* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Respiration
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
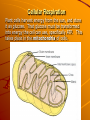
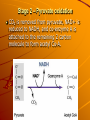
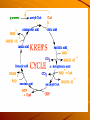
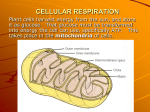
Cellular Respiration Plant cells harvest energy from the sun, and store it as glucose. That glucose must be transformed into energy the cell can use, specifically ATP. This takes place in the mitochondria of cells. There are two ways that a cell can harvest energy from the food (glucose) it takes in: Anaerobic Cell Respiration (Fermentation) – glucose metabolism in the absence of oxygen that produces 2ATP molecules and either ethanol or lactic acid. Involves 2 stages: Glycolysis Fermentation Aerobic Cellular Respiration – glucose metabolism with oxygen that produces 36 ATP molecules, CO2 and H2O. Involves 4 stages: Glycolysis Pyruvate oxidation Krebs cycle Electron transport and chemiosmosis Stage 1 – Glycolysis glucose is broken down through a series of steps to produce 2 – 3carbon molecules of pyruvate and net 2 ATP. http://instruct1.cit.c ornell.edu/courses/bi omi290/ASM/glycoly sis.dcr Stage 2 – Fermentation in the absence of oxygen, NADH generated from glycolysis passes its H atoms to either acetaldehyde to produce ethanol or to pyruvate to produce lactic acid. The miracle of fermentation Products of fermentation include: – wine – beer – soy sauce – bread – carbonated beverages – cheese Lactic acid production causes: – muscle cramps – soreness – stiffness – fatigue These are all signs of oxygen debt in the muscles. During Fermentation, NAD+ is restored. This gives cells the opportunity to continue with cellular respiration if oxygen becomes available. Cellular Respiration Stage 1 – Glycolysis glucose is broken down through a series of steps to produce 2 – 3carbon molecules of pyruvate and net 2 ATP. Stage 2 – Pyruvate oxidation CO2 is removed from pyruvate, NAD+ is reduced to NADH, and co-enzyme A is attached to the remaining 2 carbon molecule to form acetyl Co-A. Stage 3 – Krebs cycle a series of reactions that transfers energy from organic molecules to ATP, NADH, and FADH2 and removes carbon as CO2. Concepts in Biochemistry - Interactive Animations Stage 4 – Electron Transport Chain and Chemiosmosis NADH and FADH2 carry hydrogen atoms and electrons to a series of compounds in the mitochondria that pump H+ ions into the intermembrane space. As H+ ions move through channels down the concentration gradient, ATP is produced. Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the ETC. Without it, electrons cannot move through the chain and no energy is made. Electron transport system Chemiosmosis Overview of Cellular Respiration The Products of Cellular Respiration What do we get? Stage CO2 produced NADH produced FADH2 produced 2 Glycolysis ATP consumed ATP produced Net ATP produced 2 4 4 6 (NADH) 6 ( NADH) Pyruvate oxidation 2 2 Kreb’s Cycle 4 6 2 2 24 4 (FADH) 18 (NADH) TOTAL 6 10 2 38 6 36