* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Challenges to therapy for peroxisome assembly disorders
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Structural alignment wikipedia , lookup
Rosetta@home wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Protein design wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
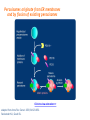
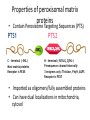
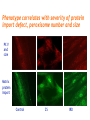
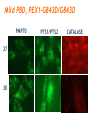
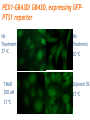
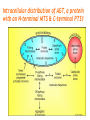
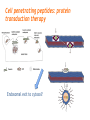
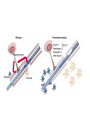
Challenges to therapy for peroxisome assembly disorders Nancy Braverman, MS, MD McGIll University-MCH-RI March 9 2010 HGEN 171-575 Properties of peroxisomes • Spherical, single membrane bound, • Diameter = 0.2 - 1 µm, several hundred/cell • All eukaryotes Peroxisomes originate from ER membranes and by fission of existing peroxisomes Click to view animation >> adapted from Annu Rev Genet. 2000;34:623-652. Sacksteder KA, Gould SJ. NEXT >> Role of peroxins in matrix protein import Click to view animation >> Gould, Raymond, Valle.In: Metab & Molec Basis of Inh Dis. Ch 129 p. 3190. Enzymatic pathways in peroxisomes • • • • • • • • Fatty acid oxidation (VLCFA, PA) H2O2 detoxification (catalase) Docohexanoic acid (DHA) synthesis Bile acid synthesis Plasmalogen (ether phospholipid) synthesis Cholesterol synthesis Glyoxylate detoxification Lysine catabolism (pipecolic acid) The 3 major metabolic pathways in peroxisomes Properties of peroxisomal matrix proteins • Contain Peroxisome Targeting Sequences (PTS) PTS1 PTS2 -SKL -SKL C - terminal (-SKL) Most matrix proteins Receptor is PEX5 R/KLX5Q/HL N - terminal (-R/KLX5 Q/HL-) Presequence cleaved internally 3 enzymes only: Thiolase, PhyH, AGPS Receptor is PEX7 • Imported as oligomers/fully assembled proteins • Can have dual localizations in mitochondria, cytosol Genetic disorders of peroxisomes • Multiple enzyme deficiencies: Peroxisomal Biogenesis Disorders (PBD) – Zellweger spectrum disorder (ZSD) (~1/60,000) – Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata spectrum (RCDP)(~1/100,000) • Single enzyme deficiencies – – – – X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) (~1/20,000) 3-methyl-CoA racemase deficiency Adult Refsum disease Hyperoxaluria Type I Some single enzyme deficiencies can mimic PBDs • VLCFA oxidation → Zellweger spectrum disorder – Acyl-CoA oxidase – D-Bifunctional protein (hydratase/dehydrogenase) • Plasmalogen biosynthesis → RCDP spectrum – DHAPAT (RCDP2) – ADHAPS (RCDP3) • Some PBDs mimic SEDs → – Adult Refsum disease causes PEX7 deficiency Develop therapies targeted to the metabolic defects A--------->B • • Phytanic acid restriction Reduction in VLCFA dietary reduction enhance VLCFA omega oxidation reduce VLCFA synthesis • Supplementation with DHA, bile acids, plasmalogens Develop therapies targeted to the molecular defects • Enhance activity of a defective PEX proteinimprove protein folding • Bypass the need for a specific PEX proteinupregulate a partner PEX protein • • • • • Induce peroxisome proliferation Enzyme/PEX protein replacement therapy ? Liver/stem cell transplant ? Gene therapy ? Manipulate the intestinal microbiome? PBD phenotypes correlate with biochemical severity Phenotype correlates with severity of protein import defect, peroxisome number and size PX # and size Matrix protein import Control ZS IRD Mild PBD, PEX1-G843D/G843D PMP70 37 30 PTS1/PTS2 CATALASE PEX1-G843D/ G843D, expressing GFPPTS1 reporter No Treatment 37 oC No Treatment TMAO 200 uM Glycerol 5% 37 oC 30 oC 37 oC Disorder-to-order conformational transitions in protein structure and its relationship to disease • Lower temperature • Chaperone (protein or drug) – Nonspecific chemical chaperone – Pharmacologic chaperone Enzyme substrate Protein ligand (protein kinase and kinase inhibitor) Vitamin cofactor Conformational changes of p97 AAA ATPase during its ATPase cycle Bind and hydrolyze ATP generating chemical energy that is converted into motion of the molecule. Motion used to pull PEX5 out of the membrane for another round of import Role of peroxins in matrix protein import Click to view animation >> Gould, Raymond, Valle.In: Metab & Molec Basis of Inh Dis. Ch 129 p. 3190. High throughput chemical screen • Cells incubated in chemicals 2 days (2000 compounds) • Negative control: media alone • Positive control: TMAO and glycerol 3 chemicals rescued import • Data indicated that they can noncompetitively bind to the ATP binding sites of proteins • Potential pharmacologic chaperones! Pipeline for new drugs 5-10 yrs… • • • • • • • • • • Develop HT assays to screen chemical libraries for compounds that recover target function Best to start with ‘in vivo’ assay, several complementary assays Confirm ‘hits’ from the screening assay Study structure-function relationships to develop best ‘lead’ compounds Evaluate mechanisms of recovery Asses pharmacokinetics: half-life, metabolism, excretion, recovery in the brain, toxicity, tissue pathology (rodents) Assay efficacy: animal models Approval of drug for clinical trials or off-use label Ensure drug supply, design and approval of clinical trial Funding for clinical trial Intracellular distribution of AGT, a protein with an N-terminal MTS & C-terminal PTS1 Primary hyperoxaluria type 1 • 15-20% European and North American population has Pro11Leu missense substitution – Decreased AGT stability – Decreased enzymatic activity – Enhances effect of additional mutations that are predicted to be innocuous in its absence – Redirects AGT to mitochondria • Gly170Arg folding delay promotes mitochondrial import Protein evolution depends on diet Cell penetrating peptides: protein transduction therapy Endosomal exit to cytosol? Role of peroxins in matrix protein import Click to view animation >> Gould, Raymond, Valle.In: Metab & Molec Basis of Inh Dis. Ch 129 p. 3190. Understanding the pathophysiology may reveal other targets for therapy Selective inactivation of PEX5 gene in neural cells Pex5-loxP x Nestin-cre (neurons, oligodendrocytes and astrocytes) Pex5-loxP x CNPase-cre (oligodendrocyte) Abnormal compaction of myelin Axonal damage and transport defects Reactive astrocytosis and microgliosis CD8+ T helper cells and increased cytokines