* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MKM803Chapter11
Ad blocking wikipedia , lookup
Advertising to children wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of advertising wikipedia , lookup
Advertising management wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Radio advertisement wikipedia , lookup
Targeted advertising wikipedia , lookup
Online advertising wikipedia , lookup
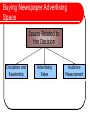
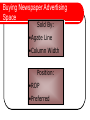
Print Media Evaluation of Magazines Allow the presentation of detailed information which the reader can process at his or her own pace. Print media are not intrusive, unlike TV and radio. Newspapers and magazines are referred to as high-involvement media. Require effort on the part of the reader for the advertising message to have an impact. Classifications of Magazines CARD divides magazines into three broad categories, based on the audience to which they are directed: Consumer Magazines Farm Publications Business Publications Consumer Magazines Major portion of the magazine industry, accounting for nearly 2/3 of all advertising dollars spent in magazines. Consumer magazines can be classified by: General interest Distribution Frequency Farm Publications There exist about 86 publications tailored to nearly every possible type of farming or agriculture. Ex. Ontario Milk Producer, Ontario Produce Farmer Business Publications Major categories include: 1. Magazines directed at specific professional groups. 2. Industrial magazines directed at businesspeople in various manufacturing and production industries. 3. Trade magazines targeted to wholesalers, dealers, distributors, and retailers. 4. General business magazines aimed at executives in all areas of business. Strengths of Magazines Creativity for Cognitive and Emotional Responses Geographic Coverage Target Audience Selectivity Permanence Media Image Selective Exposure and Attention Limitations of Magazines Absolute Cost and Cost Efficiency Reach and Frequency Long Lead Time Target Audience Coverage Clutter Buying Magazine Advertising Space Issues Related to This Decision: Circulation and Readership Audience Measurement Magazine Advertising Rates Magazine Circulation and Readership Most Important Decisions Size of Magazine / Circulation Characteristics of Reader / Readership Magazine Audience Measurement PMB Print Measurement Bureau – PMB Non-profit Canadian industry association of advertisers, print magazine publishers, and advertising agencies. Mandate is to collect readership information for print magazines. Foremost research is the PMB study. Magazine Advertising Rates Cost Depends On… Circulation Size and Position of Ad Particular Editions Chosen Special Mechanical or Production Requirements Number and Frequency of Insertions Whether Circulation is Controlled or Paid How to Buy Magazine Advertising Space Sold on the Basis of Units of Space Black and White vs. Colour Frequency The Future for Magazines Government Support Canadian Titles Online Delivery Advances in Technology Evaluation of Newspapers Types of Newspapers Daily Newspapers Community Newspapers National Newspapers Special Audience Newspapers Newspaper Supplements Types of Newspaper Advertising Local (Mostly Retail) Display Ads General (Often National) Paid Reading Notices (Editorial Look) Small Items Arranged by Topic Classified Ads Rates Based on Size, Duration Classified Display - Combination Legal Notices - Public Reports Public Notices Notices by People, Organizations Financial Reports Printed Inserts Prepared Separately by Advertisers Strengths of Newspapers Reach and Frequency Scheduling Flexibility Geographic Coverage Reader Involvement and Amount of Processing Time Media Image Creativity for Cognitive Responses Absolute Cost and Cost Efficiency Target Audience Coverage Limitations of Newspapers Creativity Impact for Emotional Responses Selective Exposure and Poor Attention Target Audience Selectivity Clutter Buying Newspaper Advertising Space Issues Related to the Decision Circulation and Readership Advertising Rates Audience Measurement Newspaper Circulation and Readership Local Coverage Advertiser can reach most of the households in a market. National Coverage Want to reach broader regions or even the entire country. Need to purchase space in a number of papers. Newspaper Audience Measurement NADbank Newspaper, advertising agency, and advertiser members. Mandate: Publish audience research information of Canadian newspapers. Provide valid readership information to facilitate buying and selling of newspaper ad space. ComBase Administers audience measurement for CCNA. Study is also named ComBase. Similar composition and mandate as NADbank. Newspaper Readership By Age Figure 11-5 Newspaper Advertising Rates Cost of advertising space depends on factors like circulation, premium charges for colour in a special section, or discounts available. National rates can be about 15% higher than local rates. Buying Newspaper Advertising Space Sold By: •Agate Line •Column Width Position: •ROP •Preferred The Future for Newspapers Problems of reproduction quality and rate differentials. Face competition for national and local advertisers’ budgets. Growth of Internet and online services as marketing tools Local TV and radio stations and Yellow Pages are competing for local ads Industry is particularly concerned about loss of advertisers to direct marketing and telemarketing.