* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Thinning of the Arctic Ice Decline in Arctic Sea Ice Extent
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Iron fertilization wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the Arctic wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Future sea level wikipedia , lookup
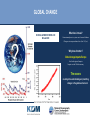
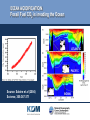
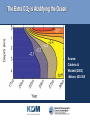
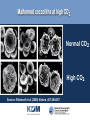
OCEANS AND GLOBAL CHANGE • • PROFESSOR A.E. HILL DIRECTOR NATIONAL OCEANOGRAPHY CENTRE, SOUTHAMPTON UK GLOBAL CHANGE • • OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE-ICE BALANCE What does it mean? Ocean-atmosphere-ice system out of normal balance Changes at an unprecedented rate (last 1 M yrs) Why does it matter? Global change impacts Europe Local and regional impacts Impacts on the Global economy The oceans are integral to understanding and predicting changes in the global environment LIVING ON A CHANGING EARTH: • • • THE CHALLENGES FOR SCIENCE What is going on now ? fundamental understanding of basic earth system processes • Continuous awareness of change sustained observing • What is going to happen next – especially locally ? predictive capability • Finding solutions evidence based policy, regulation, technology solutions, innovations to grasp opportunities and minimise risks OCEANS AND GLOBAL CHANGE - • • HOT TOPICS • SEA LEVEL CHANGE • OCEAN ACIDIFICATION • ARCTIC ICE THINNING MEAN SEA LEVEL CHANGES Past 200+ years observed, next 100 years predicted •Permanent Service for Mean Sea Level www.pol.ac.uk/psmsl • global rise of approximately 10-20 cm during the past 100 years (IPPC 3rd Assessment Report) IPCC Third Assessment Report Predicted 9-88 cm (central value 48 cm) OCEANS AND GLOBAL CHANGE EXTREME SEA LEVEL EVENTS THAT CAUSES FLOODS • • COASTAL AREAS AT RISK • • By 2100 The 1 in 100 year flood level (shown here in red) may become a 1 in 10 year level SEA LEVEL COMMITMENT – living with the consequences Sea level will continue to rise even after CO2 emissions are reduced • • Third IPCC Assessment Report EUROPEAN SEA LEVEL OBSERVING NETWORK (ESEAS) • • www.eseas.org REDUCING UNCERTAINTIES: THE ABILITY TO PREDICT? NORTHWEST EUROPE STORM SURGE SCENARIOS: Computed change in 50-year surge Source: Proudman Oceangraphic Laboratory www.pol.ac.uk • • Storm Surges with ECHAM4 – T102 Range of values -20 to +40cm. Storm Surges with HADCM2 climate OCEAN ACIDIFICATION Fossil Fuel CO2 is invading the Ocean • • ATLANTIC PACIFIC Source: Sabine et al (2004) Science, 305:367-371 INDIAN The Extra CO2 is Acidifying the Ocean • • Source: Caldeira & Wickett (2003) Nature, 425:365 Particular Concern for Organisms with Chalk Shells or Skeletons •coral reefs • coralline algae coccolithophores foraminifera pteropods Source: Royal Society report on ocean acidification (2005) Malformed coccoliths at high CO2 • • Normal CO2 High CO2 Source: Riebesell et al (2000) Nature, 407:364-367 OCEAN ACIDIFICATION • • What We Know 1. Ocean acidification is already happening 2. If emissions continue oceans will inevitably become ever more acidic 3. Coral skeletons and chalk shells will be affected OCEAN ACIDIFICATION • • What We Need to Find Out 1. How will the organisms be affected by thinner shells and weaker skeletons? 2. What other effects will follow from lowered pH? 3. What will be the knock-on effects on marine ecosystems and the ocean carbon cycle? “Thus chemical effects of CO2 on the marine environment may be as great a cause for concern as the radiative effects of CO2 on Earth’s climate.” [Caldeira & Wickett (2005) J. Geophys. Res. 110, C09S04] FISH AND CHIPS or JELLYFISH AND CHIPS ? THE ARCTIC OCEAN: • • SHRINKING SEA ICE COVER Bad news for Polar Bears ... but also... • • RAPID CLIMATE CHANGE: The freshening of Arctic and sub-Polar seas • • As the sea ice melts the Arctic ocean is freshening. This will lessen the production of dense salty deep water and could result in changes to the ocean circulation NORTHWEST EUROPE IS WARMER THAN IT SHOULD BE • • FRESHENING OF HIGH LATITUDE WATERS COULD SLOW SINKING AND RELEASE OF HEAT TO THE ATMOSPHERE • • The temperature rise/fall relative to preindustrial for the first decade after a collapse in 2050 (Hadley Centre) With a simple model the probability of collapse by 2100 is about 30% RAPID CLIMATE CHANGE SCIENCE FOR DEVELOPING A LONG TERM OBSERVING SYSTEM FOR ADVANCE WARNING • • WHO WILL EUROPE‘S MAJOR TRADING PARTNER BE IN 2025? Will Europe increasingly face north? Economic, Social and Environmental implications? • • The North West Passage in September 2005 MARINE SCIENCE THE GLOBAL ENVIRONMENTAL CHALLENGES FACING EUROPE: SOLUTIONS THROUGH PREDICTION - NOW IS THE TIME TO INVEST • • Big questions • • Massive implications (environmental, social, economic) Fundamental marine science at the heart of these Addressing • What is going on now ? • How can we be more continually aware of changes ? • What is going to happen next? • What solutions can help us live with a changing world? Needing • A healthy marine science base (people and the major infrastructure to support marine science) • Robust approach and funding mechanisms for sustained marine observing • Well focussed coordinated marine science programmes • Strong knowledge transfer - marine science into policy and business opportunity CONCLUSIONS WE LIVE ON A PLANET NOW OUTSIDE ITS NATURAL RANGE AND CHANGING AT AN UNPRECEDENTED RATE • • • The Oceans are integral to understanding global change • The consequences of global change for Europe present both risks and opportunities • Key to preparation is better sustained observation and prediction of marine systems • Coordinated research to inform policies at European level and to give European businesses the competitive edge is vital • • • • OCEANS AND GLOBAL CHANGE • •