* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Option H Further Human Physiology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
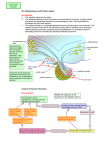
Option H Further Human Physiology Section Hormonal Control Digestion Absorption of Digested Foods Functions of the Liver The Transport System Gas Exchange Self-test Quiz Answers 2 Page 3 7 11 13 15 19 26 28 IB Biology Option H 2012 Hormonal Control Hormonal Control A genetically conditioned target cell means that it has the specific hormone receptor either on its surface or in the cytoplasm. Hormones are chemical messengers secreted into the blood by endocrine glands and transported by the blood to genetically conditioned target cells. Hormones can be – steroids, eg. progesterone; peptides, eg. oxytocin; tyrosine derivatives, eg. thyroxin. Mode of Action of Hormones 1. Steroid hormones 1 1 Steroid hormone in blood passes through plasma membrane into cytoplasm of target cell and binds to specific receptor protein. 2 Receptor-hormone complex enters nucleus through nuclear pore and binds to DNA. 3 Transcription results in mRNA which leaves nucleus and binds to ribosome. 4 Translation results in a protein such as an enzyme that alters the metabolism of the target cell. 2 3 4 blood plasma target cell 2. Peptide hormones 1 2 Peptide hormone in blood binds to specific receptor glycoprotein on plasma membrane of target cell. 1 2 This triggers the release of a second messenger system within the cell. 3 A 3 This in turn modifies the activity of the cell, usually by activating or inhibiting an enzyme controlling a specific reaction. enzyme B blood plasma target cell IB Biology Option H 2012 3 Hormonal Control The Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland Key features ¾ The pituitary gland has two parts. ¾ The posterior pituitary is part of the brain and connected to it directly. It simply stores hormones that have been produced by neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus. Examples are ADH and oxytocin. ¾ The anterior pituitary is a separate glandular structure producing its own hormones. The release of these hormones is still controlled by the brain by another set of hormones, called releasing hormones, produced by the hypothalamus. An example is thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) controlled by thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH). neurosecretory cells hypothalamus Neurosecretory cells are modified nerve cells that secrete chemicals that act as hormones. They are sometimes called neurohormones. These (neuro)hormones travel down the axon and are stored at the ends. Their release is controlled by nerve impulses from the cell body. neurosecretory cells From carotid artery The portal vessel carries the releasing hormones from the capillaries in the hypothalamus to the capillaries in the anterior pituitary. posterior pituitary portal vessel anterior pituitary To vena cava A vertical section through the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. Control of ADH Secretion Key sequence Osmoreceptors in hypothalamus + Neurosecretory cells in hypothalamus secrete ADH Blood concentration too low - negative feedback to decrease plasma ADH Blood concentration too high - negative feedback to increase plasma ADH Water potential of blood monitored by osmoreceptors in hypothalamus. The osmoreceptors control the activity of the neurosecretory cells. Relate this sequence to the structures in the diagram above. Transported by axons, stored in and released from posterior pituitary If the posterior pituitary does not release any ADH it quickly disappears from the blood as it only lasts for a few minutes. transported by blood Kidney absorbs more water (ADH present) or less water (ADH absent) 4 IB Biology Option H 2012