* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA to Protein Practice Sheet
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
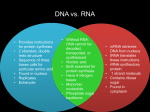
Biology II DNA to Protein Practice Sheet Completion 1. For the following DNA strands, identify the base sequence in the opposite strand. a. AACTCGATTACAGA b. CATGATTAGCCGATA c. GGCATCAACCGTTAAC True and False If the statement is true, write a T. If the statement is false, correct it by changing the underlined word(s) and writing the correct word(s). 2. DNA is composed of four different nucleotides. 3. In a nucleotide, the phosphate group is attached to the nitrogen-containing base, which is attached to the five-carbon sugar. 4. The hydrogen bonding of adenine to guanine is an example of complementary base pairing. 5. Each parent strand remains intact during replication, and a new companion strand is assembled on each of those parent strands. 6. Some of the enzymes associated with DNA assembly repair errors during the replication process. Label and Match Use the DNA Structure Diagram to identify the structures (use Figure 11.6 to help you). Then, match the correct description (A-G in the box) to each. Each letter will be used once. 7. 6)________________ ( ) 8. 7)_____________ ______________ ( ) 9. 8)________________ ( ) 10. 9)________________ ( ) 11. 10)_______________ ( ) 12. 11)_______________ ( ) 13. 12)_______________ ( ) A. The pyrimidine is thymine because it has two hydrogen bonds. B. A five-carbon sugar joined to two phosphate groups in the upright portion of the DNA ladder. C. The purine is guanine because it has three hydrogen bonds. D. The pyrimidine is cytosine because it has three hydrogen bonds. E. The purine is adenine because it has two hydrogen bonds. F. Composed of three smaller molecules: a phosphate group, five-carbon deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base (in this case, a pyrimidine). G. A chemical group that joins two sugars in the upright portion of the DNA ladder. Transcription Short Answer 14. List three ways in which a molecule of RNA is structurally different from a molecule of DNA. 15. What are the three key ways in which transcription differs from DNA replication? 16. Given the following DNA sequences, identify the sequence of the mRNA that it would form. a. TACAAGATAACA b. TTATTTCCTACCG c. ATCGGCATCGAAT Translation Matching Choose the most appropriate answer for each. 17. Codon 18. Three at a time 19. Genetic code 20. Release factors 21. Ribosome 22. Anticodon 23. “Stop” codons A. Composed of two subunits, one of which includes binding site for mRNA B. Reading frame of the nucleotide bases in mRNA C. Detach protein and mRNA from the ribosome D. UAA, UAG, UGA E. A sequence of three nucleotide bases that can pair with a specific mRNA codon F. Name for each base triplet in mRNA G. Term for how the nucleotide sequences of DNA and then mRNA correspond to the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide chain Translation Completion Use the RNA sequence (AUGUUCUAUUGUAAUAAAGGAUGGCAGUAG) to answer the following… 24. Write the corresponding mRNA sequence, breaking it into codons. 25. Use Figure 12.7 of your textbook to identify the chain of amino acids that would be formed.