* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Higher Geography - Atmosphere
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
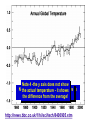
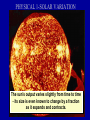
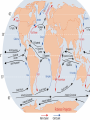
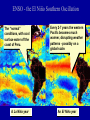
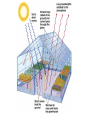
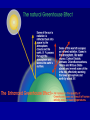
IB Geography - Atmosphere GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE • http://www.bbc.com/news/scienceenvironment-34763036 • http://www.bbc.com/news/scienceenvironment-35354579 • • • • • • • • • • Report Objective To able to discuss [a considered and balanced review that includes a range of arguments, factors or hypotheses - opinions or conclusions should be presented clearly and supported by appropriate evidence] the causes and environmental consequences of global climate change. To develop some of the skills and understanding needed to produce a DP Geography IA. Report Question To what extent are the causes of global climate change natural? [15 Marks + 4 Marks] Task Produce a report (900 words maximum) that discusses to what extent the causes of global climate change are natural. • It should be text based but supported with diagrams, images and data visualizations. • Your report should include: • • • • • • What is 'global climate change'? Discussion of the predicted levels/amounts of global climate change. What are the causes of global climate change? Discussion of whether all the causes of global climate change are human-induced or not. Don't just include images to make it look pretty - all images should be used and integrated into the reports discussion. Note 4 -the y axis does not show Note Note 1 Note -2the - since 3 graph -temperature There 1860 shows have this-also atemperature beenrise in the actual itsteady shows cooler has global than only temperature. average been years. 1°C the rise difference from theabout average! http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/sci/tech/8400905.stm GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE Physical Factors • • • • Solar variation Volcanic activity Ocean currents Milankovitch cycles Human Factors • Burning fossil fuels • Increased output of methane etc. • Deforestation • Increase of CFC’s PHYSICAL 1-SOLAR VARIATION The sun’s output varies slightly from time to time - its size is even known to change by a fraction as it expands and contracts. PHYSICAL 1 - SOLAR VARIATION • Sunspots: an increase in sunspot activity may lead to a very slight increase in the sun’s output and a temporary warming of the earth. • Sunspot activity follows 11 and 22 year cycles. •The Little Ice Age of 1450-1700 may have been linked to periods of very low sunspot activity. PHYSICAL 2 - VOLCANIC ERUPTIONS • Eruptions of volcanoes can throw millions of tonnes of ash,dust and sulphur dioxide into the atmosphere. • This produces aerosols that can reduce the amount of sunlight reaching the earth. • This can lead to a temporary cooling of the earth. VOLCANIC ERUPTIONS 2 • Major eruptions in the past which have been linked to short periods of global cooling include Tambora (1815), Krakatoa (1883), Mt. St Helens (1980) and Pinatubo (1991) When Mt. Pinatubo erupted in 1991 an estimated 22 million tons of ash was thrown into the atmosphere, cooling the world’s climate by about 1°C. When Tambora erupted in 1815 it led to 1816 being called “the year without summer”, when summer frosts and other major weather problems were experienced. It cooled the global climate by 3°C. PHYSICAL 3 - MILANKOVITCH CYCLES • Wobble! • Roll! • Stretch! • Milankovitch cycles are three variations in the earth’s orbit. Although they may be linked to very long term changes in the climate, their effect would not be noticed on a scale of a few hundred years. PHYSICAL 4 - OCEAN CURRENTS • Changes in the pattern and strength of ocean currents may lead to changes in the distribution of heat around the planet. • A short term example would be El Niño, which appears every few years. • A longer term example would be the North Atlantic Drift, which may change position every few thousand years. ENSO - the El Niño Southern Oscillation The “normal” conditions, with cool surface water off the coast of Peru. A La Niña year Every 2-7 years the western Pacific becomes much warmer, disrupting weather patterns - possibly on a global scale. An El Niño year http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldn ews/australiaandthepacific/australia/825 4976/Australia-floods-what-caused-theflooding.html http://news.bbc.co.uk/weather/hi/news/n ewsid_9340000/9340513.stm One theory suggests that global warming will increase the number of icebergs in the Atlantic, cooling the sea and switching off the North Atlantic Drift / Atlantic Conveyor system. This would be bad news for us! GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE Physical Factors • • • • Solar variation Volcanic activity Ocean currents Milankovitch cycles Human Factors • Burning fossil fuels • Increased output of methane etc. • Deforestation • Increase of CFC’s GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE - HUMAN FACTORS - 1 - THE ENHANCED GREENHOUSE EFFECT. HUMAN 1 - BURNING FOSSIL FUELS • The fossil fuels are:- • COAL • OIL • NATURAL GAS • They are called fossil fuels because they are formed from the remains of ancient plants (coal) and marine animals (oil). BURNING FOSSIL FUELS When we burn these fuels, we release millions of tonnes of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. There has been an enormous increase in these greenhouse gases since the Industrial Revolution began about 200 years ago. BURNING FOSSIL FUELS Power stations are one of the main producers of greenhouse gases such as Carbon Dioxide. Environmental campaigners all over the world are demanding cuts in CO2 emissions. Here Greenpeace uses a light display to get its message across. HUMAN 1 - VEHICLE EXHAUSTS Vehicle exhausts are the main source of Nitrous Oxides. BURNING FOSSIL FUELS Photo chemical smog in Beijing, China. HUMAN 2 - INCREASED METHANE The huge increase in world population and in the area of land given over to crops in general and to rice production in particular, has led to a rapid rise in global methane production. Farmland for rice has doubled in 45 years. When I digest grass, I produce methane - lots of it! HUMAN 2 - INCREASED METHANE • A cow can burp / fart about a quarter of a kg. of methane a day. • The number of cattle has doubled in the past 40 years. Sheep, goats and camels are also ruminants. • There are now 1.3 billion cattle, each burping / farting methane several times a minute! • The New Zealand government has a “flatulence” tax on cattle farms. HUMAN 3 - DEFORESTATION Forests absorb CO2 and release oxygen: ...if they are cut down, atmospheric levels of CO2 must rise as a consequence. HUMAN 3 - DEFORESTATION • Clearing forest by burning releases huge amounts of stored CO2 back into the atmosphere. • The smoke from the fires also adds to global air pollution. GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE - REVIEW OF MAIN POINTS Physical Factors Human Factors • • • • • Burning fossil fuels • Increased output of methane • Deforestation Solar variation Volcanic activity Ocean currents Milankovitch cycles KEY TERMS TO REMEMBER • • • • • • • • • Solar variation / Sunspots Volcanic eruptions /Sulphur dioxide /Aerosols Milankovitch cycles El Niño Enhanced Greenhouse effect Carbon Dioxide / Methane / Nitrous Oxides The Industrial Revolution / burning fossil fuels Paddy fields / cattle / methane production Deforestation Impact of climate change • What has happened already? • What could happen if temperatures continue to rise? • Summarise these from pages 115-120 and add to ‘effects’ table • Read about The ‘Kyoto Protocol’ and the ToK box pgs 122-128. • Ensure you have completed research on Paris 2015 • Qblock page 128