* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Proteins and Genes
Survey
Document related concepts
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
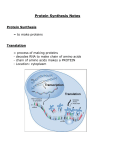
PROTEINS Proteins are used by cells to build structures and are used in chemical activities. Enzymes are proteins that aid in chemical reactions such as digestion and cellular respiration. Proteins are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They also contain nitrogen and some sulphur. They help build cell structures. Whenever cells are damaged proteins are manufactured. Cells also build proteins to help make new cells. Red blood cells are replaced at a rate of one million per second. Proteins are used to help this process. So, one million cell membranes and organelles per second and this is just for red blood cells! Proteins are composed of 20 amino acid building blocks. The order and number of amino acids determine the type of protein. The sequencing of amino acids is regulated by the genes located on the chromosomes. The genes are patterns of nucleotides in DNA. The pattern is used to build messenger RNA (mRNA) during a process called transcription. The mRNA leaves the nucleus of the cell and attaches to ribosomes in the cytoplasm. There is another type of RNA in the cytoplasm called transfer RNA (tRNA). Each tRNA is attached to a specific amino acid. The tRNA is brought into position to join with mRNA on the ribosome. As this takes place, each amino acid is brought into the correct position in the chain to build a protein. This process is called translation. A small protein may contain only 8 amino acids. while some of the longer chains may have up to 400 amino acids. A chain of amino acids may also be referred to as a polypeptide chain. Proteins are important in our diet. Our bodies can produce 12 of the amino acids. But it cannot make the other eight and we must eat foods that contain these "essential amino acids". If not it can lead to protein deficiencies and disease. NUCLEOTIDE - The basic structural units of nucleic acid. Each unit is composed of a five carbon sugar, a phosphate, and nitrogen base. TRANSCRIPTION - The process by which an mRNA molecule is built using the sequence of nucleotides in DNA as a template. TRANSLATION -The process by which polypeptides(proteins) are produced at the ribosome. Transfer tRNA positions amino acids according to the sequence of nucleotides in mRNA. POLYPEPTIDE - A chain of amino acids held together by peptide bonds. GENES Genes are sections of chromosomes, each of which contains one set of instructions. Alleles - Two or more alternate forms of a gene. The alleles are located at the same position (locus) on one pair of homologous chromosomes. DOMINANT - Alleles of this type determine the expression of the genetic trait in offspring. Usually expressed with a capital letter. EX: Brown eye colour is dominant over blue eye colour. The allele for Brown eye colour is represented by a capital B. Blue eye colour would be represented by a small case b. RECESSIVE - alleles of this type are overruled by dominant alleles. Which determine the genetic trait. GENOTYPE - The alleles an organisms contains for a particular trait. One allele or each trait is inherited from each parent. Since the alleles occur in pairs, various combinations can occur. PHENOTYPE - Refers to the observable traits of an individual. HOMOZYGOUS - Is the term used to describe the genotype of an organism that contains two alleles that are the same. example; brown eyes are dominant and the alleles would be BB. Blue eyes are recessive and the alleles would be bb. HETEROZYGOUS - is the term used to describe the genotype of an organism that contains two different alleles. Example Bb PUNNETT SQUARES - a chart used by geneticists to show the possible combinations of alleles in offspring. CHROMOSOMAL THEORY A) Chromosomes carry genes, the units of heredity. B) each chromosome carries many different genes. C) Paired chromosomes segregate during meiosis. Each sex cell or gamete(23 chromosomes n a human) has half the number of chromosomes found in the somatic cells (46 chromosomes in a regular human cell). This explains why each gamete has only one of the each paired alleles. D) Chromosomes assort independently during meiosis. This means that each gamete receives one member from each pair of chromosomes, and that each chromosome pair has no influence on the movement of any other chromosome pair. Females have two X chromosomes, while males have one X and one Y chromosome. Pathogen - a disease causing organism.