* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Roman Republic and Empire
Sino-Roman relations wikipedia , lookup
Alpine regiments of the Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman Senate wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman emperor wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Slovakia in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
First secessio plebis wikipedia , lookup
Romanization of Hispania wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Roman technology wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
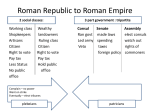
The Roman Republic and Empire Chapter 1 Section 2 Focus Questions 1. How did the government of Rome develop into an empire? 2. What modern democratic principles originate from ancient Rome? Romans Romans established a government called a republic (a government in which supreme power belongs to the citizens through their right to vote) Romans thought a republic (indirect democracy) would keep any individual from gaining too much power The 300 members of the republic’s senate were all patricians—the landholding upper class (nobles) Senators, who served for life, made the Roman laws Roman Warrior Roman Government Structure Each year, the senators elected two consuls from among the patricians The consuls supervised the business of government and commanded Rome’s armies In the event of war, the senate might choose a dictator to temporarily take complete control over the government The law granted each Roman the power to rule for six months A dictator is a person who rules with total authority and often in a cruel and brutal manner Roman Senate Roman Armies Roman Consul Roman Government Structure The common people, or plebians, influenced government to have the laws written down in the Twelve Tables They also gained the right to elect their own officials, called tribunes The tribunes could veto (preventing a bill passed by a legislature from becoming a law) laws passed by the senate that were harmful to the plebians The Twelve Tables Roman Government Expansion of Roman Political System As Rome’s political system evolved, its armies expanded Roman power into the eastern Mediterranean region On the north coast of Africa, the Romans also destroyed the city-state of Carthage and established themselves as masters of the Western Mediterranean Expansion, however, created problems At issue was who should hold power—the senate or popular political leaders looking to enact reforms Soon Rome was plunged into a civil war over this power struggle Map of Roman Empire Julius Caesar Military commander who emerged from the civil chaos and seized control Although Caesar kept the senate and other features of the republic, he forced the senate to make him dictator Jealous and fearful of his power, Caesar’s enemies stabbed him to death Caesar’s opponents believed he wanted to make himself king Caesar’s grand-nephew Octavian became the new ruler The senate gave Octavian the title Augustus Caesar, and he became the first emperor Death of Julius Caesar Pax Romana During the time known as the Pax Romana (Roman Peace), the Roman empire brought peace, order, unity, and prosperity to the lands it ruled Trade flowed freely to and from distant lands in Africa and Asia Merchants carried ivory, gold, spices, silk, and other commodities People spread/shared ideas as they traveled Ideas about democracy spread to places the Romans traveled Legal Principles From Roman Times Accused presumed innocent until proven guilty Accused had right to face the accuser Accused could offer a defense to the charges Guilt had to be established “clearer than daylight” through evidence Judges interpreted the laws and were expected to make fair decisions Legacy of Rome Greatest legacy of Rome was the establishment of justice through the law (A legacy is something that is left behind to future generations) In the 400s, the emperor Justinian, in what was now the eastern Byzantine empire, reformed the Roman law code The Roman Law Code became known as Justinian’s Code Later, this code influenced the Christian church and medieval monarchs The Christian church preserved much of the Roman culture in its teachings Powerpoint Questions (17 points) 1. Define republic 2. Who were the patricians? 3. What were the responsibilities of the two consuls elected by the senate? 4. Why would the senate elect a dictator? 5. Common people were known as ___. Powerpoint Questions (17 points) 6. Laws were written on tablets called the _________. 7. Define veto. 8. What city-state did the Romans destroy that established Rome as the master of the Western Mediterranean? 9. Identify the military commander who emerged and seized power amidst the chaos and civil wars 10. Who became the first emperor of the Roman empire? Powerpoint Questions (17 points) 11. What does Pax Romana mean? 12. What happened during the Pax Romana? 13. What modern legal principles originate from Roman times? (four points) 14. What did the Roman emperor Justinian accomplish during his reign?