* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Patterns of Inheritence - School District of La Crosse
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Sex-limited genes wikipedia , lookup
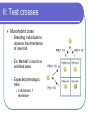
Patterns of Inheritance I: Mendel's laws Two factors called genes control each trait For each gene, organisms receive one allele (form) from each parent randomly. If an organism receives different alleles for the same trait, one allele is dominant over the other II: Test crosses Monohybrid cross Breeding individuals to observe the inheritance of one trait Ex: Mendel’s round vs wrinkled peas Expected phenotypic ratio 3 dominant: 1 recessive Test Crosses Continued… Dihybrid cross Breeding individuals to observe the inheritance of two separate traits Ex: Mendel’s cross for shape and color Expected phenotypic ratio: 9 dom dom: 3 dom rec: 3 rec dom: 1 rec rec Practice time Assume the following: A = round head a = square head B = belly button b = no button If two parents are heterozygous for belly buttons what are the odds/percentages that their child will not have a belly button? ¼ or 25% If parent #1 is homozygous dominant for both traits and parent #2 is homozygous recessive for both traits what are the odds/percentages their child will have a round head but no belly button? 0/16 or 0% III: Complex inheritance Incomplete Dominance: Blending of traits Heterozygotes, and homozygotes have different phenotypes Continued… Co-dominance: Heterozygotes express both dominant phenotypes Continued… Sex determination 23rd chromosome=X or Y XX=female XY=male Sex linked traits: Genes for the traits located on the sex chromosome Ex: fruit fly eye color XR= Red Xr= white Human color blindness Continued… Polygenic: Poly=many gen=genes Multiple genes are responsible for the expression of the trait