* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIO Cell Theory
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
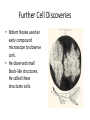
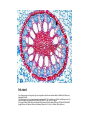
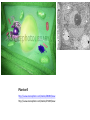
Cell Theory, Microscopes, and Cell Types Pages 171-174 Discovery of Cells • Early scientists believed in spontaneous generation, the idea that life could come from nonliving things. • This was disproved through the experiments of Francesco Redi and Louis Pasteur. • However, because the microbes that Pasteur theorized caused spoilage were too small to see, his ideas were not easily accepted. • The first cells were not observed until the 1600s. • Anton van Leeuwenhoek was the first to create a microscope to observe “animalcules” in pond water. • These animalcules are now called microorganisms. Further Cell Discoveries • Robert Hooke used an early compound microscope to observe cork. • He observed small block-like structures. He called these structures cells. • Schleiden conducted studies of plant tissues and found that plant cells arose from preexisting plant cells. • Schwann conducted similar studies of animal tissues. • Virchow formally concluded that new cells came from preexisting cells. The Cell Theory • The work of Leeuwenhoek, Hooke, Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow was formally recognized as the Cell Theory. There are three main points to the Cell Theory. 1. All living things are composed of cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. 3. New cells are produced from preexisting cells. Microscopes • Microscopes were essential to the discovery and study of cells. • The first microscopes were light microscopes. • They use light and lenses to illuminate and magnify an object. • Simple light microscopes use a single lens. Compound light microscopes use two or more lenses. • Light microscopes can magnify objects up to 1500 times their actual size. Compound light microscope http://www.google.com/imgres?q=compound+light+microscope&hl=en&safe=active&sa=X&tbo=d&biw=1366&bih=651&tbm=i sch&tbnid=3VeMvo8w5Rc6zM:&imgrefurl=http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Optical_microscope&docid=_O_7FXDN28Gt9M&imgur l=http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b1/Optical_microscope_nikon_alphaphot_%25252B.jpg/220pxOptical_microscope_nikon_alphaphot_%25252B.jpg&w=220&h=333&ei=zUPnUKu8OsHqrQGuq4Bo&zoom=1&iact=hc&vpx=2& vpy=261&dur=445&hovh=266&hovw=176&tx=48&ty=150&sig=103974099112624280923&page=1&tbnh=148&tbnw=93&start= 0&ndsp=27&ved=1t:429,r:9,s:0,i:116&surl=1 Aphid http://www.google.com/imgres?q=light+micrograph&hl=en&safe=active&tbo=d&biw=1366&bih=651&tbm=isch&tbnid=hZh7Ad8DJf0iM:&imgrefurl=http://www.sciencephoto.com/media/205120/view&docid=YR_b7wIGda4VM&imgurl=http://www.sciencephoto.com/image/205120/350wm/F0029188-Aphid,_light_micrographSPL.jpg&w=350&h=343&ei=oDjnUMrLA8n_qwHA0oBg&zoom=1&iact=hc&vpx=924&vpy=262&dur=228&hovh=222&hovw=227 &tx=94&ty=76&sig=103974099112624280923&page=1&tbnh=148&tbnw=151&start=0&ndsp=28&ved=1t:429,r:12,s:0,i:122&su rl=1 Bacteria http://www.google.com/imgres?q=gram+stain&hl=en&safe=active&tbo=d&biw=1366&bih=651&tbm=isch&tbnid =USIQusz1f2zzAM:&imgrefurl=http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gram_staining&docid=qRJU6lGTyhJneM&imgurl=htt p://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8f/Gram_stain_01.jpg/220pxGram_stain_01.jpg&w=220&h=165&ei=zjjnUIKoItPaqQHLYBo&zoom=1&iact=rc&dur=181&sig=103974099112624280923&page=1&tbnh=132&tbnw=176&start=0&ndsp=3 