* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Four Levels of Protein Structure
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein design wikipedia , lookup
Structural alignment wikipedia , lookup
Rosetta@home wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
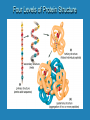
Four Levels of Protein Structure Four Levels of Protein Structure • Primary Structure: Linear Sequence of Amino Acids Each amino acid has central carbon liked to ---hydrogen (H) ---amino group (NH2) ---acid group (COOH) ---unique group (R) O H H2N C R C OH The carboxyl group of one amino acid is linked to the amino group of the next amino acid. Four Levels of Protein Structure • Primary Structure: Amino Acids are linked with a covalent bond called a peptide bond. H2N H O H H C C N C R1 R2 O C OH Four Levels of Protein Structure • Secondary Structure: Folded structure due to hydrogen bonds between the amino and acid groups of amino acids N C N C H O H O O H O H C N C N or Four Levels of Protein Structure • Tertiary Structure: Three dimensional folded structure due to attractions and repulsions between R groups All but peptide bonds are involved in tertiary structure. Four Levels of Protein Structure • Quaternary structure: Association of two or more protein chains eg. Hemoglobin is composed of 4 protein chains 2 are called alpha hemoglobin 2 are called beta hemoglobin Applying Your Knowledge 1. 2. 3. 4. Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary A. Which structure results exclusively from hydrogen bonding? B. Which structure involves an association of two or more protein chains? C. Which structure describes the linear sequence of amino acids? D. Which structure depends upon interactions between the R groups of the amino acids?