* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download p134
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
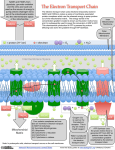
p134 #2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 10, 11, 13, 20, 22, 23 2. (a) Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm. (b) Pyruvate oxidation and the Krebs cycle occur in the mitochondrial matrix. (c) The electron transport chain and ATP synthesis occur in the inner mitochondrial membrane. 3. (a) Ubiquinone (Q) is an electron carrier. As part of the electron transport chain, it carries electrons from NADH dehydrogenase to cytochrome b-c1 complex within the membrane. (b) FADH2 is an electron carrier from the Krebs cycle that transfers its two electrons to Q. (c) Pyruvic acid is a product of glycolysis that enters the mitochondrial matrix to undergo pyruvate oxidation and then enters the Krebs cycle. (d) ATP synthase is an enzyme complex located in the inner mitochondrial membrane that uses the proton motive force to generate ATP. 4. (a) Theoretically, NADH and FADH2 should generate three and two ATP molecules, respectively. (b) NADH passes its electrons to the first protein complex in the electron transport chain, NADH hydrogenase. FADH2 transfers its electrons to the second protein in the chain, ubiquinone (Q). The free energy released by the oxidation of FADH2 is used to pump two protons into the intermembrane space, while NADH oxidation pumps out three electrons. The result is that two ATP are formed per FADH2, and three ATP molecules are formed per mitochondrial NADH. 5. (a) The net gain in ATP after one molecule of glucose undergoes cellular respiration is 36 ATP. (b) The net gain in ATP after one molecule of glucose undergoes alcoholic fermentation is 2 ATP. 8. NAD+ accepts two electrons and one proton during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. 10. (a) An electrochemical gradient is created by pumping ions into a space surrounded by a membrane that is impermeable to ions. The gradient has two components: an electrical component caused by a difference in charge across the membrane and a chemical component caused by a difference in ion concentration. (b) An electrochemical gradient is created during electron transport as the enzyme complexes move protons from NADH and FADH2 into the intermembrane space. The intermembrane space becomes an H+ reservoir because the membrane is almost impermeable to protons. There is, therefore, a much higher concentration of protons in the intermembrane space than in the matrix. Also, protons are consumed in the mitochondrial matrix as oxygen accepts electrons and form water. (c) The electrochemical gradient is used to power ATP synthesis by the enzyme complex ATP synthase. The electrochemical gradient stores free energy and this energy is referred to as proton-motive force (PMF). Protons move through ATP synthase in response to the PMF, reducing the energy of the gradient. This energy drives the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate in the mitochondrial matrix. 11. Yeast cells produce ATP from glucose by alcoholic fermentation. NADH passes its hydrogen atoms to acetylaldehyde, which is formed when a carbon dioxide molecule is removed from pyruvate using pyruvate decarboxylase. This produces ATP, ethanol, and carbon dioxide. 13. Muscle cells produce lactate from pyruvate when there is no oxygen available to accept electrons from the cytochrome oxidase complex. 20. A: inner mitochondrial membrane B: cristae C: mitochondrial matrix D: outer mitochondrial space 22. Metabolism in a heart undergoing a heart attack would switch from cellular respiration to lactic acid fermentation because of the lack of oxygen, which would be caused by a blocked coronary artery. However, lactic acid fermentation does not provide enough energy to keep the heart beating at a life-sustaining rate. 23. It is essential that muscle cells continue to convert pyruvate to lactate or else the muscle cells would cease to contract and the cells would die.