* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download C) the gain of electrons.
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Ultrasensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
VX (nerve agent) wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
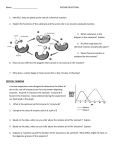
Oxidation typically involves: A) the loss of electrons. B) the loss of oxygen. C) the gain of electrons. D) the gain of water. E) none of the above Oxidation typically involves: A) the loss of electrons. B) the loss of oxygen. C) the gain of electrons. D) the gain of water. E) none of the above Reduction typically involves: A) the loss of electrons. B) the gain of oxygen. C) the gain of electrons. D) the gain of water. E) none of the above Reduction typically involves: A) the loss of electrons. B) the gain of oxygen. C) the gain of electrons. D) the gain of water. E) none of the above The reducing agent typically: A) gains electrons. B) always remains unchanged during a reaction. C) is the oxidized substance. D) is itself reduced. E) none of the above The reducing agent typically: A) gains electrons. B) always remains unchanged during a reaction. C) is the oxidized substance. D) is itself reduced. E) none of the above The oxidizing agent typically: A) loses electrons. B) gains oxygen. C) is the reactant that is reduced. D) is oxidized. E) none of the above The oxidizing agent typically: A) loses electrons. B) gains oxygen. C) is the reactant that is reduced. D) is oxidized. E) none of the above Oxidation involves which of the following? 1. Loss of electron(s). 2. Gain of electron(s). 3. Increase in oxidation state. A) 1 only B) 2 only C) 3 only D) 1 and 3 only E) 2 and 3 only Oxidation involves which of the following? 1. Loss of electron(s). 2. Gain of electron(s). 3. Increase in oxidation state. A) 1 only B) 2 only C) 3 only D) 1 and 3 only E) 2 and 3 only Reduction involves which of the following? 1. Loss of electron(s). 2. Gain of electron(s). 3. Decrease in oxidation state. A) 1 only B) 2 only C) 3 only D) 1 and 2 only E) 2 and 3 only Reduction involves which of the following? 1. Loss of electron(s). 2. Gain of electron(s). 3. Decrease in oxidation state. A) 1 only B) 2 only C) 3 only D) 1 and 2 only E) 2 and 3 only In the reaction Zn(s) + Fe2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Fe(s) A.Electrons are transferred from Zn to Zn2+ B.Electrons are transferred from Fe2+ to Fe. C.Electrons are transferred from Fe to Zn2+ D.Electrons are transferred from Zn to Fe2+ In the reaction Zn(s) + Fe2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Fe(s) A.Electrons are transferred from Zn to Zn2+ B.Electrons are transferred from Fe2+ to Fe. C.Electrons are transferred from Fe to Zn2+ D.Electrons are transferred from Zn to Fe2+ Identify the substance being oxidized in the following reaction: CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O. A) CH4 B) O2 C) CO2 D) H2O E) none of the above Identify the substance being oxidized in the following reaction: CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O. A) CH4 B) O2 C) CO2 D) H2O E) none of the above Identify the substance being reduced in the following reaction: CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O. A) CH4 B) O2 C) CO2 D) H2O E) none of the above Identify the substance being reduced in the following reaction: CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O. A) CH4 B) O2 C) CO2 D) H2O E) none of the above Identify the reducing agent in the following reaction: CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O. A) CH4 B) O2 C) CO2 D) H2O E) none of the above Identify the reducing agent in the following reaction: CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O. A) CH4 B) O2 C) CO2 D) H2O E) none of the above Identify the oxidizing agent in the following reaction: CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O. A) CH4 B) O2 C) CO2 D) H2O E) none of the above Identify the oxidizing agent in the following reaction: CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O. A) CH4 B) O2 C) CO2 D) H2O E) none of the above In the following “redox” reaction, Zn (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu (s) A) Zn is the reducing agent and CuSO4 is the oxidizing agent. B) CuSO4 is the reducing agent and Zn is the oxidizing agent. C) ZnSO4 is the reducing agent and Cu is the oxidizing agent. D) Cu2+ is the reducing agent and Zn2+ is