* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Receptor
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
5-HT3 antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
5-HT2C receptor agonist wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
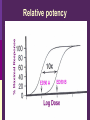
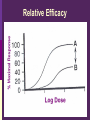
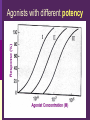
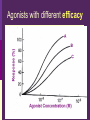
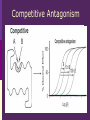
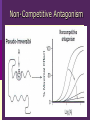
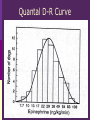
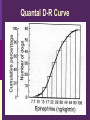
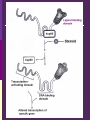
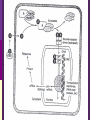
IN THE NAME OF GOD Introduction • What is pharmacology Principles • • • • of pharmacodynamics Mechanism of Drug Actions Drug-Receptor Interaction Classification of Drugs Dose-Response Relationships What is Pharmacology? Pharmakon = a drug or poison Logos = discourse or study The science that deals with: The fate of drugs in the body Pharmacokinetics The actions of drugs on the body Pharmacodynamics Pharmacy The science of preparation of drugs Pharmacotherapeutics The treatment of diseases by drugs Textbooks • Basic & Clinical Pharmacology, 2004 Bertram G. Katzung • Goodman and Gilman’s The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 2001 (J.G. Hardman and L.E. Limbard, eds.) New York: McGraw-Hill • (first published in 1941) Principles of Pharmacodynamics Pharmacodynamics Mechanisms of drug action & the relationship between drug concentration and effect Why to study Pharmacodynamics? Scientific basis for the selection & use of drugs Mechanism of Drug Action Basic Concept Interaction of a drug with its target tissue involves specific binding sites Receptor A macromolecular component of the cell to which the drug binds and leads to an effect on the cell Nonspecific binding site A biological component to which the drug binds but does not lead to any effect Nature of Drug Receptors Proteins Transmembrane proteins Receptors for neurotransmitters Transport proteins Na+/K+ ATPase Ion channels digitalis glycosides benzodiazepines Structural proteins Tubulin colchicine Enzymes Cycloxygenase ACE acetylsalicylic acid Captopril Non-protein drug receptors Lipids Anesthetics Nystatin, Amphotericin Nucleotides Antineoplastic drugs Cyclophosphamide Other Sites of Drug Action Water Osmotic Diuretics & Laxatives Ions Antacids Changing urine pH Chelators Dimercaprol Penicillamine EDTA Hg+2 , As+2 Cu+2 Pb2 Drug-Receptor Interaction Drug-Receptor Interaction R+D K1 R-D Effect K2 Affinity The tendency of a drug to combine with its receptor Kd The concentration of drug that binds to 50% of the receptors Affinity= the reciprocal of the Kd Drug-Receptor Interaction R+D K1 R-D Effect K2 Intrinsic Activity The ability of a drug to initiate a cellular effect Receptor-Effector Coupling o Receptor conformational change o Coupling Efficiency Drug-Receptor Binding Concentration-Effect Relationship Classification of drugs Agonist Full agonist Partial agonist Antagonist Competitive antagonist Non-competitive antagonist Other Drug Antagonism Chemical antagonists Heparin & protamine Physiologic antagonism Glucocorticoids & Insulin Dose-Response Relationship 1. Graded dose-response 2. Quantal dose-response Graded Dose-Response Relationship Sigmoidal D-R Curve Graded Dose-Response Relations Potency Efficacy Relative potency Relative Efficacy Agonists with different potency Agonists with different efficacy Competitive Antagonism D-R Curve for Competitive Antagonists Non-Competitive Antagonism Quantal D-R Curve Quantal D-R Curve Quantal D-R Curve Quantal-Dose Response Median Effective Dose (ED50) Median Toxic Dose (TD50) Median Lethal Dose (LD50) Therapeutic index LD50/ED50 or TD50/ED50 Signaling Mechanisms & Drug Action Transmembrane Signaling Intracellular receptors Enzyme-linked Ligand-gated receptors ion channels G-protein-coupled receptors Intracellular Receptors Steroid Receptor Superfamily Glucocorticoids Mineralocorticoids Sex hormones Vitamin D Thyroid hormone Retinoic Acid Therapeutically important consequences • Slow onset of action • Persistence of effect following withdrawal of the drug Enzyme-Linked Receptors Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Insulin Epidermal growth factor (EGF) Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Enzyme-Linked Receptors Receptor Guanylyl Cyclase Atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) cGMP (Natriuresis; Vasodilation) Receptor Serine Kinase Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-b) Cytokine Receptors Cytokine Receptor Ligand-gated Ion Channels Acetylcholine nicotinic receptors Neuromuscular blocking drugs (tubucurarine) Ganglion blockers (Mecamylamine) GABAA Benzodiazepines (sedative-hypnotic) Glutamate Topiramate (anticonvulsant) Ligand-gated Ion Channels G Protein-Coupled Receptors