* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Darwin`s Theory of Evolution
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
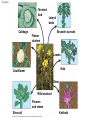
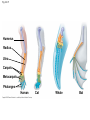
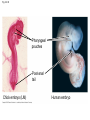
Evolution—change over time, the process by which modern species have descended from ancient organisms Darwin’s Theory of Evolution Who was Charles Darwin? http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution /library/11/2/e_s_2.html Fossil—preserved remains of ancient organisms 1. Geospiza magnirostris. 2. Geospiza fortis. 3. Geospiza parvula. 4. Certhidea olivawea Artificial Selection—selection by humans from natural variation among different organisms for breeding of useful traits Fig. 22-9 Terminal bud Lateral buds Cabbage Brussels sprouts Flower clusters Leaves Kale Cauliflower Stem Wild mustard Flowers and stems Broccoli Kohlrabi • Other examples of Artificial Selection? Selective Breeding—method of improving a species by allowing only those individual organisms with desired characteristics to produce offspring Hybridization—breeding technique that involves crossing dissimilar individuals to bring together the best traits of both organisms •Other example of hybridization? Genetic engineering—the process of making changes in the DNA code of living organisms Ex.-inducing mutations to increase genetic variation Fig. 17-6 (a) Tobacco plant expressing a firefly gene (b) Pig expressing a jellyfish gene Natural variation—genetic differences among individuals of a species Genetic variability starts with natural mutations Fig. 22-10 Struggle for Existence— members of each species compete regularly to obtain food, living space, and other necessities of life Adaptation—any inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s chance of survival Camouflage as an example of evolutionary adaptaition Signate Melanophila Moth Pandora Sphinx Moth Polyphemus Moth Luna Moth A flower mantid in Malaysia A stick mantid in Africa Fig. 23-14a (a) Color-changing ability in cuttlefish STOP - 2/29 Fig. 23-14b Movable bones (b) Movable jaw bones in snakes Question: What would happen if a well-adapted population experienced a sudden major change in its environment Answer: If the population had a variety of traits some of them may survive and reproduce in the new environment, if not they would probably become extinct Fitness—the ability to survive and reproduce viable offspring Descent with modification— principle that each living species has descended, with changes, from other species over time Common descent—principle that all living things have a common ancestor Homologous structures— structures that have different functions but develop from the same embryonic tissue Fig. 22-17 Humerus Radius Ulna Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Human Cat Whale Bat Vestigial organs—organs that serve no useful function Early development The early embryos of many animals with backbones are so similar that they can be hard to tell apart Fig. 22-18 Pharyngeal pouches Post-anal tail Chick embryo (LM) Human embryo Biogeography The study of the past and present distribution of species