the oxidizing agent. E) none of the above In the following “redox” reaction, Zn (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu (s) A) Zn is the reducing agent and CuSO4 is the oxidizing agent. B) CuSO4 is the reducing agent and Zn is the oxidizing agent. C) ZnSO4 is the reducing agent and Cu is the oxidizing agent. D) Cu2+ is the reducing agent and Zn2+ is the oxidizing agent. E) none of the above Many names for enzymes end in the suffix A. acid B. ose C. ase D. hyde Many names for enzymes end in the suffix A. acid B. ose C. ase D. hyde What is the general function of enzymes within a cell? A) to promote the synthesis of monomers B) to induce chemical reactions C) to stop chemical reactions D) to speed up chemical reactions What is the general function of enzymes within a cell? A) to promote the synthesis of monomers B) to induce chemical reactions C) to stop chemical reactions D) to speed up chemical reactions A child is brought to the hospital with a fever of 107°F. Doctors immediately order an ice bath to lower the child's temperature. Which of the following statements offers the most logical explanation for this action? A)Elevated body temperature will increase reaction rates in the child's cells and overload the limited number of enzymes found in the cell. B) Elevated body temperatures may denature enzymes. This would interfere with the cell's abilities to catalyze various reactions. C) Elevated body temperatures will increase the energy of activation needed to start various chemical reactions in the body. This will interfere with the ability of enzymes to catalyze vital chemical reactions. D) Elevated body temperatures cause molecules to vibrate more quickly and prevent enzymes from easily attaching to reactants. This would slow vital body reactions. A child is brought to the hospital with a fever of 107°F. Doctors immediately order an ice bath to lower the child's temperature. Which of the following statements offers the most logical explanation for this action? A)Elevated body temperature will increase reaction rates in the child's cells and overload the limited number of enzymes found in the cell. B) Elevated body temperatures may denature enzymes. This would interfere with the cell's abilities to catalyze various reactions. C) Elevated body temperatures will increase the energy of activation needed to start various chemical reactions in the body. This will interfere with the ability of enzymes to catalyze vital chemical reactions. D) Elevated body temperatures cause molecules to vibrate more quickly and prevent enzymes from easily attaching to reactants. This would slow vital body reactions. The chemical reaction below depicts the hydrolysis of the disaccharide sucrose into two monosaccharides as catalyzed by the enzyme sucrase. Sucrose --> Fructose + Glucose. What is/are the “substrate” for this reaction A) Sucrose B) Sucrase C) Fructose D) Glucose E) C and D The chemical reaction below depicts the hydrolysis of the disaccharide sucrose into two monosaccharides as catalyzed by the enzyme sucrase. Sucrose --> Fructose + Glucose. What is/are the “substrate” for this reaction A) Sucrose B) Sucrase C) Fructose D) Glucose E) C and D The chemical reaction below depicts the hydrolysis of the disaccharide sucrose into two monosaccharides as catalyzed by the enzyme sucrase. Sucrose --> Fructose + Glucose. What is/are the “product” for this reaction A) Sucrose B) Sucrase C) Fructose D) Glucose E) C and D The chemical reaction below depicts the hydrolysis of the disaccharide sucrose into two monosaccharides as catalyzed by the enzyme sucrase. Sucrose --> Fructose + Glucose. What is/are the “product” for this reaction A) Sucrose B) Sucrase C) Fructose D) Glucose E) C and D Substrates bind to an enzyme's ________ site. A) allosteric B) inhibitory C) phosphate D) active Substrates bind to an enzyme's ________ site. A) allosteric B) inhibitory C) phosphate D) active The effect of temperature on the relative rate of action of an enzyme is represented in the graph below. The optimum temperature for the action of this enzyme is approximately a. 15◦C b. 22◦C c. 37◦C d. 50◦C The effect of temperature on the relative rate of action of an enzyme is represented in the graph below. The optimum temperature for the action of this enzyme is approximately a. 15◦C b. 22◦C c. 37◦C d. 50◦C Use the diagram below to answer the question. Identify the parts involved. A.A and