* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 30 - HistologyforMedStudents
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
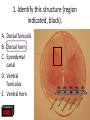
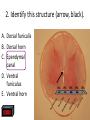
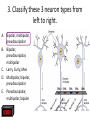
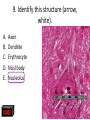
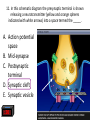
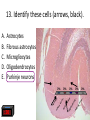
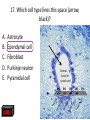
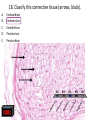
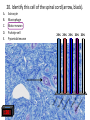
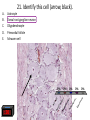
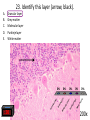
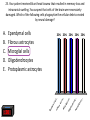
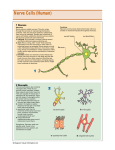
Nervous System Quiz ResponseWare Login ResponseWare Web Not Enabled ResponseCard RF Channels: NA ResponseWare App Not Enabled 1. Identify this structure (region indicated, black). or n 0% lh Ve nt ra icu lf un Ve nt ra Ep en dy m 0% ... na .. . 0% ca ho r . Do rs al cu l.. fu ni Do rs al :30 0% n 0% al A. Dorsal funiculis B. Dorsal horn C. Ependymal canal D. Ventral funiculus E. Ventral horn 2. Identify this structure (arrow, black). or n 0% lh Ve nt ra icu lf un Ve nt ra Ep en dy m 0% ... na .. . 0% ca ho r . Do rs al cu l.. fu ni Do rs al :30 0% n 0% al A. Dorsal funiculis B. Dorsal horn C. Ependymal canal D. Ventral funiculus E. Ventral horn 3. Classify these 3 neuron types from left to right. 0% 0% po l ar ,b Ps i.. eu . do un ip ol ar .. . ... ly, M ul ti ar ,p po l Bi 0% ry ,C ur ul t i. .. ar ,m Bi po l :30 0% se ud .. . 0% La r A. Bipolar, multipolar, pseudounipolar B. Bipolar, pseudounipolar, multipolar C. Larry, Curly, Moe D. Multipolar, bipolar, pseudounipolar E. Pseudounipolar, multipolar, bipolar Dynein Kinesin Lipofuscin Nissl substance Perikaryon 0% on ar y Pe r ik nc .. ub st a Lip :30 0% . 0% Ni ss ls es in 0% Ki n Dy ne in 0% of us cin A. B. C. D. E. 4. What protein is primarily responsible for axonal retrograde flow? 5. You’ve just baked a beautiful apple pie. The smell and taste of it are examples of peripheral nervous system inputs sent to the CNS by … Afferent neurons Autonomic ganglia Efferent neurons Glial cells Motor neurons on s 0% ot or ne ur lc M Gl ia Ef fe re nt 0% el ls 0% ... g.. . 0% ga n om ic Au to n :30 Af fe re nt ne ur o ... 0% ne ur o A. B. C. D. E. 6. The apple pie from the previous question was too hot and burned your finger when you touched it. A response by the CNS is sent to skeletal muscle to retract your finger using … Afferent neurons Autonomic ganglia Glial cells Motor neurons Pyramidal neurons al ne ur .. on s Py ra m id M 0% . 0% ot or ne ur el ls 0% lc g.. . 0% ga n om ic Au to n :30 Af fe re nt ne ur o ... 0% Gl ia A. B. C. D. E. 7. Multiple sclerosis is an auto-immune disorder which leads to demyleination of axons and disruption of signal transduction. The Schwann cell myelinates axons in the peripheral nervous system. What cell performs the same function in the CNS? A. B. C. D. E. Astrocyte Ependymal cell Fibrous astrocyte Microgliocyte Oligodendrocyte As tro :30 0% 0% 0% 0% cy te Ep en dy m al ce ll Fib ro us as tro c.. . M icr og lio cy Ol te ig od en dr oc yt . .. 0% 8. The glia limitans is the outermost layer of proper nervous tissue of the brain and spinal cord, underneath the pia mater. Which neuroglial cell type primarily forms this structure? Ependymal cell Fibrous astrocyte Microglial cell Oligodendrocyte Protoplasmic astrocyte :30 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% Ep en dy m al ce ll Fib ro us as tro c.. M . icr og lia lc el Ol .. . ig od en dr oc yt . .. Pr ot op la sm ic a. .. A. B. C. D. E. 9. Identify this structure (arrow, white). Axon Dendrite Erythrocyte Nissl body Nucleolus us 0% Nu cle ol od y 0% Ni ss lb oc yt e ite 0% th r :30 0% De nd r Ax on 0% Er y A. B. C. D. E. 10. Identify this synapse type (circled, red). Axoaxonic Axodendritic Axosomatic Postsynaptic Presynaptic Pr es yn ap Po st sy na p 0% tic 0% tic 0% ic on i Ax oa x :30 0% c Ax od en dr iti c 0% Ax os om at A. B. C. D. E. 11. In this schematic diagram the presynaptic terminal is shown releasing a neurotransmitter (yellow and orange spheres indicated with white arrows) into a space termed the _____. tic cle ft Sy na p Sy na p tic t.. 0% ve s ic .. . 