0&ved=1t:429,r:0,s:0,i:86&tx=77&ty=57&surl=1 Hydra http://www.google.com/imgres?q=dark+field+micrograph&hl=en&safe=active&tbo=d&biw=1366&bih=651&tbm =isch&tbnid=O4VAPO1hXczKFM:&imgrefurl=http://www.visualphotos.com/image/1x3744472/hydra_viridissima_ darkfield_light_micrograph_of&docid=vehnIlyzWEnfMM&imgurl=http://www.visualphotos.com/photo/1x374447 2/.jpg&w=700&h=479&ei=ATnnUKs0w-pAaXwgYAK&zoom=1&iact=rc&dur=426&sig=103974099112624280923&page=2&tbnh=150&tbnw=178&start=25 &ndsp=33&ved=1t:429,r:43,s:0,i:220&tx=91&ty=74&surl=1 Iris root http://www.google.com/imgres?q=light+micrograph&hl=en&safe=active&tbo=d&biw=1366&bih=651&tbm=isch &tbnid=OD5pAhNLGO7FM:&imgrefurl=http://www.sciencephoto.com/media/91252/view&docid=rcOGitfXJ4_aEM&imgurl=http://w ww.sciencephoto.com/image/91252/350wm/C0027006-Iris_root,_light_micrographSPL.jpg&w=350&h=295&ei=KDnnUIviN8mdrAHQioEY&zoom=1&iact=rc&dur=232&sig=103974099112624280923 &page=2&tbnh=135&tbnw=161&start=28&ndsp=37&ved=1t:429,r:39,s:0,i:208&tx=14&ty=69&surl=1 • More powerful microscopes use a beam of electrons to magnify objects. These are called electron microscopes. They can magnify objects up to 500,000 times their actual size. • Scanning electron microscopes (SEM) are used to scan surfaces and determine threedimensional shape. • Transmission electron microscopes (TEM) are used to determine the internal details of cells. • Scanning tunneling microscopes (STM) are used to create images of atoms on molecular surfaces. Electron microscope http://www.google.com/imgres?q=electron+microscope&hl=en&safe=active&tbo=d&biw=1366&bih=651&tbm=isch&tbnid=xP 10uRNIa4TJiM:&imgrefurl=http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electron_microscope&docid=ckl4qPpv8W4A4M&imgurl=http://upload. wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b0/Siemens-electron-microscope.jpg/220px-Siemens-electronmicroscope.jpg&w=220&h=291&ei=G0TnUJC4MMaDqgHu6YG4Ag&zoom=1&iact=hc&vpx=145&vpy=111&dur=224&hovh=232 &hovw=176&tx=50&ty=105&sig=103974099112624280923&page=1&tbnh=149&tbnw=118&start=0&ndsp=31&ved=1t:429,r:1, s:0,i:89&surl=1 Blood cells SEM http://www.sciencephoto.com/media/304709/view Human cell TEM http://www.sciencephoto.com/media/214687/view DNA STM http://www.sciencephoto.com/media/209656/view Cell Types • There are two major cell types as determined by internal structures. • Prokaryotic cells are cells whose genetic material is not enclosed by a membrane. They lack membrane-bound internal structures (organelles). These are the cells of bacteria. • Eukaryotic cells are cells whose genetic material is enclosed by a membrane (a nucleus). They also have numerous membrane-bound organelles. These are the cells of protists, fungi, plants, and animals. • All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane (or plasma membrane), contain ribosomes, and contain DNA. • Prokaryotic cells are surrounded by a cell wall made of peptidoglycan. They lack a nucleus and organelles. • Fungal cells are surrounded by a cell wall made of chitin. They have a nucleus and all organelles except the chloroplast. • Plant cells are surrounded by a cell wall made of cellulose and contain chloroplasts. They have a nucleus and all organelles. • Animal cells do not have a cell wall. They have a nucleus and all organelles except the chloroplast. Animal cell http://www.sciencephoto.com/media/482581/view http://www.sciencephoto.com/media/459923/view Plant cell http://www.sciencephoto.com/media/485869/view http://www.sciencephoto.com/media/471609/view