B are enzymes and C is the substrate B.C is the enzyme and A and B are the substrates. C.A is the enzyme, B is the monomer and C is the polymer D.A and B are the substrates and C is the polymer Use the diagram below to answer the question. Identify the parts involved. A.A and B are enzymes and C is the substrate B.C is the enzyme and A and B are the substrates. C.A is the enzyme, B is the monomer and C is the polymer D.A and B are the substrates and C is the polymer The enzyme salivary amylase will act on starch but not on protein. This action illustrates that salivary amylase A. contains starch B. is not reusable C. is substrate specific D. lacks protein The enzyme salivary amylase will act on starch but not on protein. This action illustrates that salivary amylase A. contains starch B. is not reusable C. is substrate specific D. lacks protein A person may become lactose intolerant if their intestinal glands do not produce enough A. maltase enzyme B. lactase enzyme C. lactose enzyme D. maltose enzyme A person may become lactose intolerant if their intestinal glands do not produce enough A. maltase enzyme B. lactase enzyme C. lactose enzyme D. maltose enzyme When an enzyme catalyzes a reaction, A) it lowers the activation energy of the reaction. B) it raises the activation energy of the reaction. C) it acts as a reactant. D) it is used once and discarded. When an enzyme catalyzes a reaction, A) it lowers the activation energy of the reaction. B) it raises the activation energy of the reaction. C) it acts as a reactant. D) it is used once and discarded. Which of the following statements regarding enzymes is true? A) Enzymes are inorganic. B) An enzyme's function is unaffected by changes in pH. C) Enzymes catalyze specific reactions. D) Enzymes slow down the rate of a chemical reaction. Which of the following statements regarding enzymes is true? A) Enzymes are inorganic. B) An enzyme's function is unaffected by changes in pH. C) Enzymes catalyze specific reactions. D) Enzymes slow down the rate of a chemical reaction. Heating inactivates enzymes by A) breaking the covalent bonds that hold the molecule together. B) removing phosphate groups from the enzyme. C) causing enzyme molecules to stick together. D) changing the enzyme's three-dimensional shape. Heating inactivates enzymes by A) breaking the covalent bonds that hold the molecule together. B) removing phosphate groups from the enzyme. C) causing enzyme molecules to stick together. D) changing the enzyme's three-dimensional shape. The active site of an enzyme is A) the region of a substrate that is changed by an enzyme. B) the highly changeable portion of an enzyme that adapts to fit the substrates of various reactions. C) the region of an enzyme that attaches to a substrate. D) the region of a product that detaches from the enzyme. The active site of an enzyme is A) the region of a substrate that is changed by an enzyme. B) the highly changeable portion of an enzyme that adapts to fit the substrates of various reactions. C) the region of an enzyme that attaches to a substrate. D) the region of a product that detaches from the enzyme. Which of the following characteristics of protein will remain intact if the protein is denatured? A) the shape of the protein B) the function of the protein C) the number of amino acids in the protein D) the binding properties of the protein Which of the following characteristics of protein will remain intact if the protein is denatured? A) the shape of the protein B) the function of the protein C) the number of amino acids in the protein D) the binding properties of the protein The shape of the _______________ on the enzyme determines to which ___________________ the enzyme can bind. A. active area; substrate B. active site; product C. loading dock; organelle D. active site; substrate The shape of the _______________ on the enzyme determines to which ___________________ the enzyme can bind. A. active area; substrate B. active site; product C. loading dock; organelle D. active site; substrate There are many different enzymes located in a single cell. Why do enzymes catalyze a specific reaction? A. Most enzymes can catalyze many different reactions. B. The shape of the enzyme’s active site determines to which substrate the particular enzyme can bind. C. Enzymes are transported to specific substrates (reactants) by ribosomes. There are many different enzymes located in a single