* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution - Byron High School
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
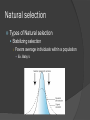
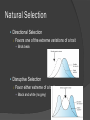
Ch. 15 - Evolution Unit 4 – Evolution (Ch. 14, 15, 16) 1. Define Evolution 2. List the major events that led to Charles Darwin’s development of his theory of Evolution by means of Natural Selection 3. Summarize the major events of the Geologic Time Scale 4. Compare and contrast early experiments that support the concept of biogenesis and disproved spontaneous generation 5. List some examples of direct and indirect evidences of evolution 6. List the 6 different types of fossils & the technique used to identify the age of them. 7. Explain what the first cells were thought to be and give characteristics of them 8. Summarize the effects of the different types of Natural Selection on gene pools 9. Relate changes in genetic equilibrium to mechanisms of speciation 10. Explain the role of natural selection in convergent and divergent evolution 11. Analyze the Endosymbiotic Theory - including why the Mitochondria and Chloroplasts were thought to be on their own. 12. Compare and contrast modern theories of the origin of life 13. Explain how the structural and physiological adaptations of organisms relate to natural selection 14. Identify adaptations of primates 15. Distinguish the evolutionary relationships of primates 16. Summarize the major anatomical changes in hominids during human evolution 17. List the phylogeny of the human species from Australopithecus to Homo sapiens. 18. Identify what probable explanation allowed humans to get to North America SWBAT Scale 4: Same as a 3.0 but I can make inferences & application to the SWBAT’s 3: I COMPLETELY understand all parts of the SWBAT 2: I understand MOST of the SWBAT’s with teacher help 1: I understand a little of the SWBAT’s but need teacher help 0: I do NOT understand any part of the SWBAT’s and need help! Natural Selection Evidence of Evolution Charles Darwin and Natural Selection ○ Evolution – Change in a population over time Darwin – wrote “Origin of Species” in 1859 Darwin was a naturalist on the HMS Beagle (1831- 35) - Collected specimens on the Galapagos Islands Natural Selection Natural Selection A mechanism for change in a population ○ Organisms with favorable traits survive to pass on traits Organisms produce more offspring that can survive Variations exist among all populations Variations that are useful in a given environment are more likely to be passed to the next generation Over time, offspring with that “beneficial” variation make up most of the population Crash Course Natural Selection Natural Selection Adaptations Inherited characteristics which increase the chances of surviving and reproducing ○ Mimicry Structural adaptation to look like another organism ○ Camouflage Blending in with the surroundings ○ Physiological adaptations Change in metabolic processes - Bacteria becoming resistant to antibiotics Evidence of Evolution Indirect Evidence of Evolution Fossils ○ Provide an early record of early life and possible relationships to current life on earth Anatomy ○ Homologous structures Structures that feature with a common evolutionary origin - Forelimbs in animals ○ Analogous structures Similar function but do not share common ancestors - Bird and insect wings Evidence of Evolution Natural Selection Vestigial structure ○ Structure of the body that is believe to no longer have a function – but may have at one time in history Skeletal legs on a snake Embryology ○ Study of early stages of development that shows similarities between fish, reptiles, birds, and mammals Tails and gill slits Biochemistry ○ Study of DNA and RNA that shows the relatedness of species Mechanisms of Evolution Population Genetics and Evolution Populations Evolve ○ Not individuals Gene Pool ○ All of the different alleles (form of a gene) in a population Allelic frequencies ○ Percentage of any specific allele in the gene pool Genetic Equilibrium ○ Frequency of alleles remains the same in a population over time Hardy-Weinberg Eq. Statement that populations will get to a point where no diversity occurs. Only when the following occurs ○ No mutations ○ No genetic drift Alterations in allelic frequencies by chance ○ No gene flow Individuals cannot migrate (must stay localized) Natural selection Types of Natural selection Stabilizing selection ○ Favors average individuals within a population Ex. Baby’s Natural Selection Directional Selection ○ Favors one of the extreme variations of a trait Birds beak Disruptive Selection ○ Favor either extreme of a trait Black and white (no grey) Evolution of a species Speciation Crash Course on Speciation Evolution of a new species ○ Members of a similar populations no longer able to interbreed to produce fertile offspring Geographic Isolation Physical barrier divides a population ○ Volcanic eruption, sea-level change Evolution of species Reproductive isolation Formerly interbreeding, organisms can no longer mate and produce fertile offspring ○ Mating seasons Polyploidy Species with multiple of the normal set of chromosomes ○ More common in plants Evolution of a species Rate of speciation Gradualism – species originate through a gradual change of adaptations Punctuated Equilibrium – speciation occurs relatively quickly, in rapid bursts with long periods of genetic equilibrium in between Patterns of Evolution Adaptive Radiation Ancestral species evolves into an array of species to fit a number of diverse habitats ○ Galapagos finches and Hawaiian honeycreepers Divergent Evolution One species adapt to different environments and become different species Convergent Evolution Distantly related organism evolve similar traits. Convergent Evolution Unit 4 – Evolution (Ch. 14, 15, 16) 1. Define Evolution 2. List the major events that led to Charles Darwin’s development of his theory of Evolution by means of Natural Selection 3. Summarize the major events of the Geologic Time Scale 4. Compare and contrast early experiments that support the concept of biogenesis and disproved spontaneous generation 5. List some examples of direct and indirect evidences of evolution 6. List the 6 different types of fossils & the technique used to identify the age of them. 7. Explain what the first cells were thought to be and give characteristics of them 8. Summarize the effects of the different types of Natural Selection on gene pools 9. Relate changes in genetic equilibrium to mechanisms of speciation 10. Explain the role of natural selection in convergent and divergent evolution 11. Analyze the Endosymbiotic Theory - including why the Mitochondria and Chloroplasts were thought to be on their own. 12. Compare and contrast modern theories of the origin of life 13. Explain how the structural and physiological adaptations of organisms relate to natural selection 14. Identify adaptations of primates 15. Distinguish the evolutionary relationships of primates 16. Summarize the major anatomical changes in hominids during human evolution 17. List the phylogeny of the human species from Australopithecus to Homo sapiens. 18. Identify what probable explanation allowed humans to get to North America SWBAT Scale 4: Same as a 3.0 but I can make inferences & application to the SWBAT’s 3: I COMPLETELY understand all parts of the SWBAT 2: I understand MOST of the SWBAT’s with teacher help 1: I understand a little of the SWBAT’s but need teacher help 0: I do NOT understand any part of the SWBAT’s and need help!