* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Theory Timeline
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
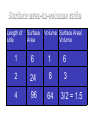
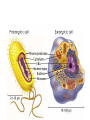
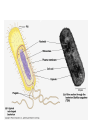
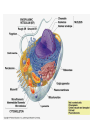
UNIT 4: Cells BIG IDEA: There are different levels of organization in organisms, with cells being the basis of all life. Cell Theory Timeline What is a cell? • The basic unit of structure and function of life. 1665: Robert Hooke • Builds compound microscopes and first to observe cork cells. Late1600’s: Anton van Leeuwenhoek • Builds simple, powerful microscopes and 1st to see living cells • Observes blood cells, animal sperm cells, & bacteria from his own teeth! He called them “animalcules” Cell Theory • The observations about cells from the past 150 years is becoming more organized in the 1800’s • Schleiden, Schwann and Virchow are the scientists who contribute to developing a unifying cell theory • 1838: Matthias Schleiden Concludes all plants are made of cells • 1839: Theodor Schwann Concludes all animals are made of cells. • 1855: Virchow Concludes that all cells come from pre-existing cells Cell Theory 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in an organism. 3. Cells come only from the reproduction of existing cells. Cell Diversity • Shape: There are many cell shapes. The function of the cell influences the shape of the cell. • Size: Different types of cells have different sizes. 0.1 μm – 100 μm –The size of a cell is limited by the surface area-to volume ratio. Surface area-to-volume Ratio larger the surface• As the cell gets ______, smaller area-to-volume ratio gets _________. • If the cell grows beyond a certain limit, not enough material will be able to cross the membrane fast enough to provide for the increased volume. Surface area-to-volume ratio Length of side Surface Area Volume Surface Area/ Volume 1 6 1 6 2 24 8 3 4 96 64 3/2 = 1.5 Surface area-to-volume ratio • Materials must enter through the surface. • The bigger the cell, the smaller the surface area-to-volume ratio. • If a cell is too large, there is not enough surface area to allow materials to pass through quickly enough. Types of Cells Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Cells 1. Very simple cell 2. Generally smaller 3. NO membrane-bound organelles (compartments) 4. No true nucleus. – DNA is found in the nucleoid region and is NOT separated by a membrane. 5. Example is bacteria. Eukaryotic Cell 1. More complex cells 2. Generally bigger 3. Contains membrane-bound organelles 4. Has a true nucleus – Region of where DNA is stored and is separated by a membrane. 5. Examples are animals & plants Pop Quiz! 1. Who is credited for first seeing cells? 2. According to the Cell Theory, where do all cells come from? 3. Which cells are simpler: Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic? 4. Which cells contain membranebound organelles? 5. Which type of cells do you have?