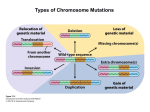
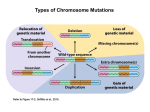
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RNA-dependent RNA polymerase is an essential component of a
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase is an essential component of a self-enforcing loop coupling heterochromatin assembly to siRNA production What is already known? • Without rdp1, heterochromatin is lost • Ago1 and other RITS (RNAi effector complex) proteins bind constitutive heterochromatin at all known loci • Deletion of RNAi components impair silencing at centromeres, initiation of heterochromatin assembly at mat locus • RdRPs thought to convert single stranded to dsRNA, enhancing RNAi effect What are they asking? • Is RdRP (RNA dependent RNA Polymerase) activity responsible for heterochromatin formation, chromosome segregation, centromere silencing? • Is Rdp1 recruited to the centromeres? • Is there a self-inducing pattern where siRNA are generated by the RNAi pathway, then target heterochromatin proteins to homologous sequences. (This should maintain heterochromatin) How did they address these questions? • Model: schizosaccharomyces pombe • ChIP analysis – otr1R::ura4+ construct. Otr1R is not important except that is usually kept as heterochromatin Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Otr1R BEAD Rdp1 O t r 1 R Centrifugation pulls down the beads, chemically dissociate Load result into a gel, run electrophoresis Stain for reporter gene (ura4) Rdp1 on constitutive heterochromatic domains ChIP analysis for Rdp1 at the centromeres, telomeres and mat locus (constitutive heterochromatin areas) WCE= Whole Cell Extract ChIP analysis of Rdp1 at centromeric repeats with one RITS constituent protein knocked out in each; as well as Dcr1 (involved in RNAi), Clr4 (H3K9 methylation) and Swi6 (heterochromatin formation). What have they shown? • Rdp1 localized at heterochromatin (centromeres, telomeres, mat locus) • Rdp1 localization depends of RITS, Dcr1, and heterochromatin assembly factors S. Pombe N Crassa C. Elegans C. Elegans A. thaliana expressing ura4 sensitizes cells to FOA Coomassie Brilliant Blue What have they shown? • Rdp1 localized at heterochromatin (centromeres, telomeres, mat locus) • Rdp1 localization depends of RITS, Dcr1, and heterochromatin assembly factors • Their Rdp1 mutant construct is expressed at the same level, but with the mutation normally silent genes are expressed There is a similar level of Swi6 and H3K9me in the whole cell, but less at the otr1R region and centriole in the mutant; problem with heterochromatin assembly What have they shown? • Rdp1 localized at heterochromatin (centromeres, telomeres, mat locus) • Rdp1 localization depends of RITS, Dcr1, and heterochromatin assembly factors • Their Rdp1 mutant construct is expressed at the same level, but with the mutation normally silent genes are expressed • There is a similar level of Swi6 and H3K9me in the whole cell, but less at the otr1R region and centriole in the mutant; problem with heterochromatin assembly Similar viability with no treatment, but the mutant is more sensitive to TBZ, indicating failure of centromeres Wild types rarely show “lagging chromosomes”-which fail to split in anaphase, and don’t get incorporated into the new cells– but about 1/5 of rdp1 mutants Taz1 is a telomere binding protein, and colocalizes with Swi6 because of its heterochromatin state. This shows problems in telomere clustering (there are too many in the mutants) What have they shown? • Rdp1 localized at heterochromatin (centromeres, telomeres, mat locus) • Rdp1 localization depends of RITS, Dcr1, and heterochromatin assembly factors • Their Rdp1 mutant construct is expressed at the same level, but with the mutation normally silent genes are expressed • There is a similar level of Swi6 and H3K9me in the whole cell, but less at the otr1R region and centriole in the mutant; problem with heterochromatin assembly • Mutation causes mitosis problems, possibly due to failure of heterochromatin assembly A) Mutation of Rdp1 at D903 abolishes activity in affinity purified samples. B) siRNAs were lost in mutants of RdRP activity, reducing it to background levels C) Shows that this is exclusively an RNA effect; pattern not affected by DNase What have they shown? • Rdp1 localized at heterochromatin (centromeres, telomeres, mat locus) • Rdp1 localization depends of RITS, Dcr1, and heterochromatin assembly factors • Their Rdp1 mutant construct is expressed at the same level, but with the mutation normally silent genes are expressed • There is a similar level of Swi6 and H3K9me in the whole cell, but less at the otr1R region and centriole in the mutant; problem with heterochromatin assembly • Heterochromatin assembly problem causes mitosis problems • RdRP-affecting mutation removed ability to create siRNA The RITS components, Ago1 Chp1 and Tas3, fail to localize with the mutant strain. In this ChIP, they are not associated with otr1R or the centriole Rdp1 mutant does not associate with the heterochromatin either What have they shown? • Rdp1 localized at heterochromatin (centromeres, telomeres, mat locus) • Rdp1 localization depends of RITS, Dcr1, and heterochromatin assembly factors • Their Rdp1 mutant construct is expressed at the same level, but with the mutation normally silent genes are expressed • There is a similar level of Swi6 and H3K9me in the whole cell, but less at the otr1R region and centriole in the mutant; problem with heterochromatin assembly • Heterochromatin assembly problem causes mitosis problems • RdRP-affecting mutation removed ability to create siRNA • RdRP-afecting mutation prevents the formation of the RITS complex and association of the Rdp1 to heterochromatin So what is the point? • Rdp1 required for creating dsRNAs that activate Dicer, which in turn amplifies siRNAs • siRNA target heterochromatin in cis, help maintain heterochromatin state: if the heterochromatin opens and expresses, the siRNA will silence it again • siRNA needed for H3K9 methylation, RITS localization STEPS in cycle • Bidirectional transcription of repeat elements creates dsRNA • Dicer cleaves the dsRNA into siRNA • siRNA targets histone methyltransferase and RITS to the repeat element • RITS binds Rdp1, others at heterochromatic loci • Ago1 binds siRNA, uses Rdp1’s RdRP activity to create more dsRNA So what? • Support idea that RNAi maintains heterochromatin in a loop, not a line • Rdp1 converts “aberrant” transcripts into siRNA to resilence the gene • Keeping certain genes off is critical for the differentiation of cells or reactions to the environment