* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download chapter-16-worksheet
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Pituitary apoplexy wikipedia , lookup
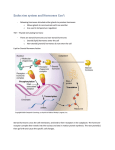
Chapter 16: Endocrine System 1. Sort the list into major endocrine glands and secondary endocrine tissues: Pituitary, adipose cells, thymus, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal, cells in the cell intestine, stomach, kidney, heart) Major endocrine glands walls (small Secondary endocrine tissues 2. How do hormones travel to long distance target organs? 3. Fill out the chart for the 3 different classes of hormones Proteins Catecholamine Steroids Hydrophobic or Hydrophilic Synthesis Release Carrier in blood Half-life Receptors Examples 4. What type of stimuli are these examples? (humoral, neural, or hormonal) The hypothalamus secretes hormones that stimulate the anterior pituitary to release hormones. __________ Neurons in the hypothalamus send a signal to release stored hormones. ___________ Parathyroid gland senses a decline in blood Ca2+ concentration and responds by releasing parathyroid hormone. ___________ 5. Hormones travel from the hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary via ________________. Hormones travel from the hypothalamus to the posterior pituitary via _______________. 6. Define the different terms for hormone interactions at target cells. Permissiveness: Synergism: Antagonism: 7. Diabetes insipidus is caused by a decrease in what hormone? What are the symptoms of this disorder? 8. What hormones secreted by the Anterior Pituitary activate a cyclic AMP second-messenger system at their targets? Define trophic. 9. What is the structural difference between the thyroid hormones Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3)? Which is the active form circulating the blood? How is a goiter developed? 10. Explain the steps involved in thyroid hormone synthesis. 11. What two hormones maintain the balance of calcium (Ca2+)? What are the specific functions of each one? 12. What type of corticosteroids are aldosterone and cortisol? What do they do? 13. What are the differences between Diabetes Mellitus 1 and 2? What are the symptoms of these disorders? How are these disorders treated? 14. Back in the day what was the simplest way they tested for Diabetes Mellitus? REREAD LECTURE NOTES MULTIPLE TIMES fill out hormone table because it is a great summarization of the chapter focus of the disorders caused by hypo- and hyper-secretion of certain hormones know about the feedback loops with hormone production