* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bacteria and Viruses
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
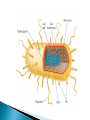
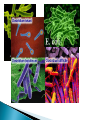
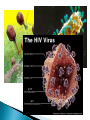
Ch. 19 Eubacteria ◦ Largest kingdom of living things ◦ Live everywhere ◦ Cell wall contains peptidoglycan Archaebacteria ◦ Cell wall lacks peptidoglycan ◦ DNA sequences more similar to eukaryotes ◦ Live in extreme environments Shapes ◦ Rod (bacilli) ◦ Spiral (spirilla) ◦ Spherical (cocci) Cell walls ◦ Gram-positive stained have peptidoglycan call walls (violet) ◦ Gram-negative lack peptidoglycan (red) Movement ◦ Variety of ways…. Heterotrophs ◦ Chemoheterotrophs and photoheterotrophs majority Autotrophs ◦ Photoautotrophs Cyanobacteria ◦ Chemoautotrophs Obligate aerobes ◦ Require oxygen all the time; aerobic respiration Mycobacterium tuberculosis Obligate anaerobes ◦ Killed by oxygen; anaerobic respiration Clostridium botulinum Facultative anaerobes ◦ Can survive with or without oxygen; both types of respiration Eschericia coli Binary fission ◦ Mitotic; asexual Conjugation ◦ Gene swapping; sexual Sporulation ◦ When conditions become unfavorable DNA and a little cytoplasm is enclosed in an endospore Decomposers Nitrogen fixers Food industry Mining Cleaning oil spills Pharmaceuticals Oxy Clean Bits of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat. That’s it. ◦ They come in a variety of shapes and sizes ◦ They must infect a host cell to reproduce. ◦ Bacteriophages are viruses that infect bacteria. Viruses enter a host cell and use the cell’s machinery to reproduce. ◦ In lytic infections the virus reproduces immediately until the cell bursts. ◦ In lysogenic infections the viral DNA is incorporated into the host’s DNA as prophage and may remain dormant for a period of time until reproduction begins. Contain RNA instead of DNA ◦ After infecting a cell the RNA is copied in reverse to make DNA which is then incorporated into the host cell’s genome as prophage. ◦ RNA viruses mutate frequently. Rhino virus (colds) HIV Are viruses alive? Bacteria and viruses can act a pathogens – disease causing agents (pathos = disease; gen = generating). ◦ Louis Pasteur helped formulate the germ theory of disease. ◦ Bacteria cause disease by either using cells for food or by releasing toxins (poisons) that are harmful. Sterilization with heat Disinfectants Cold storage Vacuum packing Nitrogen/inert gases Some target the cell wall of bacteria and others disrupt protein synthesis. ◦ Antibiotics are specific to the type of bacteria they act upon. Can’t be treated with antibiotics! They don’t have a cell wall or make proteins… ◦ Best treatment is prevention; once infected it has to run its course. Symptoms may be treated. Vaccines provide some protection and immunity to bacterial and viral diseases. ◦ More to follow…