* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download sheet of notes
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Major histocompatibility complex wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
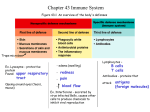
Chapter 43: The Body’s Defenses Lines of Defense First Line – Nonspecific Skin Mucous Second Line – Nonspecific Phagocytic White Blood Cells (WBC) Inflammatory Response Antimicrobial Proteins Third Line – Specific Lymphocytes Antibodies First Line Skin and Mucous Intact skin usually cannot be penetrated by microorganism Mucous Membrane o Digestive Tract, Respiratory Tract, Genitourinary Tract Chemical Defenses o Low pH in sweat and stomach o Washing by tears and saliva Second Line Nonspecific White Blood Cells Phagocytosis – ingesting of invading organisms Neutrophils o Chemotaxis – migration toward chemical attractant Monocytes o Form macrophages, “big eaters” Eosinophils o Take care of larger parasitic invaders Natural Killer (NK) cells o Attack cell’s membrane causing it to lyse (burst open) Antimicrobial Proteins Attack microbes directly or impede reproduction Complement System – set of 20 serum proteins that carry out a cascade of steps leading to the lysis of microbes Interferon o Secreted by virus infected cells o Induce neighboring cells to produce chemical that inhibit viral reproduction Inflammatory Response Triggered by damage to tissue by physical injury or entry of microorganism Precapillary arterioles dilate and postcapillary venules constrict to increase blood supply Full capillaries leak fluid into near tissue to cause edema(swelling) Inflammatory response initiated by chemical signal o Histamine – release by cells of body, the basophils and mast cells o Basophils – circulating white blood cells o Mast cells – in connective tissue Soon phagocytic migration begins and is mediated by chemotactic factors called chemokines Pyrogens are released and set body’s temperature higher causing fever Third Line Specific Two main types of lymphocytes • B lymphocytes (B Cells) • T lymphocytes (T Cells) B Cells combat antigens by secreting receptors called antibodies T Cells have special receptors called T Cell Receptors that is not secreted Lymphocytes • Key to the immune system • Migrate from bone marrow • The different lymphocytes specialize in different types of antigens and respond accordingly • Antigen – foreign molecule that elicits a response from lymphocytes When Lymphocytes are activated they divide and differentiate into two clones of cells (Clonal Selection) • Effector cells, short lived clones that combat the same antigen that activated • Memory cells, long lived cells that have receptors for the same antigen Primary Immune Response – when lymphocytes are activated upon first exposure to antigen Secondary Immune Response - If the same antigen comes at a later time. Response is faster, greater magnitude, and more prolonged Lymphocyte development gives rise to an immune system that distinguishes self from nonself Lymphocytes that have receptors for molecules in the body exhibit apoptosis • Leaves only one that react with foreign molecules T Cells interact with group of native molecules called Major Histocompatibility Complex(MHC) • Each MHC presents fragments of protein antigen to a T Cell • Two main classes of MHC Class I MHC – found all nucleated cells Class II MHC – few specialized cell types T Cells Cytotoxic T Cells (Tc) have antigen receptors that bind to fragments of antigens displayed by the body’s class 1 MHC molecules Helper T Cell (TH) have receptors that bind to fragments of antigens displayed by the body’s class 2 MHC molecules Suppressor T Cell (TS) function in turning off the immune response once antigen has been eliminated from body Immune System Humoral Immunity • Have receptors that bind to fragments of antigens displayed by the body’s class 2 MHC molecules • Defends against free bacteria, toxins, and viruses present in body fluids • The repeated subunits of these antigens bind simultaneously to a number of membrane antibodies on the B cell surface Cell-mediated immunity • Active against bacteria and viruses within infected body cells and against fungi, protozoa, and parasitic worms • It kills target cell primarily by releasing perforin, a protein that forms pores in the target cell’s membrane • As water flows into the target cell it swells and eventually lyses Antibodies An antibody interacts with a small accessible portion of the antigen called an epitope or antigenic determinant Antibodies constitute a group of globular serum proteins called immuniglobulings The secreted antibodies bind to antigen Typical antibody molecule has: • 2 identical antigen binding sites specific for • 2 identical light chains the epitope that provoked its production • Joined by disulfide bridges to form a Yshaped molecule • 4 polypeptide chains • 2 identical heavy chains Opsonization, the bound antibodies enhance macrophage attachment to and thus phagocytosis of the microbes Immunity Active immunity • Immunity conferred by recovering from • Can be by immunization (vaccination) an infectious disease Passive immunity • Antibodies can be transferred from one • Can be transferred by injecting individual to another(mother to nursing antibodies from animal that is already infant in breast milk) immune to another • Passive immunity persists only as long as antibodies last Autoimmune and Immunodeficiency Disease Autoimmune • Immune system looses tolerance for self and turns against certain molecules of the body Immunodeficiency • Severe combined immunodeficiency- both branches of immune system fail to function