0% . 0% tic id -sy . M te nt i.. po io n Ac t :30 0% na ps e 0% Po st sy na p A. Action potential space B. Mid-synapse C. Postsynaptic terminal D. Synaptic cleft E. Synaptic vesicle 12. Glial fibrillary acidic protein, an intermediate filament protein, is now known to be expressed in several cell types, however, it is still identified as key marker for this CNS cell type. A. B. C. D. E. Astrocyte Ependymal cell Microgliocyte Oligodendrocyte Schwann cell As tro :30 0% 0% 0% 0% cy te Ep en dy m al ce ll M icr og lio cy Ol te ig od en dr oc yt . .. Sc hw an n ce ll 0% 13. Identify these cells (arrows, black). Astrocytes Fibrous astrocytes Microgliocytes Oligodendrocytes Purkinje neurons nj en cy t. . . Pu rk i Ol ig 0% eu ro ... 0% od en dr o cy te s 0% og lio us a st ro c.. cy te s Fib ro As tro :30 0% . 0% M icr A. B. C. D. E. 14. The choroid plexuses, which produce CSF, are essentially specialized structures involving which two epithelial cell types? A. Endothelial cell + Fibroblast B. Ependymal cell + endothelial cell C. Goblet cell + ependymal cell D. Keratinocyte + endothelial cell E. Serous cell + Endocardium .. . Se ro us c el l+ e+ t in oc yt Ke ra el l+ 0% ... 0% .. . 0% et c Go bl al lc e. .. Ep en dy m ot he lia En d :30 0% ce ll. .. 0% 15. The neuroglial microgliocyte derives from which blood-borne precursor? 0% Py ra m id al nj ec ne ur .. el l . 0% Pu rk i ce ll 0% sm a on oc y M ph a ac ro M :30 0% te 0% Pl a Macrophage Monocyte Plasma cell Purkinje cell Pyramidal neuron ge A. B. C. D. E. 16. Which cellular junction is primarily responsible for the formation of the blood-CSF barrier within the choroid plexuses? A. B. C. D. E. Astrocyte Desmosome Fascia adherens Gap junction Zonula occludens :30 0% 0% 0% 0% De sm os om Fa e sc ia ad he re n. .. Ga p ju nc tio Zo n nu la oc clu de ... As tro cy te 0% 17. Which cell type lines this space (arrow, black)? Astrocyte Ependymal cell Fibroblast Purkinje neuron Pyramidal cell Central Canal of spinal cord al Py ra m id nj en bl a 0% ce ll 0% eu ro ... st 0% Pu rk i As tro :30 0% cy te Ep en dy m al ce ll 0% Fib ro A. B. C. D. E. 18. Classify this connective tissue (arrows, black). Endocardium Endoneurium Endothelium Perineurium Percicardium m 0% rd iu ica Pe rc Pe r in eu r ot he liu En d 0% iu m 0% m m 0% on eu r iu En d :30 oc a rd i um 0% En d A. B. C. D. E. 20. Identify this cell of the spinal cord (arrow, black). Astrocyte Macrophage Motor neuron Purkinje cell Pyramidal neuron . ne ur .. el l Py ra m id al nj ec Pu rk i ot or ne ur M ph a ac ro M As tro :30 on ge 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% cy te A. B. C. D. E. 21. Identify this cell (arrow, black). Astrocyte Dorsal root ganglion neuron Oligodendrocyte Primordial follicle Schwann cell 0% 0% ce ll n an Sc hw or d ial fo l cy t. . . ... 0% Pr im ro ot ga . .. 0% Ol ig :30 Do rs al As tro cy te 0% od en dr o A. B. C. D. E. 22. The autonomic nervous system has 3 target effectors – glands, cardiac muscle and …. Astrocytes Ependymal cells Fibroblasts Smooth muscle Striated muscle 0% 0% St ri at ed m us c le m us c le st s 0% bl a al ce lls 0% Sm oo th :30 Ep en dy m As tro cy te s 0% Fib ro A. B. C. D. E. 23. Identify this layer (arrow, black). Granular layer Grey matter Molecular layer Purkinje layer White matter te W hi ay nj el Pu rk i 0% m at te r 0% er e. .. 0% lar ol ec u Gr ey m at te r 0% M :30 Gr an u lar lay er 0% lay A. B. C. D. E. 200x 24. What is true of an efferent sympathetic impulse from the ANS? 0% Re tro gr a de ax o. .. el ls. .. 