example of a Schedule I drug Ketamine Special K Very similar to PCP, not as powerful Liquid, but can be powdered for snorting or smoking But just as dumb, stupid, useless and unsafe Another perfect example of a Schedule I drug Subjective Effects of PCP/Ketamine Sensations of light coming through the body and/or colorful visions Complete loss of time sense Bizarre distortions of body shape or size Altered perception of body consistency Sensations of floating or hovering in space Feelings of leaving one’s body Visions of spiritual or supernatural beings Emotions ranging from euphoria to hositlity Dalgarno & Shewan (1996) Dextromethorphan Active ingredient in most OTC cough medicine NMDA receptor blockade at high doses Mostly teenage males abuse it Like PCP and K at 20-30 X OTC dose Coricidin –Bad news Cholinergic Hallucinogens Muscarine/Muscimol Found in mushrooms (Amanita Muscaria) Muscimol is a GABAA agonist Trance-like, dreamy state with dreamlike illusions Like Ambien Muscarine is an Acetylcholine agonist (muscarinic receptors) Not psychotropic Peripheral effects: sweating, limb twitching, seizure activity Found in – Atropa belladonna, Datura Stramonium, Henbane Acetylcholine receptor (muscarinic) antagonists Dissociatives that induces delirium , hallucinations, and amnesia Classic anticholinergic symptoms Hot as hell Dry as a bone Mad as a hatter Blind as a bat Red as a beet Used in the treatment of motion sickness & to dilate pupils during eye-exams. Atropine & Scopolamine Comes from a plant in the mint family Salvia Divinorum Affinity for kappa opioid receptors Agonist action Like LSD and psilocybin Fresh leaves are chewed and left in mouth Dried leaves smoked Not effective if taken orally Most potent, but not most powerful, of all naturally occurring hallucinogens It’s still legal, but not likely for long Opioid Hallucinogen - Salvinorin A