* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
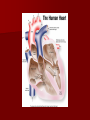
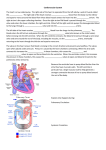
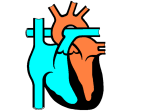
Cardiovascular System: Heart Chapter 12 Heart Anatomy Wall: Composed of 3 layers – endocardium, epicardium, myocardium. Epicardium – thin serous membrane outermost surface of the heart (same as the visceral pericardium). Myocardium – thick middle layer, cardiac muscle – allows for contraction of the heart. Endocardium – simple squamous over a layer of connective tissue – smooth innermost layer allows blood to move easily through (valves are formed by a fold in this layer – it is a double layer with connective in between. Myocardium Histology Special Features. . . Musculi pectinati – muscular ridges with in the atria. Crista Terminalis – smooth portion with in atria. Trabeculae carneae – columns of “meat” External Anatomy 2 atria – superior posterior 2 ventricles – anterior inferior Auricles – flaplike extensions of the atria – anterior between the atria and ventricles. Blood Flow - vessels To the heart (superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, coronary sinus) – into the right atrium. (4) Pulmonary veins – from the lungs into the left atrium. From the heart (Aorta from the left ventricle to the body and Pulmonary Trunk from the right ventricle to the lungs). More Anatomy . . . A large coronary sulcus runs around the heart separating the atria from the ventricles. Right and Left coronary arteries supply blood to cardiac tissue and leave off of the aorta where it leaves the heart. Great cardiac vein drains tissue on the left side and small cardiac vein drains the right margin. Chambers and Valves Right atrium – fed by the superior and inferior vena cava and the coronary sinus. Left atrium – fed by the pulmonary veins Atria separated by the interatrial septum. The atria open into the ventricles through the atrioventricular canals. Right ventricle opens into the pulmonary trunk. Left ventricles open to the aorta. Ventricles are separated by the interventricular septum. Atrioventricular Valves Keep blood from flowing back into the atria. Composed of cusps and flaps. Bicuspid (Mitral) is on the left side. Tricuspid is on the right side. Papillary muscles are attached by the chordae tendonae. Semilunar valves: Aorta and pulmonary trunk – from the ventricles to the main blood vessels. They have free inner boarders which meet in the center to block blood flow.