* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SNC2P (1.3) Cell Differences rev
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
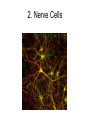
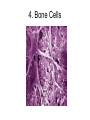
1.3 Cell Differences (p40-43) KEY CONCEPTS Cell Development • All cells start their lives as identical cells called stem cells. Stem Cells • Each stem cell has the potential to become a specialized cell as it matures. • Some will become blood cells, some nerve cells, and some muscle cells. Cell Specialization • Different types of cells have different structures and abilities that enable them to perform their functions efficiently. A nerve cell Cell Differentiation • Cell Differentiation: This is the series of events through which stem cells develop into specialized cells. • Scientists are very interested in studying how stem cells differentiate. • They might be used to replace or repair damaged tissues in humans. Specialized Cells • Each different kind of cell has different structures that allow them to perform a unique function. • There are 200 different types of cells in the human body. • We will be looking at only five of these in more detail. 1. Muscle Cells 2. Nerve Cells 3. Red Blood Cells 4. Bone Cells 5. Skin Cells Classwork • Read textbook pg. 40 – 43 • Complete table on “1.3 Cell Differences” handout • Answer the following and hand in: – pg. 41 # 1, 2 – pg. 43 #1 - 3