* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Biology
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
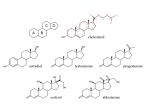
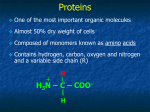
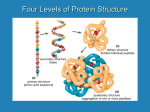
AP Biology Ch. 5 Learning Team Questions Part 1 Name_______________________ Polymer Principle and Carbohydrates 1. What is a polymer and what are the building blocks of polymers called? Give an example of each? 2. Explain the process of dehydration synthesis. Why is hydrolysis the opposite of dehydration synthesis? 3. There is a tremendous variety of macromolecules found in living organisms. What is the basis for such diversity in life’s polymers? 4. What is the main structural difference between an aldose and a ketose? Why are these terms useful in classifying monosaccharides? 5. Why is it inaccurate to draw glucose with a linear carbon skeleton? 6. Define glycosidic linkage. Name 3 major disaccharides and the monosaccharides that compose each. 7. Describe how the starch molecules amylose and amylopectin are formed. What is the general shape of a starch molecule? 8. What is glycogen? 9. What is the difference between alpha glucose and beta glucose? 10. Describe the three dimensional structure of cellulose and how this structure applies to the function of cellulose. AP Biology Ch. 5 Learning Team Questions Part 2 Name_______________________ Proteins 11. Describe the structure of an amino acid. What is the alpha carbon? Do any of the amino acids contain alpha carbons that are not asymmetric? 12. What is an R group? Discuss the various properties that the R group (side chains) possess. Give an example of each type of amino acid. 13. Describe the process of polymerization of amino acids. What is a peptide bond? What is located at the each end of a polypeptide chain? 14. Explain why the term polypeptide is not synonymous with protein. What ultimately determines the three-dimensional structure of a protein? 15. Is there a relationship between the structure of a protein and its function within a cell? Give a specific example. 16. How is the specific function of a protein an emergent property resulting from the order of the amino acids in a polypeptide chain 17. What is the primary structure of a protein? What determines the specific order of amino acids in a polypeptide chain like the enzyme lysozyme? 18. Discuss what might happen if the primary structure of a polypeptide chain is changed even slightly. Describe the example of normal hemoglobin verses sicklecell hemoglobin. 19. Discuss the work that Frederick Sanger did to figure out the primary structure of the insulin hormone 20. What type of bond contributes to the secondary structure of a protein? Which parts of the amino acid are involved? How are they involved? 21. What are the two possible secondary structures of proteins? Briefly describe each structure and give examples of proteins that illustrate these structures. 22. What part of an amino acid is directly involved in the tertiary structure of a protein? Explain how hydrophobic interactions work. What is the relationship between hydrophobic interactions and van der Waals interactions? 23. What role do sulfhydryl groups (-SH) play in the tertiary structure of a protein? Which amino acids contain sulfhydryl groups? 24. Discuss situations of tertiary structure that would involve hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds. Be specific. 25. Define quaternary protein structure. Explain how quaternary structure contributes to the macromolecules collagen and hemoglobin.