* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Archaea 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
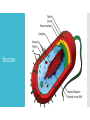
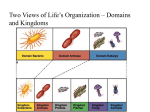
Archaea Shauna Menzella Domain Archaea wasn’t recognized as a major domain until the 20th century Although many books and articles refer to them as “Archaebacteria” the term has since been abandoned They aren’t bacteria at all- they’re Archaea Overview Similar to bacteria in size and simplicity Radically different in molecular organization What is Archaea? Intermediate between bacteria and eukaryotes Unicellular Inhabiting extreme conditions Prokaryotes Structure No nucleus Do not possess packaging proteins Possess proteins similar to histones Structure (continued) Single cellular chromosome Two nucleotides One type of RNA polymerase Wide variety of shapes (flat, square, etc.) Some have flagella Three Types of Archaea Crenarchaeota Characterized by their ability to tolerate extreme temperatures in acidity Three Types of Archaea (continued) Euryarchaeota Includes methaneproducers and salt-lovers Three Types of Archaea (continued) Korarchaeota Diverse and widely encompassing group of which little is known Asexual Reproduction Binary or multiple fission Fragmentation Budding Cell division is controlled in a cell cycle If a species of Archaea exists in more than one form, they will all have the same genetic material Extremophiles Live in extreme environments and temperatures Some love the heat, often above 100 degrees C Geysers at Yellowstone National Park Some love the cold Polar seas Ecology Some love salt (halophiles) Hyper-saline environments