* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Species Change Over Time
Survey
Document related concepts
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
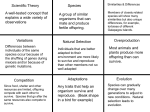
Species Change Over Time Sec 1.2 Evolution refers to the process through which species change over time. The Change results from a change in the genetic material. This change can then be Passed from one generation to the next! Has communication changed over time? How so? Why have phones changed over time? Early Ideas Early 1800’s Jean Lamarck was first to propose a model of how life evolved. Lamarck proposed that an organism could acquire a trait and then pass it on to its’ offspring. Darwin’s Observations 50 years after Lamarck, Charles Darwin, a naturalist, spent 5 years traveling around the world, aboard the Beagle, studying rock formations and collecting fossils On the Galapagos Islands, a group of volcanic islands, Darwin found many differences between plants and animals from the mainland but also from the various islands Darwin observed similar looking birds with very different beaks. These birds are closely related finch species that are suited to different food sources on the island Natural Selection when members of a species are better suited to their environment, they will survive and reproduce at a higher rate than other members of the species Key Principles of Natural Selection Overproduction: producing more offspring than the environment could possibly support, thus ensuring that the strongest, best suited will live AND reproduce offspring Variation: Differences in their genetics. Mutations can occur causing a new variation. This variation can be passed on to the offspring. Adaptations: When a variation makes an individual better able to survive than other members of the group. Any inherited trait that gives an organism an advantage in its environment Selection: Individuals with a particular adaptation are more likely to survive long enough to reproduce, thus the trait is becoming more popular in the next generation. The trait has been selected for the environment Natural Selection Overproduction Producing more than can survive to ensure that the strongest survive to adulthood and reproduction ↓ Variation One of some organisms have it ↓ Adaptation Those that have it use it to survive ↓ Selection Those that survive reproduce. Others die off early. What natural selection is NOT!! Speciation: the evolution of a species from an existing species Due to Isolation: species are separated due to geographic isolation, feed on different things or reproduce at different times of the year neok12.com Natural Selection Made Easy Carl Sagan Explains Natural Selection