* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gene Expression and Protein Synthesi
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
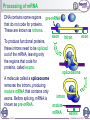
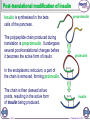
1 of 10 © Boardworks Ltd 2016 2 of 10 © Boardworks Ltd 2016 Processing of mRNA DNA contains some regions pre-mRNA that do not code for proteins. These are known as introns. exon To produce functional proteins, these introns need to be spliced out of the mRNA, leaving only the regions that code for proteins, called exons. intron exon spliceosome A molecule called a spliceosome removes the introns, producing mature mRNA that contains only exons. Before splicing, mRNA is known as pre-mRNA. 3 of 10 intron mature mRNA exons © Boardworks Ltd 2016 Translation 4 of 10 © Boardworks Ltd 2016 Cracking the code In 1961, Nirenberg and Heinrich deciphered which amino acids are coded for by which codons. They used synthetic mRNA made from only one base type, e.g. uracil. They radioactively labelled an amino acid and assessed the radioactivity of each protein produced. They discovered that mRNA made from just uracil codes for phenylalanine (codon UUU). 5 of 10 © Boardworks Ltd 2016 Post-translational modifications Once translated, a polypeptide chain may undergo changes. These post-translational modifications include: removal of methionine – the start codon for each gene codes for a methionine; in many cases this will be removed addition of functional groups – e.g. phosphate or acetate structural changes – e.g. the addition of disulfide bridges or cleavage of a part of the chain Modifications of the primary structure give the protein its specific secondary structure that allows it to perform its function. 6 of 10 © Boardworks Ltd 2016 Post-translational modification of insulin Insulin is synthesised in the beta cells of the pancreas. The polypeptide chain produced during translation is preproinsulin. It undergoes several post-translational changes before it becomes the active form of insulin. preproinsulin proinsulin In the endoplasmic reticulum, a part of the chain is removed, forming proinsulin. The chain is then cleaved at two points, resulting in the active form of insulin being produced. 7 of 10 insulin © Boardworks Ltd 2016 Protein synthesis 8 of 10 © Boardworks Ltd 2016 The stages of protein synthesis 9 of 10 © Boardworks Ltd 2016 Want to see more? This is only a sample of one of thousands of Boardworks Science presentations. To see more of what Boardworks can offer, order a full presentation completely free: www.boardworks.co.uk/sciencepresentation 10 of 10 © Boardworks Ltd 2016