* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A.P.day52 proteins
Protein design wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Structural alignment wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
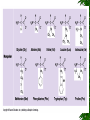
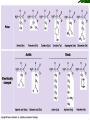
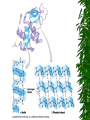
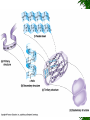
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
A.P. Biology-Day 52 Take out your organic molecules packet Should high schools perform urine tests for steroids in athletes? How are you doing with memorizing functional groups and example compounds that have them? This will help understand the organic compounds properties. Figure 5.14 Cholesterol, a steroid Amino Acids=Protein Dehydration Synthesis Structures of Protein Primary ---the order of amino acids ---polymer of peptide bonds Secondary ---helix or beta sheet, discovered by Linus Pauling Tertiary Structure ---folded on itself with hydrogen bonds ---determines the active site of the protein ---determined by the R-site Quaternary Structure ---multiple chains Tertiary Structure support between R-groups…like a phone cord Disulfide linkage: S-H helps hold proteins together to form a tertiary structure. The phosphate group is what makes DNA a negative charged molecule which then can be separated with gel electrophoresis Hydrophobic Van der wall interactions – Nonpolar amino acids avoid water and move to one side and attract to each other by Van der wall interactions Ionic Hydrogen bonds: H---O, H---N Functions of Proteins Structural support Catalysis of reactions (enzymes) Defense (antibodies) Movement (contractile proteins) Signaling (protein hormones) Transport (cell membrane) Receptors Storage Figure 5.19 A single amino acid substitution in a protein causes sickle-cell disease The order of amino acids determine the tertiary structure which determines the function of the protein The order of amino acids are coded by the order of nitrogen bases found in nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) Nucleotides make up nucleic acids