* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stearns 6
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic feminism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Medieval Muslim Algeria wikipedia , lookup
Liberalism and progressivism within Islam wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic socialism wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Gender roles in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Afghanistan wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Iran wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Hindu–Islamic relations wikipedia , lookup
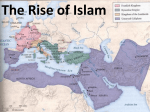
The First Global Civilization: The Rise and Spread of Islam & Abbasid Decline and the Spread of Islamic Civilization to South and Southeast Asia STEARNS 6 AND 7 GEOGRAPHY MATTERS Desert Clanish Bedouin Camel and goat herding Scattered Oases Areas of commerce and agriculture Tradition of long-distance trade CLANS, IDENTITIES, RIVALRIES Desert-living promotes group dependence Conflict over water and pastures CULTURE Majority polytheistic; small Jewish populations Less patriarchal Women had economic roles in clan life Descent traced through female line Men paid a “bride-price” to wife’s family Both genders could have multiple spouses Women not shrouded in veils BUT men still considered superior, especially in cities Poetry MUHAMMAD AND ISLAM 6th Century C.E. Orphaned, raised in a merchant family Widely travelled; introduced to monotheism 610 C.E. first revelation from Gabriel Revelations collected in the Qur’an ISLAMIC TRIUMPH Initial oppression by Quraysh Mecca v. Medina 629 C.E. conquest of Mecca ISLAM’S CONSEQUENCES End of clan conflicts New missionary zeal Problem of succession UMAYYAD EMPIRE Ethnically Arab Governed by warrior elite Establishment of the Caliph Seeds of Sunni-Shi’a Split Rapid expansion Mesopotamia, North Africa, Persia Later Spain, France, Northwestern India Unable to topple Byzantines Economic motives as important as religious motives Desire to conquer for booty Need to limit converts to secure taxes and shares in booty Role of the Dhimmi (“People of the Book”) SUNNI-SHI’A SPLIT Succession struggle Third Caliph, Uthman, murdered Ali wins caliphate but rejected by Umayyads Umayyads promote Mu’awiya; assassinate Ali Shi’a recognize only Ali’s line for caliphate NEW FAMILY AND GENDER ROLES Initial improvement for women Conquered areas had been strictly patriarchal Muhammad promoted equality before Allah Adultery denounced Female infanticide outlawed Men had to treat all wives (up to four) equally Women had legal rights in inheritance and divorce But patriarchal cultures of conquered people prevails These mores not to be confused with Islamic belief UMAYYAD DECLINE Expansion creates new tensions Unequal distribution of booty Fear that luxury and conquest at the expense of Islamic principles Men in provinces develop regional loyalties Abbasid clan revolts, 750. Allies with Shi’a; assassinate most Umayyad leaders ABBASID EMPIRE Less “Arab” identity (so many regional identities) Bureaucratic expansion Capital moved to Baghdad Elevation of Persian ruling concepts Persian influence Power of wazir Absolutism Actual office of royal executioner! Turned against Shi’a allies; support less tolerant Sunni Enjoyed luxurious living NEW ISLAM No more distinction between Mawali and older believers Most conversions peaceful New artistic expression Mosque and palace construction Islamic scholarship alongside mathematics and science Sufism Ulama—will ultimately stifle mathematic and scientific achievements ABBASID ECONOMY Preeminence of merchant and landlord classes Urban expansion Artisan handicraft Goods traded from South China Sea to the Western Mediterranean Tapestries Rugs Ceramics Bronzes Glass Tenant farming Slavery SCIENTIFIC ACHIEVEMENTS Chemistry created the objective experiment Classification of material substances Animal Vegetable Mineral Mathematics: built on Greek theories Astrolabe Medicine Paper-making (from China) ABBASID DECLINE Begins in 9th century Overly luxurious living Caliphs depend on Persian advisors The Thousand and One Nights Persian becomes the court language and literary preference; Arabic for religion, law, and natural sciences Weaker caliphs More court intrigue Peasant revolts Slave armies Increased tax burdens Abandonment of agricultural villages Failure to reconcile with moderate Shi’a Succession disputes WOMEN’S SOCIAL DECLINE Myth of women’s incurable lust Leads to jealousy Need to cloister them Harem and veil symbolize this Poor women were more active—had to be NO-GOOD NOMADS Persian Buyids capture Baghdad, 945 Caliphs controlled by sultans Seljuk Turks defeat Buyids, 1055 Push Byzantines out of Anatolia Purge Shi’a Mongols sack Baghdad, 1258—end Abbasid CRUSADES Causes Political Religious Cultural Effects For Europeans For Muslims HINDUISM V. ISLAM Hinduism Open Tolerant Inclusive polytheism Social division by caste Islam Doctrinaire Monotheistic Evangelical Egalitarian MUSLIMS INVADE INDIA Umayyad conquered first Treat Hindus as Dhimmi Many Hindus welcome Muslim conquerors Lower taxes Not much effort to convert; tolerant Missionary activity by traders and Sufis Appeal to low and outcaste Hindus Many Buddhist converts Mosques become centers of learning and regional political power Hindu revival and backlash Brahmins denounce Muslims for destroying temples Use of the Race Card INDIA’S INFLUENCE India influenced Islam more than Islam influenced India Mathematics (numbers) Science and astronomy Medicine Music Foods, hierarchies, and attitudes toward women ISLAM IN SOUTHEAST ASIA Spread peacefully through trading contacts More influenced by Sufi More mystical Better positions for women