* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download muscular system
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
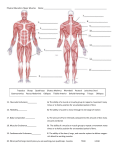
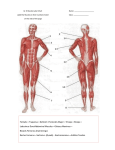
MUSCULAR SYSTEM Almost all movement results from muscle contraction. Running a marathon Beating of the heart FUNCTIONS OF MUSCLE Allows movement Produce heat Keep body erect and maintains posture Protection of internal organs 2 Types of Muscle Movement 1. Voluntary- muscles that can be made to contract by a person’s desire to move. 2. Involuntary- muscles which contract automatically. Ex. Heartbeat, digestion Voluntary muscle Involuntary Muscle TYPES OF MUSCLE TISSUE Smooth--involuntary, found in internal organs. AKA visceral muscle Striated--voluntary, attached to the skeletal system. Cardiac--involuntary, makes up the heart Striated Muscle (attached to the skeleton) STRIATED (SKELETAL) MUSCLES NAMED ACCORDING TO: Direction of muscle fibers Ex. Sternocleidomastoid Location Originates at the sternum and Size clavicle and connects to the mastoid bone Number of origins Shape Origin and insertion Action TERMS RELATING TO MUSCLE Tendons- strong cords of tissue which connect muscle to bone Sphincter muscles- special circular muscles that control an opening. Found in the walls of the anus, urethra and intestines. Myoglobin-a red pigment found in muscle fiber. It is a protein that provides O2. It is similar to hemoglobin that is found in RBC. HOW DO MUSCLES MOVE? Muscles move bones by pulling on them. Most muscles extend from one bone to another and cross at least one joint. Contraction of the muscle causes body movement by pulling one of the bones toward the other across the joint. POINTS OF ATTACHMENT ORIGIN--also called the head of the muscle. Attaches to the more stationary bone. (doesn’t move) INSERTION--attaches to the more movable bone. This is the part that moves when the muscle contracts. Some muscles will have multiple origins, ie biceps brachii and triceps brachii Muscles tend to function together to accomplish specific movements. example: deltoid, biceps brachii, and pectoralis major all help to flex the arm. many muscles are members of more than one group, depending on the type of movement. WHAT MAKES A MUSCLE MOVE?? Muscle cells are stimulated by a nervous impulse that enters the muscle fiber through a motor neuron. Point of contact between a nerve ending and muscle fiber is a neuromuscular junction. When muscles are stimulated repeatedly without rest, the contraction strength will decrease resulting in fatigue. When O2 supplies run low, muscle cells produce lactic acid. Higher lactic acid levels are what makes muscles sore after exercise. MUSCULAR DISORDERS Muscular Dystrophy--inherited, chronic disease. Unknown cause. Muscles degenerate and become weak. Muscles atrophy. Myasthenia Gravis--chronic, progressive disease results from destruction of receptors at the neuromuscular junction. Muscular weakness leads to paralysis. Defect in immune system. MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY WHAS CRUSADE FOR CHILDREN Mattie Stepanik – Oprah Show http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YTqIIoVwvN0 Muscle Atrophy muscle shrinkage due to disuse. muscle will lose tone, this leads to flaccid muscle. caused by: poliomyelitis paralysis prolonged bedrest immobilization-cast MUSCLE ATROPHY Muscle hypertrophy muscles increase in size because of increased use-such as exercise. cardiomegaly other disorders Fallen arches (flatfeet)-weakening of leg muscles that support the arch. Hernia-weak place in the muscular abdominal wall. the intestines bulge through an opening in the wall. Tetanus (lockjaw)-infectious disease. Continous series of spasms of voluntary muscles. Puncture wound is entry. Spores of the bacteria C. tetani live in the soil and are found around the world. In the spore form, C. tetani may remain inactive in the soil, but it can remain infectious for more than 40 years. Infection begins when the spores enter the body through an injury or wound. The spores release bacteria that spread and make a poison called tetanospasmin. This poison blocks nerve signals from the spinal cord to the muscles, causing severe muscle spasms. The spasms can be so powerful that they tear the muscles or cause fractures of the spine. The time between infection and the first sign of symptoms is typically 7 to 21 days. Most cases of tetanus in the United States occur in those who have not been properly vaccinated against the disease. Inguinal Hernia Fallen Arches (Flat-feet) Myalgia-muscle pain Myopathy-any muscle disease Charley horse-tearing of muscle. Trauma induced. Severe, prolonged pain. Fibromyalgia syndrome -chronic disorder. Widespread aching pain, tender points and fatigue. Unknown cause. Common Tender Points of Fibromyalgia Nocturnal myoclonus -jerking of the limbs that may occur normally when a person is falling asleep.