cell. Why do enzymes catalyze a specific reaction? A. Most enzymes can catalyze many different reactions. B. The shape of the enzyme’s active site determines to which substrate the particular enzyme can bind. C. Enzymes are transported to specific substrates (reactants) by ribosomes. List at LEAST THREE environmental factors that affect the reaction rate of an enzyme: 1. _____________________ 2. _____________________ 3. _____________________ List at LEAST THREE environmental factors that affect the reaction rate of an enzyme: 1. pH 2. TEMPERATURE 3. CONCENTRATION OF SUBSTRATE 4. CONCENTRATION OF ENZYME 5. SALT CONCENTRATION When an enzyme has become misfolded or unfolded and can no longer perform it’s function, we say that the enzyme is “_____________________.” When an enzyme has become misfolded or unfolded and can no longer perform it’s function, we say that the enzyme is “DENATURED.” List TWO environmental factors that tend to denature enzymes: 1. _____________________ 2. _____________________ List TWO environmental factors that tend to denature enzymes: 1. Changes in pH 2. INCREASE IN TEMPERATURE 3. Changes in SALT CONCENTRATION Which of the following statements about enzymes is false? A) They increase the rate of chemical reactions. B) They function as chemical catalysts. C) They regulate virtually all chemical reactions in a cell. D) They are monomers used to build proteins. Which of the following statements about enzymes is false? A) They increase the rate of chemical reactions. B) They function as chemical catalysts. C) They regulate virtually all chemical reactions in a cell. D) They are monomers used to build proteins. When you add acid to a solution, _____. A. the hydrogen ion concentration increases and lowers the pH B. the hydrogen ion concentration decreases and raises the pH C. the hydrogen ion concentration increases and raises the pH D. the hydrogen ion concentration decreases and lowers the pH When you add acid to a solution, _____. A. the hydrogen ion concentration increases and lowers the pH B. the hydrogen ion concentration decreases and raises the pH C. the hydrogen ion concentration increases and raises the pH D. the hydrogen ion concentration decreases and lowers the pH Grapefruit juice is approximately pH 3, and tomato juice is approximately pH 4. A glass of grapefruit juice contains _____ H+ as a glass of tomato juice. A. half as much B. ten times as much C. one-tenth as much D. twice as much Grapefruit juice is approximately pH 3, and tomato juice is approximately pH 4. A glass of grapefruit juice contains _____ H+ as a glass of tomato juice. A. half as much B. ten times as much C. one-tenth as much D. twice as much A pH of 6 is how many times more acidic than a pH of 9? A. 3 B. 100 C. 300 D. 1,000 A pH of 6 is how many times more acidic than a pH of 9? A. 3 B. 100 C. 300 D. 1,000 An acid is _____. A. a solution with a pH between 7 and 14 B. a material that resists pH changes C. any compound that accepts hydrogen ions D. a compound that donates hydrogen ions to a solution An acid is _____. A. a solution with a pH between 7 and 14 B. a material that resists pH changes C. any compound that accepts hydrogen ions D. a compound that donates hydrogen ions to a solution Adding a base tends to _____ of a solution. A. increase the hydrogen ion concentration and increase the pH B. lower hydrogen ion concentration and increase the pH C. lower hydrogen ion concentration and lower the pH D. increase hydrogen ion concentration and lower the pH Adding a base tends to _____ of a solution. A. increase the hydrogen ion concentration and increase the pH B. lower hydrogen ion concentration and increase the pH C. lower hydrogen ion concentration and lower the pH D. increase hydrogen ion concentration and lower the pH Which of the following statements about pH is true? A) The pH scale is a measure of oxygen ion concentration. B) A single unit change on the pH scale is equivalent to a 1% change in hydrogen ion concentration. C) An increase in hydrogen ion concentration means a decrease in pH scale units. D) Basic pH levels are less than 7. Which of the following statements about pH is true? A) The pH scale is a measure of oxygen ion concentration. B) A single unit change on the pH scale is equivalent to a 1% change in hydrogen ion concentration. C) An increase in hydrogen ion concentration means a decrease in pH scale units. D) Basic pH levels are less than 7.