* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 1 The Cell PowerPoint
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
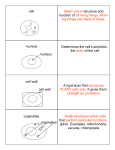
Do Now!! What characteristics are common to all living things? What are cells? Name different types of cells you know of... THE CELL Chapter 1 Do Now!! What are the two main types of cells? Do all cells have the same structure? Look at the cells to the right. What are some similarities? Differences? Objectives Describe how cells were discovered and named. Identify the scientists that discovered and observed cells. List the 3 parts of the cell theory. What is a cell? Basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms! They come in different shapes + sizes Unicellular vs. Multicellular Unicellular – a single cell Multicellular – made up of many cells How were cells discovered? The microscope helped discover cells! Who discovered the cell? ROBERT HOOKE Observed DEAD cork cells Said boxes looked like tiny rooms or jail “cells”. Used a microscope at 30x magnification Cork cells! *Cork is from tree bark (dead cells) Animalcules Who else discovered the cell? ANTON VAN LEEUWENHOEK Observed pond water 1st to observe “living” cells Used a microscope at 300x magnification Spirogyra Protist Do you have these recipes at home? People thought organisms grew from non-living materials! Francisco Redi Experiment Placed meat in both an open container and a closed container to see what happened. Redi’s Conclusion Maggots come from flies, NOT the meat! Life must come from life, which proved that spontaneous generation is not real! People still did not believe him but he was right. Louis Pasteur Experiment Showed that bacteria are present in air and do not appear spontaneously. Louis Pasteur Conclusions Discovered that cells MUST come from other cells Disproved “Spontaneous Generation” and said life cannot just appear out of nowhere. Helped verify Redi’s research! Pasteurization Pasteur came up with the idea of Pasteurization after discovering bacteria could contaminate milk from the air. This process kills the bacteria so that it does not harm us! Used in milk, cheese, yogurt, etc. Cell Theory = 1. Every living thing is made of one or more cells 2. Cells carry out the functions needed to support life 3. Cells come only from other living cells Do Now!! Describe the experiment for the scientists listed below: Robert Hooke Anton Van Leeuwenhoek Francisco Redi Louis Pasteur Objectives Compare and contrast a scanning electron microscope vs. a transmission electron microscope. Describe prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Section 1.2 - Microscopes How small are cells? Unit used = micrometer (um) One millionth of a meter Most cells range from 1 um to 1000 um. Types of Microscopes 1. Light Microscope 2. SEM Microscope 3. TEM Microscope Light Microscope Uses light Looks at thin specimen Total Magnification = 40x-1000x Use to see cells, but not detailed organelles SEM vs. TEM SEM 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. “Scanning electron microscope” Beams of electrons bounce off the surface of the coated cell. Images appear 3DOutside Specimen Total Magnification = 100,000x Must be dead . Specimen coated in metal TEM 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. “Transmission electron microscope” Electrons pass through the think section. Images appear 2D Total Magnification = 300,000x Allows us to see organelles inside the cell SEM TEM Do Now!! What are the three types of microscopes? Which would you use if you wanted to see detailed organelles? What is found INSIDE a cell? Do plant cells and animal cells have the same stuff inside? Objectives To compare and contrast animal vs. plant cells. Identify each organelle in a diagram of a cell. Explain the function of each organelle To create flash cards for the next test Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic cells What are the differences you can see? Prokaryotic Cells Have circular DNA NO nucleus Do not have membrane bound organelles Most unicellular organisms are prokaryotes Example: Bacteria Eukaryotic Cells Have linear DNA – double helix shape Have nucleus Have membrane bound Example: You! organelles All multicellular organisms are eukaryotic cells. Some are unicellular. Cheek Cells Cell Organelles 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Plasma membrane Cytoplasm/cytoskeleton Nucleus Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus Lysosomes Centrioles 9. Cilia and Flagella 10. Mitochondria 11. Central Vacuole 12. Chloroplasts 13. Cell Wall Each organelle has its own purpose and function!! Index Cards! Front: Name of Organelle Drawing Back: Location Function Plasma Membrane THE OUTSIDE – protects the internal structures of the cell. Selective permeability Determines what comes in and out of the cell A.K.A- Cell Membrane! Found in: Animal and Plant cells Cytoplasm/Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm- Clear FLUID that contains the organelles. Cytoskeleton- Provides the FRAMEWORK for the cell, holds organelles in place. Found in: Plant and Animal cells Nucleus- CONTROLS the cell Nucleolus- produces ribosomes Nuclear Pores- Allows things in and out of the nucleus. Nuclear EnvelopeMembrane surrounding nucleus Found in: Plant and Animal Nucleus Do Now!! Challenge Question Where do you find the DNA in a eukaryotic cell? If prokaryotes do not have a nucleus, where is their DNA? Ribosomes Produces Proteins! Proteins are made up of one or more polypeptide chains of amino acids. Found in: Plant and Animal Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough- Contains ribosomes and synthesizes PROTEINS Smooth- No Ribosomes, synthesizes LIPIDS (fats) Found in: Plant and Animal Golgi Apparatus Modifies proteins and fats and gets them ready for export! (proteins are eventually released to outside of cell) Found in: Animal and Plant Do Now!! Think of the lab with cheek and onion cells. What were some differences you noticed between the two kinds of cells? Similarities? Lysosomes *The clean-up crew! Contains ENZYMES that break down cellular waste product and debris Found in: Mainly animal Centrioles Organelles made of microtubules involved in cell division (located in cytoplasm)! (will talk about this later when we do mitosis!) Found in: Animal Cilia and Flagella Cilia- Used in stationary cells for moving substances around the outside of the cell (look like hairs). Flagella- Used in cells for movement (longer & less numerous than cilia). Found in: Animal and Prokaryote Mitochondria Convert oxygen into ENERGY (ATP) (we will talk about this more when we do cellular respiration!!) Found in: Animal and Plant *Powerhouse of the cell!! Central Vacuole LARGE WATER “bubble” in the plant cell Maintains the SHAPE of the cell, without it, the plant cell would shrink and the plant would wilt Stores water, along with ions, nutrients, and waste. Found in: Plant Chloroplasts Captures LIGHT ENERGY and converts it to chemical energy (sugar) Found in: Plant Cell Wall Supports the plant cell and maintains its shape Works with central vacuole to maintain “Turgor Pressure” Found in: Plant Do Now!! Challenge Question! How can the chloroplast, a structure found in plant cells but not in animal cells, provide energy for both plants and animals? Objectives To compare and contrast animal vs. plant cells. Identify each organelle in a diagram of a cell. Explain the function of each organelle To create flash cards for the next test To label animal and plant cells Animal vs. Plant cells Please create a Venn diagram: Plant Animal Endosymbiotic Theory Explains the origin of chloroplasts and mitochondria and their complex, double membranes. Theory: Chloroplasts and Mitochondria were once prokaryotes that were engulfed!! Theory = Evidence!! •Have circular DNA like bacteria •Replicates(reproduces) like bacteria separate from the host cell •Make their own proteins •Two membranes (one from the host cell and one from their own cell membrane) Specialization Specific cells perform specific functions. Ex: Blood cells can only be blood cells. Muscle cells cannot be turned into blood cells. • Organization Organisms are organized: Cells Tissue Organ Organ System Organism Organization: plants too! Cell Tissue Organ (leaf) Organ system (leaves, stems, roots) Organism Do Now!! o Which is a plant cell? Animal cell? How do you know? o What is the role of the mitochondria?