0% nj ec Pu rk i ub st a nc .. i.. . n 0% . 0% eu ro Fir st n :30 An ax on is no t. . . 0% Ni ss ls A. An axon is not needed B. First neuron is always in the CNS C. Nissl substance is destroyed D. Purkinje cells are always involved E. Retrograde axonal flow stops 25. Your patient received blunt head trauma that resulted in memory loss and intracranial swelling. You suspect that cells of the brain were excessively damaged. Which of the following cells phagocytize the cellular debris created by neural damage? Ependymal cells Fibrous astrocytes Microglial cells Oligodendrocytes Protoplasmic astrocytes a. .. pl a sm ic cy t. . . Pr ot o od en dr o el .. lc Ol ig og lia M icr st ro c.. us a Fib ro Ep en dy m al :30 . . 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% ce ll. .. A. B. C. D. E. 26. Which of the following form the choroid plexus? A. Arachnoid barrier cells B. Ependymal cells and endothelium C. Meningeal dura D. Pia mater and arachnoid E. Pia mater and the overlying epithelium Ar a :30 ch no id ba rr. Ep .. en dy m al ce ll. .. M en in ge al du ra Pi a m at er an d .. . Pi a m at er an d .. . 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 27. Which of the following serve to allow CSF to exit the subarachnoid space? Arachnoid barrier cells Arachnoid villi Choroid plexus Fenestrated capillaries Vessels within the subarachnoid space in . .. w ith ... ca Ve ss el s te d id Fe ne st ra ll. .. Ch or o ch no id vi rr. Ar a ba ch no id Ar a :30 pl ex us 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% .. A. B. C. D. E. 28. A pathologist is examining a stained section of an unknown tissue. He notices cells with an extremely large, flask-shaped body and multiple dendrites lying in parallel. Which of the following tissues is the pathologist examining? A. Cerebellar cortex B. Cerebral cortex C. Gray matter of the spinal cord D. White matter of cerebrum E. White matter of the spinal cord ... m at te ro ... W hi te m at te ro te W hi m at t er o f.. . te .. . Gr ay lc or Ce re br a :30 Ce re be lla rc or ... 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 29. During early brain development, myelination of axons is a critical event. Which of the following cells is responsible for this important function? Fibrous astrocytes Microglial cells Oligodendrocytes Protoplasmic astrocytes Schwann cells ce lls n an Sc hw pl a sm ic cy t. . . Pr ot o . od en dr o el .. lc Ol ig og lia M icr st ro c.. us a Fib ro :30 a. .. 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% . A. B. C. D. E. 32. Which of the following events occurs immediately after an action potential reaches an axon terminal at its synapse? xa tt ns he m Ne ... i t ur te rb ot ra in ns di n. m Ve .. it t er sic le re le fu as s io e. n .. wi th th e p. .. flu io n c iu m Ca l Bi :30 nd i ng o ft he ne ur ot E. ot ra D. ra .. . C. 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% in B. Binding of the neurotransmitter to the presynaptic terminal Calcium ion influx at the presynaptic terminal Neurotransmitter binding to the receptor on the postsynaptic terminal Neurotransmitter release into the synaptic cleft Vesicle fusion with the presynaptic terminal membrane Ne ur A. 33. A 60-year old woman has suffered from a neurologic disorder for several years. Analysis of the CSF revealed the presence of antibodies to myelin proteins. From which of the following disorders does she suffer? A. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis B. Guillain-Barre syndrome C. Multiple sclerosis D. Oligodendroglioma E. Parkinson’s disease . di .. so n’ s kin gli .. . Pa r od en dr o pl e ul ti Ol ig e. .. M Gu ill ai nBa rr a. .. ic l tro ph yo Am :30 sc le r.. . 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 34. A brain tumor is removed and analyzed by immunocytochemistry. It was shown that the tumor expressed high levels of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). Which of the following tumors was being analyzed? Astrocytoma Ependymoma Meningioma Neuroblastoma Oligodendroglioma As tro :30 20% 20% 20% Ep en dy m om a M en in gio m a Ne ur ob la sto m Ol a ig od en dr og li. .. 