* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mechanisms of Danger-signal mediated Immune Modulation
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Plasmodium falciparum wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
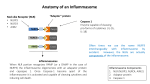
Mechanisms of Danger-signal Mediated Immune Modulation The Self-Non-Self theory • Dominant model in immunology since the 1950s • The body is able to discern between self and non-self • Thus an immune response is triggered against all foreign entities • No immune response is triggered against an organism’s endogenous entities Danger Theory • Rooted in Janeway’s work (Infectious non-self theory) • Proposed by Polly Matzinger in a 1994 article title “Tolerance, Danger and the Extended Family” • States that the immune response is a result of the organism reacting to the emission of “danger signals” by the organism, not “non-self” entities • Self constituents can trigger an immune response if they are dangerous (cellular stress) and non-self constituents can be tolerated (commensal bacteria) Predications made by Self-non-self, Infectious non-self theory and Danger Theory Burnet 1969 Janeway 1989 Matzinger 1994 Danger Theory *Alarm Signals = DAMPs, damage associated molecular patterns DAMPs – Damage signal criteria • Should be active as a highly purified molecule • Biological activity should not be due to contamination with microbial molecules (LPS) • Should be active at concentrations that are actually present in pathophysiological situations • Selective elimination or inactivation of a DAMP should ideally inhibit the biological activity of dead cells (in vitro and vivo) Molecular identification of Danger Signals • Cellular stress – when a cell is stressed, even in the absence of any foreign substance, it emits molecules that activate APCs • Heat-shock proteins – expression increased with elevated temperature and other stresses, can bind antigen and activate APCs • Necrotic cell death – intracellular contents, including damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). Apoptosis? • Uric Acid – released by injured cells, dendritic cell maturation, with antigen it enhances respsonses from CD8+ cells • High-mobility-group box 1 – signals damage, initiates inflammatory response/repair • Inflammasomes? Inflammasomes • Component of innate immunity, triggered by danger signals; stress/infection • Multiprotein complex • Expressed in myeloid cells • Senses damage activate caspase1 production of IL-1β • Subsets – NLRP1, NLRP3 (codes Nalp3 inflammasome), NLRC4 • Consists of caspase-1, caspase recruitment domain (CARD), NALP and ASC (adaptor) • NALP – NOD like receptor that contains NACHT (nucleotide binding domain), LRR and Pyrin domain NLRP3 Inflammasome Structure Malaria • Infects 300-500 million • Kills over 1 million children annually • Causative agent is a parasitic protozoan; Plasmodium species • Complex life cycle involving a mosquito vector and a human host • Erythrocyte (RBC) lysis resulting in fever, anemia and death • 1-2% cases develop Cerebral Malaria (deadly) Life Cycle of the Malaria Parasite Immune response and Plasmodium infection Adaptive: • Induces an immune response characterized by IFNγ producing T cells • Production of antibodies against infected RBCs Innate: • Several molecular conserved structures of Plasmodium act as pathogenassociated molecular patterns (PAMPs) • PAMPs activate Toll-like receptors (TLRs) on macrophages and dendritic cells • Hemozoin activation of a Nalp3 inflammasome Hemozoin • • • • Heme crystal formed by Plasmodium During the intraerythrocytic cycle hemoglobin is digested Results in free heme Parasite is able to convert free heme into insoluble hemozoin crystals as a means of detoxification • RBC lysis results in hemozoin entering the blood stream Studies about the immuno-modulatory capacity are conflicting • Activation of TLR9 signaling • Dependence upon the presence of malarial DNA complexed to hemozoin • Inflammasome Hypothesis Hemozoin acts as a Nalp3 inflammasome activating danger signal resulting in IL-1β production. Hemozoin induces IL-1β secretion in myeloid cells • Experiments used synthetic hemozin; β-hematin • Bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM) produced low levels of TNF, IL-6 and MIP-1α with hemozoin, relative to CpG (TLR9 activator). • BMDM robustly secreted IL-1β and IL18 when primed and stimulated with HZ. IL-1β HZ induction in THP1 cells and Murine BMDCs THP1 cells: human macrophage like cell line BMDCs: murine bone marrow-derived Dendritic cells Hemozoin IL-1β secretion is NALP3 inflammasome dependent Hemozoin IL-1β secretion is independent from P2X7 activation HZ induced IL-1B not mediated by ATP released from dying cells. Uric acid crystals have no effect on hemozoin IL-1B, uric acid itself can act as danger signal Toxic heme cannot activate caspase1, but is toxic (PARP cleavage) Hemozoin IL-1β secretion is independent from MyD88-mediated signaling pathways Chloroquine – anti-malarial drug Performed in order to remove any implication of DNA-mediated TLR9 signaling Bafilomycin – shown to inhibit inflammasome activation, no effect seen in these experiments Phagocytosis, K+ Efflux and activation of a NADPH oxidase are all essential for Hz-mediated inflammasome Phagocytosis, K+ Efflux and activation of a NADPH oxidase are all essential for Hz-mediated inflammasome Phagocytosis, K+ Efflux and activation of a NADPH oxidase are all essential for Hz-mediated inflammasome Role of the Inflammasome in a mouse model of Hz-induced peritonitis Role of the Inflammasome in a mouse model of Hz-induced peritonitis Role of the Inflammasome in a mouse model of Hz-induced peritonitis Role of Nalp3 in a mouse model of Cerebral Malaria Role of Nalp3 in a mouse model of Cerebral Malaria H & E Stain CD45 Stain Conclusion • Were able to show that Malarial Hemozoin is a Nalp3 inflammasome activating signal, therefore enhancing the pro-inflammatory activity along with TLRs • May lead to novel more efficient anti-malaria drugs • Investigate the mechanism for inflammasome activation by agonists and therefore the exact role of hemozoin • Self-non-self vs Danger? Maybe a combination of both.