* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Islamic Empires
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Afghanistan wikipedia , lookup
Medieval Muslim Algeria wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
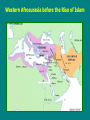
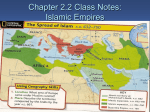
The Rise of Islam Terms to Know • • • • Muhammad (c. 571 – 632) The Qur’an Umayyad Dynasty, 661 – 750 Abbasid Dynasty, 750 – 1258 Arabia Before Islam • Commercial cities • Nomadic culture • Polytheistic Western Afroeurasia before the Rise of Islam Muhammad (c. 571 – 632) • Born into a commercial family in Mecca • 610: visited by Gabriel; becomes prophet of Islam • 622, Hegira: Forced to leave Mecca for Medina • By 627, Muhammad united Medina under Islam with protection for other faiths, peace & prosperity; Islam spread rapidly amongst Arabs • 630: returned to Mecca in triumph and worked for unification of Arabia The Practice of Early Islam • Five Pillars: Recitation; Prayer; Alms; Ramadan; Pilgrimage (Hajj) • The Qur’an: 114 surahs (chapters) lay out creation, life & laws • Sunni: recognized authority of Caliphs • Shi’ite: followed lineage of Muhammad Decorations in the Great Mosque of Aleppo demonstrate the sophistication of Islamic decorative art and architecture Creating an Empire • Four Rightly Guided Caliphs: Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, Ali – incorporated Persia, Syria, Egypt & North Africa into Islamic Empire • Ali’s assassination in 661 ended the direct line of Muhammad’s household in leading Islam The Dome of the Rock, one of the most sacred sites in Islam, was begun in 684 after the Islamic conquest of Jerusalem Umayyad Dynasty, 661 – 750 • Mu'awiyah, governor of Damascus, rebelled against Ali and, after Ali’s asssassination, seized control • Umayyad Caliphs focused on expansion in the East (against Byzantium) and the West (against Vandals, Visigoths and Franks) This example of Islamic architecture comes from eighth century Cordoba in Spain The Empire Grows & Divides Abbasid Dynasty, 750 – 1258 • Caliphs of Baghdad, rebelled against Umayyad caliphs, 747-750 • Islam quickly fragmented – – – – Umayyad dynasty re-emerges in Spain Africa soon declared its independence Critics complained of persecution against Shi’a Harun al-Rashid (763-809) was a scholar, poet and military leader who bested the Byzantines – Al-Mu'tasim (833-842) began practice of passing power to Turkish household slaves The Muslim World to 1500 C.E.