20% 20% cy to m a A. B. C. D. E. 35. Tissue from the CNS of an 80-year old man is examined by electron microscopy. Cells in this tissue sample have several residual bodies and lipofuscin within their cytoplasm. Which of the following cells are being described? A. Astrocytes B. Endothelial cells of capillaries C. Fibroblasts of dura mater D. Neurons E. Oilgodendrocytes cy t. . . od en dr o on s Oi lg Ne ur f.. . bl a st so lc e. .. ot he lia Fib ro :30 En d As tro cy te s 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 36. Which of the following cellular structures is found within the cytoplasm of perikarya but is not within axoplasm? A. Membrane-bound vesicles B. Microtubules C. Mitochondria D. Neurofilaments E. Rough endoplasmic reticulum M as .. . en do pl m en ts of ila nd ria Ne ur M ito ch o ot ub ul icr M Ro ug h :30 em br a ne -b ou nd .. . es 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 37. Which of the following structures prevent toxic materials from attacking an axon of a peripheral nerve? Pe r in eu r ol em m 20% iu m 20% a 20% Ne ur m on eu r iu En d ch w of S Cl ef ts :30 20% ne ur iu m 20% Ep i Clefts of Schwann cells Endoneurium Epineurium Neurolemma Perineurium ... A. B. C. D. E. 39. Which of the following is a primary component or characteristic of a sensory ganglion? A. Multipolar neurons B. Neurons with eccentric nuclei C. Pseudounipolar neurons D. Scattered neuron cell bodies E. Synaptic contacts ith Ps e. .. eu do un ip ol ar Sc .. . at te re d ne ur Sy ... na pt ic co nt a. .. w on s Ne ur M :30 ul ti po l ar ne u. .. 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 41. Which of the following is the most critical event in regeneration of a peripheral nerve? A. Chromatolysis of the damaged perikaryon B. Distal axon degeneration C. Hypertrophy of Schwann cells D. Phagocytic activity of macrophages E. Proliferation of Schwann cells . .. t io n Pr ol ife ra ac t.. . ic go cy t yo f. . . Ph a op h Hy pe rtr xo n al a Di st :30 Ch ro m at ol ys is ... de ... 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 43. Which of the following components of the meninges are most similar to the endoneurium that covers a peripheral nerve? Arachnoid border cells Dural border cells Meningeal dura Pia mater Subarachnoid space s.. . oi d a ac hn Pi a m Su ba r M en in ge al du r ... or de rc Du ra lb bo ch no id Ar a :30 at er 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% rd ... A. B. C. D. E. 44. Which of the following best characterizes the difference in myelinated axons of the PNS compared with the CNS? A. All axons have nodes of Ranvier B. All axons surrounded by Schwann cells C. No intraperiod line D. No myelin basic protein E. Schwann cells myelinate at multiple axonal cites no de so f. . ur . ro un de No d b. in .. tra No pe rio m ye d lin lin Sc e ba hw s ic an pr n ot ce ei lls n m ye lin at e .. ax on ss av e Al l ax on sh Al l :30 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 45. Which of the following structures primarily functions to monitor the degree of stretch of muscles? Golgi tendon organ Merkel’s disk Myoneural junction Neuromuscular spindle Pacinian corpuscle rp u. .. .. Pa c in ia n co r. . om us cu la ju nc .. al di yo ne ur M er ke l’s M it en do n Go lg :30 Ne ur sk 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% o. .. A. B. C. D. E. 46. Which of the following cells of the PNS functions equivalent to the oligodendrocyte within the CNS? ce lls n an te el li Sc hw ge s ac ro M 20% 20% ce ll. .. 20% ph a bl a Fib ro ot he lia En d :30 st s 20% 20% Sa t Endothelial cells Fibroblasts Macrophages Satellite cells Schwann cells lc e. .. A. B. C. D. E.