* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FERM domain proteins
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
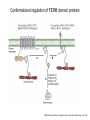
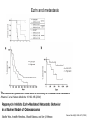
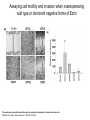
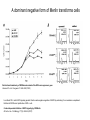
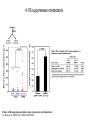
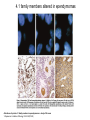
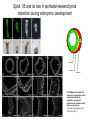
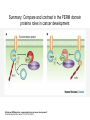
FERM domain proteins and their involvement in metastasis Merlin and ERM proteins: unappreciated roles in cancer development? A McClatchey Nat Rev Cancer 3(11):877-83 (2003) The phylogeny of the FERM domain ERM proteins and Merlin: Integrators at the cell cortex, Bretscher A et al. 2002 Conformational regulation of FERM domain proteins ERM proteins and Merlin: Integrators at the cell cortex, Bretscher A et al. 2002 The role of ERM Perturbation of cell adhesion and microvilli formation by antisense oligonucleotides to ERM family members, K Takeuchi et al, J Cell Bio 125:1371-1384(1994) Ezrin and metastasis The membrane-cytoskeleton linker ezrin is necessary for osteosarcoma metastasis Khanna C et al. Nature Medicine 10:182-186 (2004) Cancer Res 65(6): 2406-2411 (2005) Assaying cell motility and invasion when overexpressing wild type or dominant negative forms of Ezrin The membrane cytoskeletal crosslinker ezrin is required for metastasis of breast carcinoma cells BE Elliott et al. Breast Cancer Research 7:R365-R373 (2005) A dominant negative form of Merlin transforms cells Cellular transformation by a FERM domain mutant of the Nf2 tumor suppressor gene Johnson KC et al. Oncogene 21: 5990-5997 (2002) In confluent Nf2-/- cells EGFR signaling persists. Merlin creates negative regulation of EGFR by restraining it to a membrane compartment. Inhibitors of EGFR arrest proliferation of Nf2-/- cells. Contact-dependent inhibition of EGFR signaling by Nf2/Merlin M Curto et al. J Cell Biology 177(5): 893-903 (2007) 4.1B suppresses metastasis Protein 4.1B suppresses prostate cancer progression and metastasis SY Wong et al. PNAS 104: 12784-12789 (2007) 4.1 family members altered in ependymomas Alterations of protein 4.1 family members in ependymomas: a study of 84 cases V Rajaram et al. Modern Pathology 18:991-997(2005) Epb4.1l5 and its role in epithelial-mesenchymal transition during embryonic development epiblast mesoderm endoderm The FERM protein Epb4.1l5 is required for organization of the neural plate and for the epithelial-mesenchymal tranition at the primitive streak of the mouse embryo JD Lee et al. Development 134: 2007-2016 (2007) ERM protein interactions and implications: CD44 Inhibition of human melanoma growth and metastasis in vivo by anti-CD44 monoclonal antibody Y Guo et al. Cancer Research 54:1561-1565 (1994) ERM protein interactions and implications: NHERF QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Suppression of breast cancer cell growth by Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor 1 (NHERF1) Y Pan et al. Breast Cancer Research 9:R63-R73 (2006) ERM protein interactions and implications: ER Extra-nuclear signaling of estrogen receptor to breast cancer cytoskeletal remodeling, migration and invasion MS Giretti et al. PLoS ONE 3(5):e2338 (2008) ERM protein interactions and implications: 4.1R and the cell cycle Downregulation of Protein 4.1R, a mature centriole protein, disrupts centrosomes, alters cell cycle progression, and perturbs mittotic spindles and anaphase Summary: Compare and contrast in the FERM domain proteins roles in cancer development Merlin and ERM proteins: unappreciated roles in cancer development? A McClatchey Nat Rev Cancer 3(11):877-83 (2003)