* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2.3: EUKARYOTIC CELLS
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
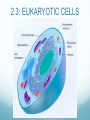
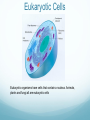
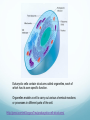
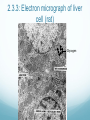
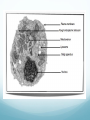
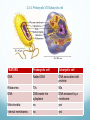
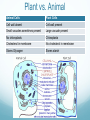
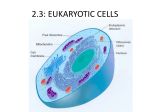
The Raft is a short story by Stephen King. In the story a couple of boys skip school to go fishing in the upper state of Maine. While they are on the lake they come in contact with a giant amoeba, that eventually eats them. How can you explain scientifically that this story is fiction? 2.3: EUKARYOTIC CELLS Assessment Statements • Draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example of an animal cell • Annotate the diagram with the functions of each named structure. • Identify named structures in an electron micrograph of liver cells. • Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. • State three differences between plant and animal cells. • Outline two roles of extracellular components. Eukaryotic Cells Eukaryotic organisms have cells that contain a nucleus. Animals, plants and fungi all are eukaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells contain structures called organelles, each of which has its own specific function. Organelles enable a cell to carry out various chemical reactions or processes in different parts of the cell. Http://prezi.com/nk1brgors7mu/prokaryotic-cell-structures/ 2.3.1, 2.3.2: Liver cell Refresher What organelle is the energy provider for the eukaryotic cell? What is the function of pili in prokaryotic cells? What organelle is this? . 2.3.3: Electron micrograph of liver cell (rat) Glycogen 2.3.4: Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic cell FEATURE Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell DNA Naked DNA DNA associated with proteins Ribosomes 70s 80s DNA DNA inside the cytoplasm DNA enclosed by a membrane Mitochondria no yes Internal membranes no yes 2.3.5: Plant VS Animal cell 1. Plant cells have large vacuoles and animal cells do not have large vacuoles. 2. Plant cells have a cell wall and animal cells do not have a cell wall. 3. Plant cells (may) have chloroplasts and animals do not have chloroplasts. 4. Plant cells store excess glucose as starch and animal cells store excess glucose as glycogen. Plant vs. Animal Animal Cells Plant Cells Cell wall absent Cell wall present Small vacuoles sometimes present Large vacuole present No chloroplasts Chloroplasts Cholesterol in membrane No cholesterol in membrane Stores Glycogen Stores starch 2.3.6: Extracellular components The plant cell wall maintains cell shape, prevents excessive water uptake, and hold the whole plant up against the force of gravity. Animal cells secrete glycoproteins that form the extracellular matrix. This functions in support, adhesion and movement. Glycoproteins