* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Natural Selection - Hicksville Public Schools
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
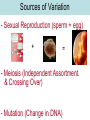
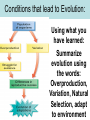
Aim: How does evolution occur by natural selection? How Does Evolution Occur? • EVOLUTION is a slow change in a species over time. • Evolution occurs by a process called NATURAL SELECTION. Read this cartoon, what do you think NATURAL SELECTION is? Darwin •Considered the “father” of evolution. Charles Darwin traveled to the Galapagos island, an uninhabited environment, where he studied evolution (Darwin’s Finches) Darwin’s Theory of Evolution Natural Selection: • Individuals with favorable traits are able to survive and reproduce. • Nature controls which traits are favorable. Natural Selection • NATURAL SELECTION is the KEY to Darwin’s theory. •According to this theory, evolution is controlled by NATURE. •Only the organisms that are able to SURVIVE and REPRODUCE will pass on their genes. Natural Selection vs. Artificial Selection People select the Environment selects desirable traits that the desirable traits will appear in the that will appear in the offspring. offspring. Mechanisms of Evolution: • Overproduction • Variation • Natural Selection: –Struggle For Survival –Best Adapted To Survive •Darwin did NOT have knowledge of the genetic basis of inheritance Overproduction • More offspring are produced than can survive. • Overproduction leads to “Struggle for Existence” or Competition. – Compete for limited resources (food, water and shelter). – Only certain individuals are able to survive and reproduce. Overproduction • More offspring are produced than can survive (most die young). Overproduction leadsfish, • Organisms such as bacteria, to have high reproinsects, and rabbits ductive rates because the chance that COMPETITION!! their young will survive is minimal. Variation • Variation: Individuals of the same species have differences in their appearance, structure, or genes. • Increases the chance that some members of a species will survive an environmental change. Sources of Variation - Sexual Reproduction (sperm + egg) + = - Meiosis (Independent Assortment. & Crossing Over) - Mutation (Change in DNA) Mutations • Mutations change the base sequence of DNA • Therefore Protein is changed • Most mutations are HARMFUL, but some can help the organism SURVIVE. Adaptive Value • Adaptive Value: a change that produces a trait that helps an organism survive. – Ex: Camouflage • If all the members of a species were the same then an environmental change could wipe out the entire species. • VARIATION increases the chance that some members of a species will survive. Natural Selection Best Adapted To Survive • The ENVIRONMENT ‘chooses’ which traits have adaptive value. Organisms with favorable traits in a certain environment will live to reproduce and pass on those traits, others will die out. Struggle For Survival • “Survival of the fittest” “Only those BEST suited will survive because of competition for finite (limited) resources (oxygen, water, food, and shelter) Conditions that lead to Evolution: Using what you have learned: Summarize evolution using the words: Overproduction, Variation, Natural Selection, adapt to environment Patterns Of Change • Species with SHORT reproductive cycles that produce MANY offspring tend to evolve more quickly than species with LONG life spans and FEW offspring. • Types: 1) Gradualism – evolution occurs steadily through time (Slow & Continuous) . 2) Punctuated Equilibrium- species stay the same for long periods of time and then change rapidly. No Change ------------- No Change ----------- No Change ------------- Extinction • The disappearance of an entire species (ex. Dinosaurs) • It can be caused by temperature changes, pollution, or landscape changes.